Sakana AI introduces a novel framework for reasoning language models (LLMs) with a focus on efficiency and reusability: Reinforcement-Learned Teachers (RLTs). Traditional reinforcement learning (RL) approaches in LLMs are plagued by sparse reward signals and prohibitively high computational demands. By contrast, RLTs redefine the teacher-student paradigm by training smaller models to act as optimized instructors, producing step-by-step explanations instead of solving problems from scratch. This design shift enables significant gains in distillation quality, cost-efficiency, and transferability across domains—without the need for large model footprints.

Rethinking Reinforcement Learning for Teaching, Not Solving
Conventional RL setups train models to solve problems autonomously using sparse, correctness-based rewards. These models are often repurposed to teach smaller models, generating reasoning traces for distillation. However, the mismatch between the RL objective (solving problems) and the actual downstream use (teaching) results in inefficiencies. RLTs directly address this by prompting models with both the problem and its solution, requiring them only to generate detailed, pedagogical explanations. The reward signal is dense and student-aligned: it measures how well the student model understands the explanation and reproduces the solution.
Core Concept: Dense, Student-Aligned Rewards
The RLT training objective is constructed around two key reward terms:
- Solution Score (rSS): Quantifies the student’s ability to reconstruct the correct solution given the explanation and the problem.
- Explanation Score (rKL): Measures how logically coherent the teacher’s explanation is from the student’s perspective.
These are combined into a dense reward signal that encourages explanations which are both instructive and understandable. Importantly, this bypasses the exploration bottleneck of traditional RL, enabling smaller models to effectively train via RL.

Surprising Efficacy of Small Teachers
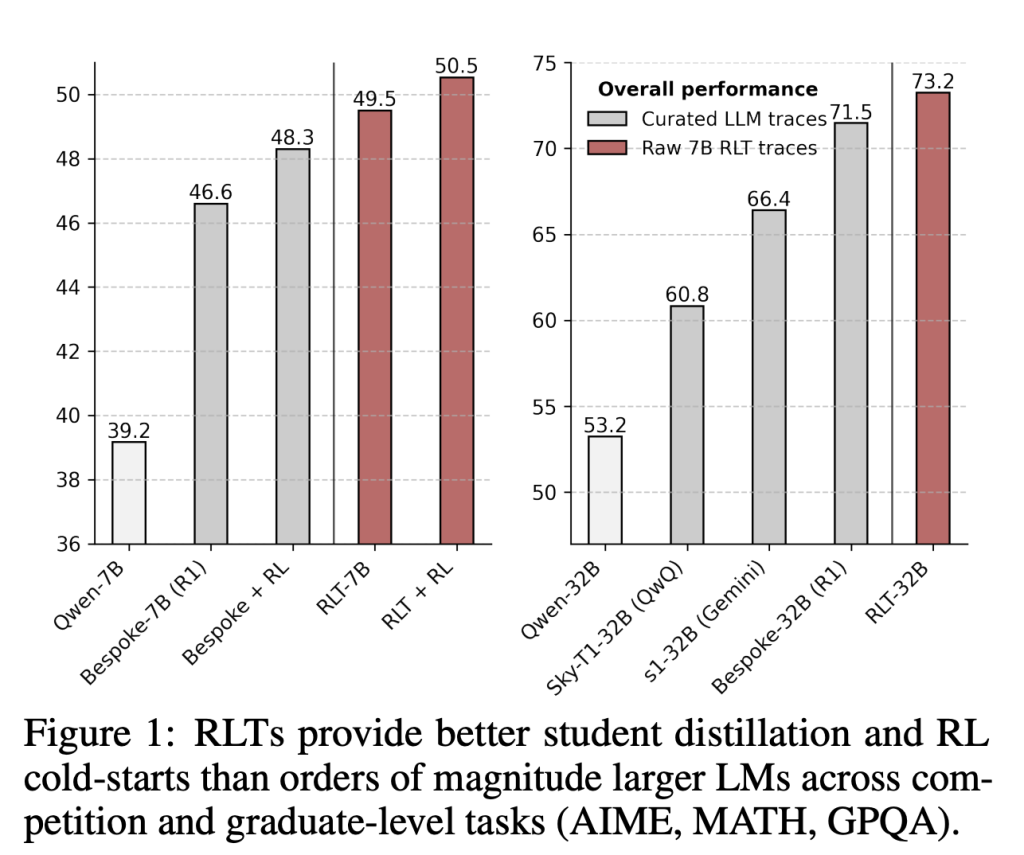
Sakana AI demonstrates that a 7B parameter RLT outperforms much larger LLMs (e.g., 32B+ models) on distillation tasks across multiple challenging datasets, including AIME 2024, MATH 500, and GPQA Diamond. On a 17K-question corpus:
- RLT-7B outperforms DeepSeek R1, Bespoke-7B, and even post-processed RL traces.
- RLT-32B outperforms all 32B baselines across the board, despite being distilled from a smaller teacher.
The impact is not just parameter efficiency—RLTs achieve better generalization, fewer formatting errors, and higher interpretability.
Cold-Starting Reinforcement Learning with RLTs
Another critical use case is RL cold-starting, where an initial model is bootstrapped with external data before formal RL training. Traces generated by RLTs serve as more effective cold-start material than those from larger RL-trained models. In fact, even without post-processing or external refinement (e.g., via GPT-4.1), RLT-generated explanations yield higher performance gains after RL fine-tuning.
Out-of-Domain Generalization and Zero-Shot Transfer
RLTs also show strong zero-shot transfer capabilities. When applied to a novel domain—such as the arithmetic-based “Countdown” task—the RLT-trained traces enable student models to surpass even direct RL on the new domain. This indicates that the skill of “explaining a solution” generalizes across tasks more easily than the skill of “solving from scratch,” providing evidence for better reusability of teaching-focused RL models.
Training Pipeline: Efficient and Scalable
The training process is computationally lean:
- 250 RL steps (~1 epoch), batch size 256, group size 64.
- Trained using a single-node setup with Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct.
- Code and pretrained checkpoints are available: GitHub
Unlike traditional RL pipelines, RLTs do not require post-processing, formatting corrections, or verification filters—raw outputs are directly usable.
Evaluation Highlights

TL;DR (100 words)
Sakana AI introduces Reinforcement-Learned Teachers (RLTs), a lightweight yet powerful framework for teaching LLMs to reason. Unlike traditional RL models that learn by solving tasks from scratch, RLTs are given both the question and its solution and are trained to generate step-by-step explanations. This setup aligns RL rewards with student learning outcomes, enabling 7B parameter RLTs to outperform much larger LLMs in distillation and cold-start scenarios. RLTs are cost-efficient, transferable across domains, and eliminate the need for expensive post-processing—offering a scalable blueprint for building reasoning-capable LLMs using modest compute and open-source tools.
Check out the Paper and Technical details All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post Sakana AI Introduces Reinforcement-Learned Teachers (RLTs): Efficiently Distilling Reasoning in LLMs Using Small-Scale Reinforcement Learning appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ