Bridging Perception and Action in Robotics
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) hold promise for enabling machines, such as robotic arms and legged robots, to perceive their surroundings, interpret scenarios, and take meaningful actions. The integration of such intelligence into physical systems is advancing the field of robotics, pushing it toward autonomous machines that don’t just see and describe but also plan and move within their environments based on contextual understanding.
Despite the growing power of MLLMs, one persistent issue is their inability to combine vision, reasoning, and physical interaction into one cohesive system. Typically, models trained to understand images or text fall short when asked to control robots in real-world spaces. The core problem is that understanding a scene is fundamentally different from acting within it. Multimodal understanding focuses on perception and analysis, while physical control needs precise, real-time decision-making based on that perception. This disconnect creates bottlenecks when attempting to build agents that must simultaneously observe, reason, and act in varied environments.
Limitations of Prior VLA Models
Previous tools designed for robot control rely heavily on vision-language-action (VLA) models. These models train on extensive robotic datasets to convert visual observations into control signals. While some solutions try to preserve the reasoning capability of MLLMs by translating commands into text-based actions, they face difficulty in maintaining accuracy and adaptability during control tasks. For instance, VLAs often degrade in performance when applied to diverse or long-horizon robotic operations. Furthermore, due to the gap between image-based understanding and motion control, these tools usually fail to generalize across different environments or robot types.
Introducing VeBrain: A Unified Multimodal Framework
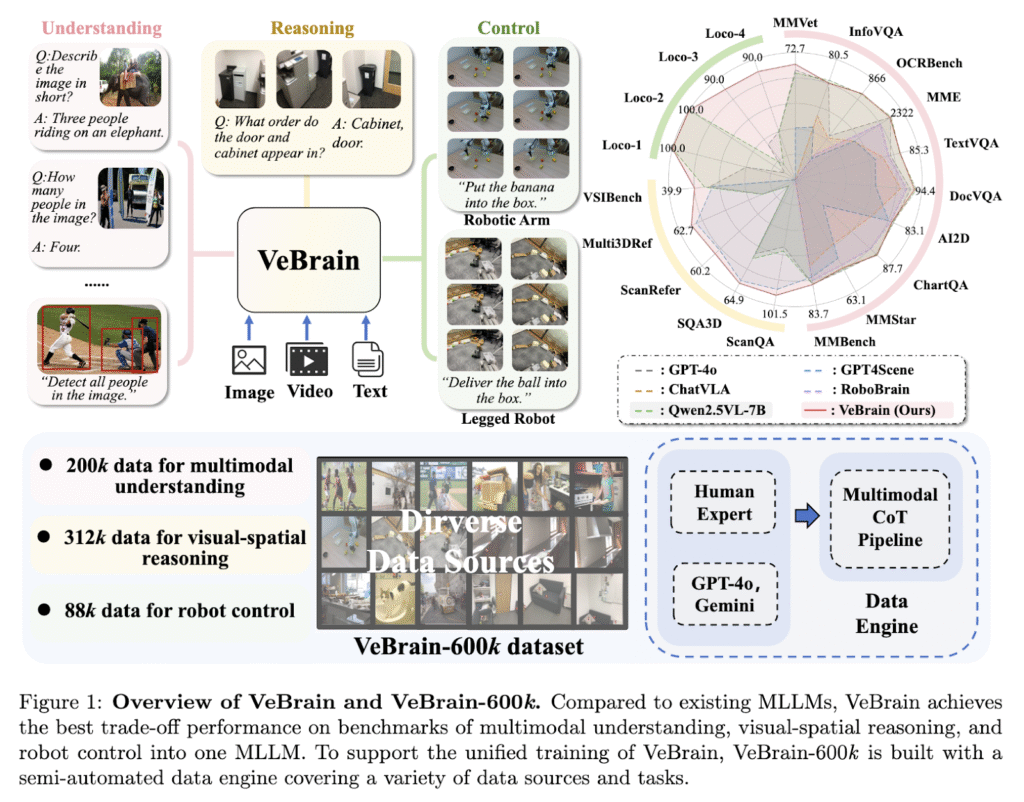
Researchers from Shanghai AI Laboratory, Tsinghua University, and SenseTime Research have introduced a unified framework called Visual Embodied Brain (VeBrain) in collaboration with multiple other institutes. VeBrain reformulates robot control as text-based tasks within a 2D visual space, aligning it more closely with how MLLMs function. The framework integrates multimodal understanding, spatial reasoning, and robotic control into one structure. A specially designed robotic adapter processes the MLLM’s output into executable movement policies, enabling a single model to manage perception, reasoning, and control. VeBrain is also supported by a high-quality instruction dataset called VeBrain-600k, which combines over 600,000 samples of multimodal tasks, including robot motion and reasoning steps.
Technical Components: Architecture and Robotic Adapter
To carry out its functions, VeBrain utilizes an architecture based on Qwen2.5-VL, augmented with components that enable real-world control. The robotic adapter contains four key modules. The point tracker updates 2D keypoints as the robot’s view changes, ensuring accurate targeting. The movement controller transforms 2D key points into 3D movements by combining image data with depth maps. The skill executor maps predicted actions, such as “turn” or “grasp,” to pre-trained robotic skills. Lastly, the dynamic takeover module monitors failures or anomalies, handing control back to the MLLM when needed. These modules form a closed-loop system that makes decisions, acts, and self-corrects, allowing robots to operate effectively in diverse situations.
Performance Evaluation Across Multimodal and Robotic Benchmarks
VeBrain was evaluated across 13 multimodal and 5 spatial benchmarks. On MMVet, it achieved a 5.6% improvement over Qwen2.5-VL. It achieved a score of 101.5 on the CIDEr metric for ScanQA and scored 83.7 on MMBench. On the VSI benchmark, it averaged 39.9, outperforming Qwen2.5-VL’s 35.9. In robotic evaluations, VeBrain showed 86.4% success across seven-legged robot tasks, significantly surpassing models like VLA and π0, which scored 32.1% and 31.4%, respectively. On robotic arm tasks, it achieved a success rate of 74.3%, outperforming others by up to 80%. These results show VeBrain’s ability to handle long-horizon and spatially complex control challenges with high reliability.
Conclusion
The research presents a compelling direction for embodied AI. Researchers succeeded in redefining robot control as a language task, enabling high-level reasoning and low-level action to coexist. The method bridges the gap between image understanding and robot execution in a way that’s both functional and scalable. With a robust design and strong performance, VeBrain signals a shift toward more unified, intelligent robotics systems capable of operating autonomously across diverse tasks and environments.
Check out the Paper and GitHub Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 99k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post VeBrain: A Unified Multimodal AI Framework for Visual Reasoning and Real-World Robotic Control appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ