LLMs are increasingly seen as key to achieving Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), but they face major limitations in how they handle memory. Most LLMs rely on fixed knowledge stored in their weights and short-lived context during use, making it hard to retain or update information over time. Techniques like RAG attempt to incorporate external knowledge but lack structured memory management. This leads to problems such as forgetting past conversations, poor adaptability, and isolated memory across platforms. Fundamentally, today’s LLMs don’t treat memory as a manageable, persistent, or sharable system, limiting their real-world usefulness.
To address the limitations of memory in current LLMs, researchers from MemTensor (Shanghai) Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Renmin University of China, and the Research Institute of China Telecom have developed MemO. This memory operating system makes memory a first-class resource in language models. At its core is MemCube, a unified memory abstraction that manages parametric, activation, and plaintext memory. MemOS enables structured, traceable, and cross-task memory handling, allowing models to adapt continuously, internalize user preferences, and maintain behavioral consistency. This shift transforms LLMs from passive generators into evolving systems capable of long-term learning and cross-platform coordination.
As AI systems grow more complex—handling multiple tasks, roles, and data types—language models must evolve beyond understanding text to also retaining memory and learning continuously. Current LLMs lack structured memory management, which limits their ability to adapt and grow over time. MemOS, a new system that treats memory as a core, schedulable resource. It enables long-term learning through structured storage, version control, and unified memory access. Unlike traditional training, MemOS supports a continuous “memory training” paradigm that blurs the line between learning and inference. It also emphasizes governance, ensuring traceability, access control, and safe use in evolving AI systems.
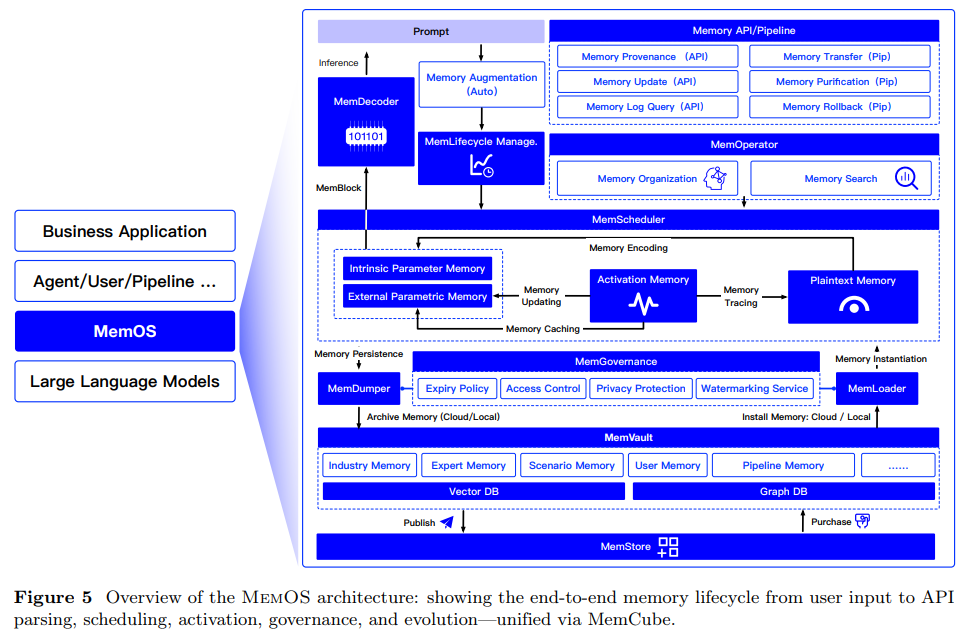
MemOS is a memory-centric operating system for language models that treats memory not just as stored data but as an active, evolving component of the model’s cognition. It organizes memory into three distinct types: Parametric Memory (knowledge baked into model weights via pretraining or fine-tuning), Activation Memory (temporary internal states, such as KV caches and attention patterns, used during inference), and Plaintext Memory (editable, retrievable external data, like documents or prompts). These memory types interact within a unified framework called the MemoryCube (MemCube), which encapsulates both content and metadata, allowing dynamic scheduling, versioning, access control, and transformation across types. This structured system enables LLMs to adapt, recall relevant information, and efficiently evolve their capabilities, transforming them into more than just static generators.
At the core of MemOS is a three-layer architecture: the Interface Layer handles user inputs and parses them into memory-related tasks; the Operation Layer manages the scheduling, organization, and evolution of different types of memory; and the Infrastructure Layer ensures safe storage, access governance, and cross-agent collaboration. All interactions within the system are mediated through MemCubes, allowing traceable, policy-driven memory operations. Through modules like MemScheduler, MemLifecycle, and MemGovernance, MemOS maintains a continuous and adaptive memory loop—from the moment a user sends a prompt, to memory injection during reasoning, to storing useful data for future use. This design not only enhances the model’s responsiveness and personalization but also ensures that memory remains structured, secure, and reusable.
In conclusion, MemOS is a memory operating system designed to make memory a central, manageable component in LLMs. Unlike traditional models that depend mostly on static model weights and short-term runtime states, MemOS introduces a unified framework for handling parametric, activation, and plaintext memory. At its core is MemCube, a standardized memory unit that supports structured storage, lifecycle management, and task-aware memory augmentation. The system enables more coherent reasoning, adaptability, and cross-agent collaboration. Future goals include enabling memory sharing across models, self-evolving memory blocks, and building a decentralized memory marketplace to support continual learning and intelligent evolution.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post MemOS: A Memory-Centric Operating System for Evolving and Adaptive Large Language Models appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ