This blog explores how to work with various form inputs in Vue.js, such as text fields, checkboxes, radio buttons, select boxes, and more. Aimed at beginners, it focuses on Vue’s powerful data binding features for creating interactive forms in dynamic web applications.
Text Input Bindings
Text inputs are the most basic form elements, allowing users to enter single-line text. In Vue.js, you can use the ‘v-model’ directive to create a two-way data binding between the input element and the data property in your Vue instance.
Multiline Text Input
For multiline text input, you can use the <textarea> element, which also supports ‘v-model’ for two-way binding.
Checkbox Input
Checkboxes are great for boolean options. You can use ‘v-model’ to bind the checkbox’s checked state to a data property.
Radio Buttons
Radio buttons allow users to select one option from a group. Again, you can use ‘v-model’ to bind the selected value.
Select Dropdown
Select dropdowns let users choose one option from a list. Use ‘v-model’ to bind the selected value to a data property.
Multiselect Dropdown
For selecting multiple options, use the ‘<select>’ element with the ‘multiple’ attribute. ‘v-model’ can bind an array of selected values.
Value Bindings
Vue’s reactivity system makes it easy to manage and manipulate input values. You can also create computed properties or methods to handle complex scenarios, such as validating inputs or transforming data.
Example
Here’s a practical example that demonstrates how to implement these form input bindings in Vue.js:
<template>
<div class="form-container">
<h3>Vue.js Form Input Bindings</h3>
<!-- Text Input with Validation -->
<div class="text-input">
<label for="username">Username:</label>
<input id="username" v-model="username" placeholder="Enter your username" @blur="validateUsername" />
<p v-if="usernameError" class="error">{{ usernameError }}</p>
<p>Your username is: {{ username }}</p>
</div>
<!-- Multiline Text Input with Character Count -->
<div class="multiline-input">
<label for="description">Description:</label>
<textarea id="description" v-model="description" placeholder="Enter a description" maxlength="200"></textarea>
<p>Characters remaining: {{ 200 - description.length }}</p>
<p>Your description is: {{ description }}</p>
</div>
<!-- Checkbox Input -->
<div>
<div class="checkbox-input">
<input type="checkbox" id="agreement" v-model="isAgreed" />
<label for="agreement">I agree to the terms</label>
</div>
<p>Agreement status: {{ isAgreed }}</p>
</div>
<!-- Radio Buttons -->
<div class="radio-input">
<label>Choose an option:</label>
<label>
<input type="radio" value="option1" v-model="selectedOption" />
Option 1
</label>
<label>
<input type="radio" value="option2" v-model="selectedOption" />
Option 2
</label>
<p>Selected option: {{ selectedOption }}</p>
</div>
<!-- Select Dropdown with Dynamic Industries -->
<div class="select-dropdown">
<label for="industries">Select an industry:</label>
<select id="industries" v-model="chosenIndustry">
<option disabled value="">Select an industry</option>
<option v-for="industry in industries" :key="industry">{{ industry }}</option>
</select>
<p>Selected industry: {{ chosenIndustry }}</p>
</div>
<!-- Multiselect Dropdown for Technologies -->
<div class="multiselect-dropdown">
<label for="multipleTechnologies">Select multiple technologies:</label>
<select id="multipleTechnologies" v-model="selectedTechnologies" multiple>
<option v-for="technology in technologies" :key="technology">{{ technology }}</option>
</select>
<p>Selected technologies: {{ selectedTechnologies.join(', ') }}</p>
</div>
<!-- Value Binding with Transformation -->
<div class="value-binding">
<label for="rawInput">Raw Input:</label>
<input id="rawInput" v-model="rawInput" placeholder="Type something" />
<p>Uppercase: {{ upperCasedInput }}</p>
<p>Reversed: {{ reversedInput }}</p>
</div>
<!-- Submit Button -->
<button @click="submitForm">Submit</button>
<p v-if="submissionMessage">{{ submissionMessage }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
username: '',
usernameError: '',
description: '',
isAgreed: false,
selectedOption: '',
chosenIndustry: '',
selectedTechnologies: [],
rawInput: '',
industries: [],
technologies: ['JavaScript', 'React.js', 'Next.js', 'Vue.js', 'SCSS'],
submissionMessage: ''
};
},
computed: {
upperCasedInput() {
return this.rawInput.toUpperCase();
},
reversedInput() {
return this.rawInput.split('').reverse().join('');
}
},
methods: {
validateUsername() {
this.usernameError = this.username.length < 3 ? 'Username must be at least 3 characters long.' : '';
},
async fetchIndustries() {
// Simulating an asynchronous API call to fetch industries
this.industries = await new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(['Technology', 'Finance', 'Healthcare', 'Education', 'Retail']);
}, 1000);
});
},
submitForm() {
if (this.usernameError || !this.isAgreed) {
this.submissionMessage = 'Please fix the errors before submitting.';
return;
}
this.submissionMessage = 'Form submitted successfully!';
// Handle form submission logic here (e.g., API call)
}
},
mounted() {
this.fetchIndustries(); // Fetch industries on component mount
}
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.form-container {
max-width: 600px;
margin: auto;
padding: 20px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 10px;
background-color: #f9f9f9;
}
label {
display: block;
margin: 10px 0;
}
.checkbox-input {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.checkbox-input label{
margin: 0 0 0 10px;
}
.error {
color: red;
}
.checkbox-input {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
</style>
Code Explanation
Template Section
- Each form input is wrapped in a ‘div’, and we use ‘v-model’ to bind the input fields to corresponding data properties in the Vue instance.
- For the text input and textarea, users can see their input reflected immediately in the paragraphs below.
- The checkbox and radio buttons use ‘v-model’ to maintain their checked state and selected value.
- The select and multiselect dropdowns allow users to choose from predefined options, with the selected values displayed dynamically.
- The raw input field demonstrates how computed properties can transform input data (converting it to uppercase).
Script Section
- The ‘data’ function returns an object containing the reactive properties used in the template.
- The ‘computed’ property ‘upperCasedInput’ transforms the ‘rawInput’ to uppercase, showcasing Vue’s reactivity.
Style Section
- Basic styling enhances the visual layout, ensuring that the form is easy to read and interact with.
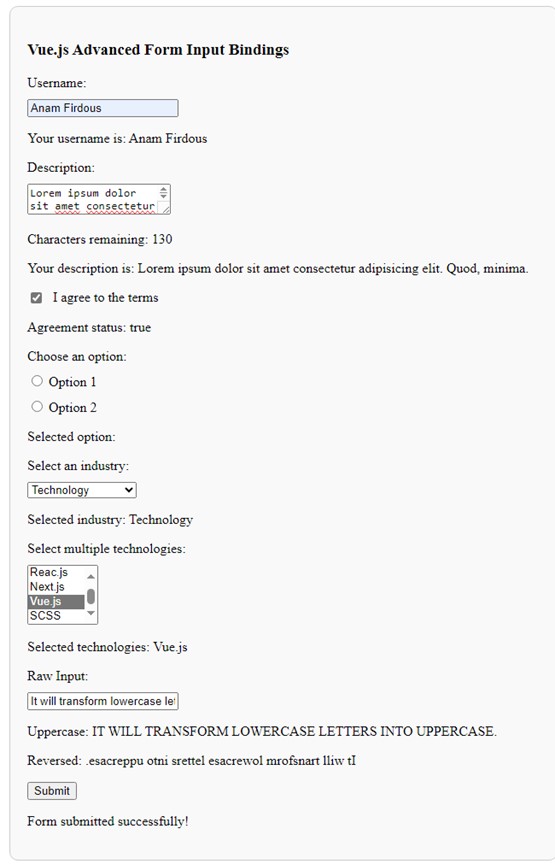
Output:

Real-World Applications
These input bindings can be applied in various real-world scenarios, such as:
- User registration forms
- Surveys and feedback forms
- E-commerce checkout processes
- Any application that requires user input
Conclusion
Vue.js provides a powerful and intuitive way to handle form inputs through its binding system. Whether you’re dealing with text inputs, checkboxes, or dropdowns, the ‘v-model’ directive simplifies managing state in your application. With these tools, you can create dynamic, responsive forms that enhance user experience.
Try implementing these Vue.js form bindings in your own projects, and feel free to share your experiences or questions in the comments below. Happy coding!
Source: Read MoreÂ