Reinforcement Learning’s Role in Fine-Tuning LLMs
Reinforcement learning has emerged as a powerful approach to fine-tune large language models (LLMs) for more intelligent behavior. These models are already capable of performing a wide range of tasks, from summarization to code generation. RL helps by adapting their outputs based on structured feedback. As demand grows for models to be not just accurate but also aligned with complex preferences or rules, RL provides a crucial mechanism to enhance their performance. Consequently, RL has become a central component in the post-training process of many advanced LLM systems.
The Infrastructure Challenges of Scaling RL for LLMs
A major challenge in applying RL to large-scale LLMs lies in its significant resource requirements. Training these models involves not just massive computation but also coordination between different components. Notable components include policy models, reward scorers, and critics. Model sizes scale into hundreds of billions of parameters, and issues like memory usage, data communication latency, and GPU idle time present difficult engineering problems. Without efficient design, these limitations hinder the ability to apply RL to newer, larger models. Achieving high GPU utilization and minimizing inter-process bottlenecks are vital for scalable and timely training.
Limitations of Previous RL Frameworks for LLMs
Prior solutions have struggled with either being too rigid or inefficient when scaled. Traditional synchronous frameworks execute generation and training in sequential steps, often causing GPU idle time due to mismatched task durations. Tools like DeepSpeed-Chat employ hybrid memory strategies but require models to share memory space. This results in performance bottlenecks during generation. Some distributed methods try to decouple components but still rely on heavy orchestration tools, limiting flexibility. Additionally, earlier frameworks often fail to optimize memory use for varying parallelism needs during training and inference.
Meta’s LlamaRL: A PyTorch-Based Distributed Asynchronous RL Framework
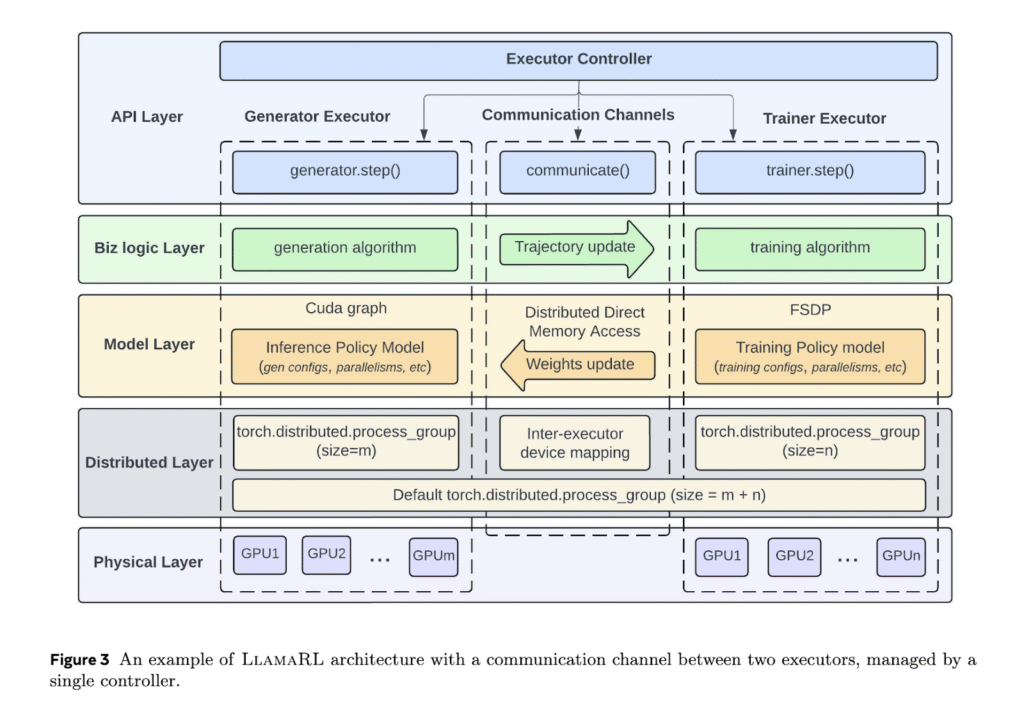
Meta researchers introduced LlamaRL, a fully asynchronous and distributed reinforcement learning framework. It is tailored for training massive LLMs on clusters ranging from a few to thousands of GPUs. They built LlamaRL entirely in PyTorch and implemented a single-controller design to simplify coordination. This design enables modular customization. Separate executors manage each RL component—such as the generator, trainer, and reward model—and operate in parallel. This asynchronous setup reduces waiting time throughout the RL pipeline. It also enables independent optimization of model parallelism and memory usage.
Key Features: Offloading, Memory Efficiency, and Asynchronous Execution
LlamaRL’s architecture prioritizes flexible execution and efficient memory usage. It offloads generation processes to dedicated executors, allowing the trainer to focus exclusively on model updates. Distributed Direct Memory Access (DDMA) supports this offloading. It uses NVIDIA NVLink to synchronize weights in under two seconds—even for models with 405 billion parameters. The framework applies Asynchronous Importance-weighted Policy Optimization (AIPO) to correct for off-policyness caused by asynchronous execution. Each executor operates independently, leverages fine-grained parallelism, and applies quantization techniques to inference models to further reduce compute and memory demands.
Real-World Performance Benchmarks: 10.7x Speedup on 405B Models
LlamaRL delivers significant improvements in training speed without compromising quality. On an 8B parameter model with 256 GPUs, it cuts the training step time from 22.45 seconds to 8.90 seconds. For the 70B model, the reduction is from 82.32 to 20.67 seconds. Most impressively, on a 405B parameter model across 1024 GPUs, LlamaRL slashes the RL step time from 635.8 to just 59.5 seconds and achieves a 10.7× speedup over the synchronous baseline. These gains results not only from asynchronous execution but also its decoupled memory and compute strategies. Benchmark evaluations on MATH and GSM8K confirm that LlamaRL maintains consistent performance. Some metrics even show slight improvements.
Final Thoughts: LlamaRL as a Scalable Path Forward in LLM Training
This research presents a practical and scalable solution to one of the most significant bottlenecks. The bottleneck is in training large language models (LLMs) using reinforcement learning. The introduction of asynchronous training through LlamaRL marks a substantial shift from traditional reinforcement learning (RL) pipelines. By addressing memory constraints, communication delays, and GPU inefficiencies, the framework provides a well-integrated solution for future developments in language model training.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 99k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter. ▷ Want to promote your product/webinar/service to 1 Million+ AI Engineers/Developers/Data Scientists/Architects/CTOs/CIOs? Lets Partner..
The post Meta Introduces LlamaRL: A Scalable PyTorch-Based Reinforcement Learning RL Framework for Efficient LLM Training at Scale appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ