Documenting an API in Laravel often involves using packages that rely on manual PHPDoc annotations. While this method works, it is time-consuming, error-prone, and often leads to documentation becoming outdated as the codebase evolves.
This disconnection between code and documentation can result in inaccuracies that mislead developers and hinder project maintenance.
There is also the option to maintain an OpenAPI spec file manually, but this too can become a ton of work and easily outdated.
Generating API documentation with static code analysis
On the other hand, there is the static code analysis approach.
Unlike traditional methods where documentation and code can diverge, static code analysis scans your codebase to infer types, parameters, and responses directly from the code. This means that as your code changes, your documentation changes with it, ensuring that the two are always in sync without requiring additional effort from developers.
For example, take a look at this simplified controller’s method code:
// app/Http/Controllers/Api/ExpensesController.php
public function index(Request $request)
{
$this->authorize(‘readAny’, Expense::class);
$expenses = Expense::query()
->when(
$request->has(‘category’),
fn ($q) => $q->where(‘category’, $request->enum(‘category’, ExpenseCategory::class)),
)
->get();
return ExpenseResource::collection($expenses)->additional([
‘can_create’ => (bool) $request->user()->can(‘create’, Expense::class),
]);
}
Just by looking at it you already know that:
this endpoint returns a successful response with a collection of expense resources with additional data showing if a user can create an expense
this endpoint may fail with 403 response when user is not authorized
user can pass status of the expense to the request which can be one of the available ExpenseStatus enum’s values
This is exactly what the static code analysis approach does: by scanning the codebase and inferring types, it can determine how requests and responses of the API look like, hence the generated documentation is always accurate and stays in sync with the codebase.
Meet Scramble
In this article I want to introduce you to Scramble: https://scramble.dedoc.co/
This is a package for Laravel that generates API documentation by relying on static code analysis. Using it, you won’t need to manually write and maintain PHPDoc annotations and will always have up-to-date API documentation which is in sync with your codebase.
Let’s install Scramble by simply requiring it in the Laravel API project:
composer require dedoc/scramble
Before we check the documentation, I want to briefly show you the API we’ll document:
GET /api/expenses
POST /api/expenses
This application is a simple expense tracker, allowing users to list all their expenses and also store an expense.
Now, let’s check the documentation. After you install Scramble, it is available at /docs/api by default.
Documentation of GET /api/expenses endpoint
Here is the documentation for the GET /api/expenses endpoint, whose code we saw in the prior example.
Just by analyzing the codebase, Scramble could:
Document the successful (200) response type from this endpoint.
Document the error (403) response when the user doesn’t have permission.
Document the error (401) response when the user is not authenticated.
Document the request’s status parameter, noting that this parameter is an enum (including available values).
Under the hood
Let’s take a closer look at how this works under the hood.
Documenting the successful response
To determine what a successful response looks like, Scramble infers the return type of the controller’s method. By analyzing the ExpenseResource::collection expression, the inference system understands this is an anonymous collection of ExpenseResource, and after analyzing the subsequent call to additional, it also knows that there is an additional array in this collection instance. Based on this, Scramble can determine what the response looks like.
Documenting the 403 response
Due to the call to the authorize method, Scramble knows that this method can throw an authorization exception. So after analyzing the controller method, we know the list of exceptions that can possibly be thrown. Since these exceptions are rendered as responses, Scramble documents them as well.
This also means that you can have some custom exceptions thrown in your controller, and as long as they extend HttpException, Scramble will document them with the correct status code.
Error responses can be inferred not only from possible exceptions but also from explicit response returns:
return response()->json([‘message’ => ‘You are not authorized’], 403);
Documenting the 401 response
The routes of our application are registered like this:
<?php
use IlluminateSupportFacadesRoute;
Route::middleware(‘auth:sanctum’)->group(function () {
Route::apiResource(‘expenses’, AppHttpControllersApiExpensesController::class);
});
Based on this, Scramble understands that there is an auth middleware, which returns a 401 response if the user is not authenticated.
Documenting the request
In this specific example, Scramble can see the call to a method on the request, which indicates that there is a parameter with this specific type.
Additionally, Scramble analyzes validation calls as well as the list of rules on form request objects.
In the case of the expense creation endpoint, we’ll write validation code like this:
$data = $request->validate([
‘description’ => [‘string’],
‘category’ => [‘required’, Rule::enum(ExpenseCategory::class)],
‘amount’ => [‘required’, ‘integer’],
/**
* The date of the transaction. Will use current date when not passed.
* @format date-time
*/
‘date’ => [‘date’],
]);
Here, we’ve added PHPDoc annotations to manually include a relevant description for request parameters, clarifying how the API behaves if a parameter is missing.
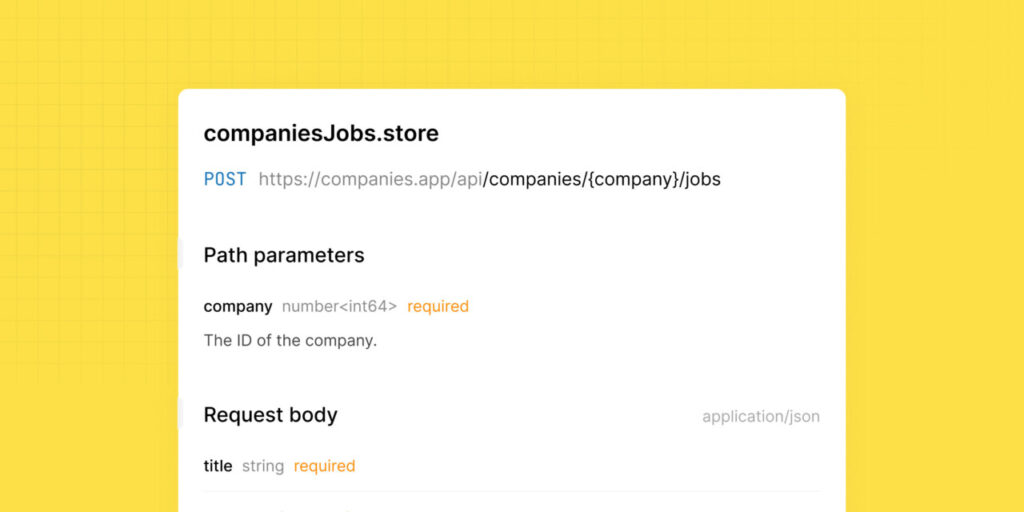
The resulting documentation looks like this:
The documentation of POST /api/expenses endpoint
Ensuring the documentation is always up to date
Now imagine you make some changes to your endpoint: you want to add some new filters for expenses, return other additional data, or add a new possible status to the category enum.
// app/Http/Controllers/Api/ExpensessController.php
public function index(Request $request)
{
$this->authorize(‘readExpenses’, Expense::class);
$expenses = Expense::query()
->when(
$request->has(‘category’),
fn ($q) => $q->where(‘category’, $request->enum(‘category’, ExpenseCategory::class)),
)
+ ->when(
+ $request->has(‘q’),
+ fn (Builder $q) => $q->where(DB::raw(‘lower(title)’), ‘like’, ‘%’.Str::lower($request->get(‘q’)).’%’),
+ )
->get();
return ExpenseResource::collection($expenses)->additional([
‘can_create’ => (bool) $request->user()->can(‘createExpenses’, Expense::class),
+ ‘can_update’ => (bool) $request->user()->can(‘createExpenses’, Expense::class),
]);
}
// app/Enums/ExpenseCategory.php
enum ExpenseCategory: string
{
case Travel = ‘travel’;
case Food = ‘food’;
+ case Utilities = ‘utilities’;
}
And here is the resulting documentation:
The documentation of updated GET /api/expenses endpoint
As you can see, the documentation stays up to date with all the changes in the codebase. And you only changed your codebase, not the PHPDoc annotations.
PHPDoc annotations can still be useful, though! When you want to add a human description for properties or request parameters, you can still do it. Or when you know the type better than Scramble does, you can always take control.
Demo
Here is a simple demo repository of a project that uses Scramble for API documentation.
Demo documentation website: https://scramble.dedoc.co/demo/scramble#/
Demo documentation repository: https://github.com/dedoc/demo-scramble
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve taken a closer look at Scramble and how it can simplify API documentation in Laravel projects.
Traditional methods, like manually writing PHPDoc annotations or maintaining an OpenAPI spec file, can be both time-consuming and prone to errors. Scramble changes that by using static code analysis to keep your documentation automatically up to date.
With Scramble, your documentation is a direct reflection of your codebase. As you make changes to your API, Scramble updates the documentation accordingly—no extra effort required.
This approach not only saves time but also ensures that your documentation is always accurate, reducing the chances of it becoming outdated.
If you’re working on a Laravel API project, give Scramble a try! Visit https://scramble.dedoc.co to learn more!
The post Automated API documentation generation for Laravel with static code analysis using Scramble appeared first on Laravel News.
Join the Laravel Newsletter to get all the latest
Laravel articles like this directly in your inbox.
Source: Read MoreÂ