Multimodal reasoning ability helps machines perform tasks such as solving math problems embedded in diagrams, reading signs from photographs, or interpreting scientific charts. The integration of both visual and linguistic information enables these systems to more closely mirror human thought processes, making them suitable for tasks that require visual interpretation combined with logical progression.
A major challenge in this area is the inability of current systems to revisit specific parts of an image while reasoning dynamically. Traditional models usually begin by analyzing an image once and then proceed with the rest of the reasoning in pure text. This approach limits accuracy in situations that require revisiting the image to confirm a detail or extract new visual cues during mid-reasoning. These shortcomings are particularly pronounced in tasks that require fine-grained spatial awareness, such as identifying small labels in scientific documents or resolving ambiguities in visually complex scenes.
Some tools and models have been introduced to address this gap, but they often treat visual grounding as a one-time operation. For example, existing systems like LLaVA-CoT or Qwen2.5-VL offer some visual-text integration. Still, they don’t let the model repeatedly and selectively query parts of an image based on the evolving reasoning process. The grounding, if performed, is generally static and lacks the flexibility to adapt based on intermediate reasoning steps. Moreover, these methods do not train models to determine the importance of specific image regions, leading to limitations in complex problem-solving.
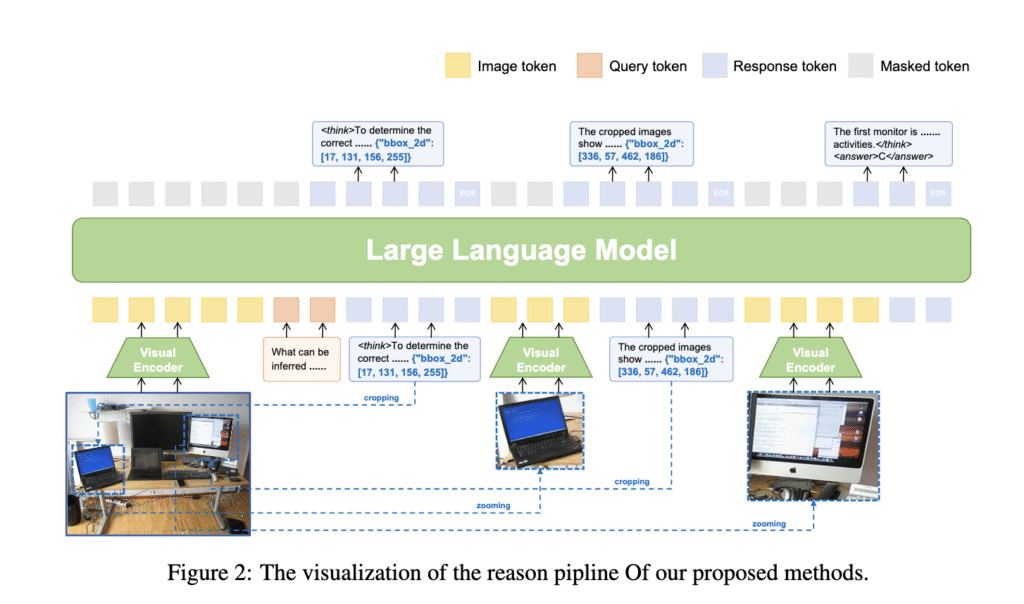
Researchers from Peking University, Alibaba Group, and ZEEKR Intelligent Technology have introduced a model called VLM-R³. This model tackles the challenge by allowing a more interactive connection between vision and reasoning. It equips the model with the capacity to determine when visual clarification is needed, identify the exact image region for analysis, and re-integrate this visual content into the reasoning process. This approach mimics human problem-solving, where one might zoom into a chart or revisit a paragraph to verify a detail before making a decision. The model’s structure emphasizes refining its decisions iteratively by relying on visual evidence throughout the reasoning process.
To accomplish this, the researchers built a dataset named Visuo-Lingual Interleaved Rationale (VLIR), designed to train models in a stepwise interaction between images and text. VLM-R³ incorporates this dataset and operates using a method called Region-Conditioned Reinforcement Policy Optimization (R-GRPO). This training strategy encourages the model to selectively focus on informative parts of an image, perform transformations such as cropping or zooming, and incorporate those changes into subsequent logical steps. It simulates how humans shift their attention across different visual elements in response to their thoughts. The architecture integrates a pipeline that loops reasoning with visual inspection in real time, enhancing the system’s ability to interact with visual data during inference.
The results demonstrate a strong performance across multiple benchmarks. On MathVista, the model reached 70.4%, an increase from 68.2% in the baseline. For MathVision, the improvement was from 25.1% to 30.2%. On ScienceQA, it posted a 14.3% improvement, reaching 87.9% over the baseline’s 73.6%. On the hallucination test (HallusionBench), the model achieved 62.0%, outperforming others like Mulberry, which scored 54.1%. VLM-R³ also showed superior results on document understanding in DocVQA with a 96.8% score. Comparisons showed that even though it uses fewer parameters than closed-source models like Gemini-2 Flash or GPT-4o, it delivers competitive accuracy, particularly in tasks requiring detailed visual analysis and interleaved reasoning.
This work clearly outlines a problem that exists in how models handle vision during reasoning and presents a well-structured solution. By integrating a method for ongoing image analysis, researchers from the Alibaba Group, Peking University, and ZEEKR have advanced a powerful idea—models that look again, think, and refine. The proposed framework significantly improves accuracy in complex tasks and provides a blueprint for more robust, visually aware AI systems.
Check out the Paper and GitHub Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 99k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post This AI Paper Introduces VLM-R³: A Multimodal Framework for Region Recognition, Reasoning, and Refinement in Visual-Linguistic Tasks appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ