Autoregressive video generation is a rapidly evolving research domain. It focuses on the synthesis of videos frame-by-frame using learned patterns of both spatial arrangements and temporal dynamics. Unlike traditional video creation methods, which may rely on pre-built frames or handcrafted transitions, autoregressive models aim to generate content dynamically based on prior tokens. This approach is similar to how large language models predict the next word. It offers a potential to unify video, image, and text generation under a shared framework by using the structural power of transformer-based architectures.
One major problem in this space is how to accurately capture and model the intrinsic spatiotemporal dependencies in videos. Videos contain rich structures across both time and space. Encoding this complexity so models can predict coherent future frames remains a challenge. When these dependencies are not modeled well, it leads to broken frame continuity or unrealistic content generation. Traditional training techniques like random masking also struggle. They often fail to provide balanced learning signals across frames. When spatial information from adjacent frames leaks, prediction becomes too easy.
Several methods attempt to address this challenge by adapting the autoregressive generation pipeline. However, they often deviate from standard large language model structures. Some use external pre-trained text encoders, making models more complex and less coherent. Others bring significant latency during generation with inefficient decoding. Autoregressive models like Phenaki and EMU3 try to support end-to-end generation. Despite this, they still struggle with performance consistency and high training costs. Techniques like raster-scan order or global sequence attention also do not scale well to high-dimensional video data.
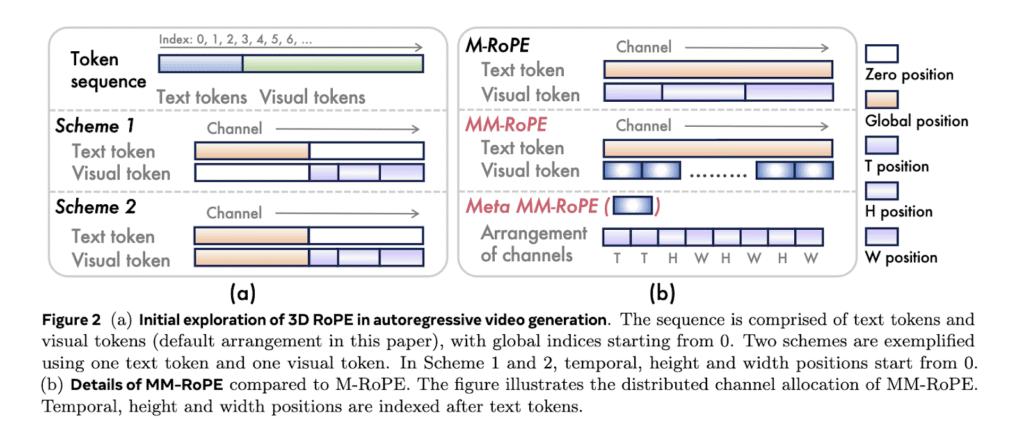
The research team from Alibaba Group’s DAMO Academy, Hupan Lab, and Zhejiang University introduced Lumos-1. It is a unified model for autoregressive video generation that stays true to large language model architecture. Unlike previous tools, Lumos-1 eliminates the need for external encoders and changes very little in the original LLM design. The model uses MM-RoPE, or Multi-Modal Rotary Position Embeddings, to address the challenge of modeling video’s three-dimensional structure. The model also uses a token dependency approach. This preserves intra-frame bidirectionality and inter-frame temporal causality, which aligns more naturally with how video data behaves.
In MM-RoPE, researchers expand existing RoPE methods to balance frequency spectrum for spatial and temporal dimensions. Traditional 3D RoPE misallocates frequency focus, causing detail loss or ambiguous positional encoding. MM-RoPE restructures allocations so that temporal, height, and width each receive balanced representation. To address loss imbalance in frame-wise training, Lumos-1 introduces AR-DF, or Autoregressive Discrete Diffusion Forcing. It uses temporal tube masking during training, so the model does not rely too much on unmasked spatial info. This ensures even learning across the video sequence. The inference strategy mirrors the training, allowing high-quality frame generation without degradation.
Lumos-1 was trained from scratch on 60 million images and 10 million videos, using only 48 GPUs. This is considered memory-efficient given the training scale. The model achieved results comparable to top models in the field. It matched EMU3’s results on GenEval benchmarks. It performed equivalently to COSMOS-Video2World on the VBench-I2V test. It also rivaled OpenSoraPlan’s outputs on the VBench-T2V benchmark. These comparisons show that Lumos-1’s lightweight training does not compromise competitiveness. The model supports text-to-video, image-to-video, and text-to-image generation. This demonstrates strong generalization across modalities.
Overall, this research not only identifies and addresses core challenges in spatiotemporal modeling for video generation but also showcases how Lumos-1 sets a new standard for unifying efficiency and effectiveness in autoregressive frameworks. By successfully blending advanced architectures with innovative training, Lumos-1 paves the way for the next generation of scalable, high-quality video generation models and opens up new avenues for future multimodal research.
Check out the Paper and GitHub. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project.
The post This AI Paper from Alibaba Introduces Lumos-1: A Unified Autoregressive Video Generator Leveraging MM-RoPE and AR-DF for Efficient Spatiotemporal Modeling appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ