Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) are designed to process and generate content across various modalities, including text, images, audio, and video. These models aim to understand and integrate information from different sources, enabling applications such as visual question answering, image captioning, and multimodal dialogue systems. The development of MLLMs represents a significant step toward creating AI systems that can interpret and interact with the world in a more human-like manner.
A primary challenge in developing effective MLLMs lies in integrating diverse input types, particularly visual data, into language models while maintaining high performance across tasks. Existing models often struggle with balancing strong language understanding and effective visual reasoning, especially when scaling to complex data. Further, many models require large datasets to perform well, making it difficult to adapt to specific tasks or domains. These challenges highlight the need for more efficient and scalable approaches to multimodal learning.
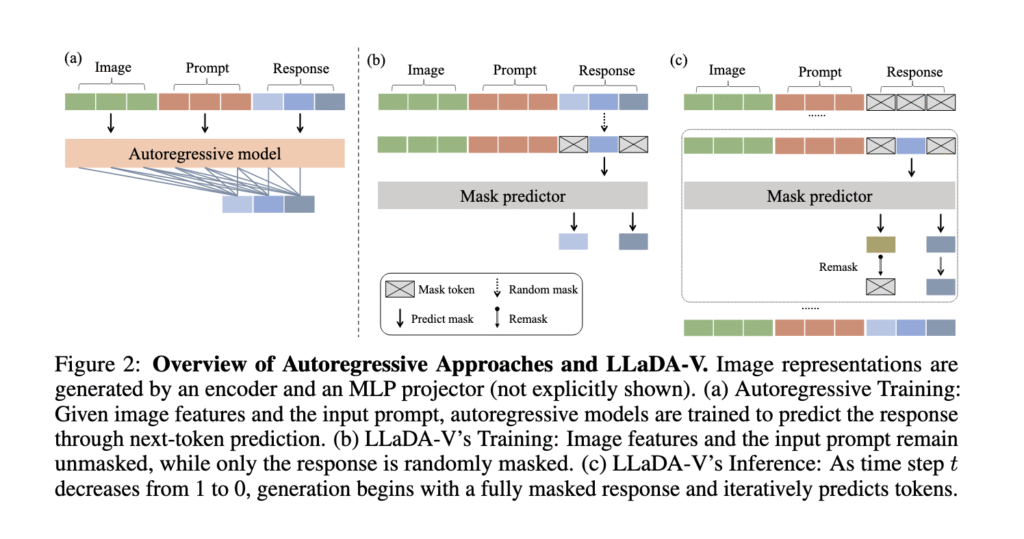
Current MLLMs predominantly utilize autoregressive methods, predicting one token at a time in a left-to-right manner. While effective, this approach has limitations in handling complex multimodal contexts. Alternative methods, such as diffusion models, have been explored; however, they often exhibit weaker language understanding due to their restricted architectures or inadequate training strategies. These limitations suggest a gap where a purely diffusion-based model could offer competitive multimodal reasoning capabilities if designed effectively.
Researchers from the Renmin University of China and Ant Group introduced LLaDA-V, a purely diffusion-based masked language modeling (MLLM) model that integrates visual instruction tuning with masked diffusion models. Built upon LLaDA, a large language diffusion model, LLaDA-V incorporates a vision encoder and an MLP connector to project visual features into the language embedding space, enabling effective multimodal alignment. This design represents a departure from the autoregressive paradigms dominant in current multimodal approaches, aiming to overcome existing limitations while maintaining data efficiency and scalability.
LLaDA-V employs a masked diffusion process where text responses are gradually refined through iterative prediction of masked tokens. Unlike autoregressive models that predict tokens sequentially, LLaDA-V generates outputs by reversing the masked diffusion process. The model is trained in three stages: the first stage aligns vision and language embeddings by mapping visual features from SigLIP2 into LLaDA’s language space. The second stage fine-tunes the model using 10 million single-image samples and 2 million multimodal samples from MAmmoTH-VL. The third stage focuses on reasoning, using 900K QA pairs from VisualWebInstruct and a mixed dataset strategy. Bidirectional attention improves context comprehension, enabling robust multimodal understanding.
In evaluations across 18 multimodal tasks, LLaDA-V demonstrated superior performance compared to hybrid autoregressive-diffusion and purely diffusion-based models. It outperformed LLaMA3-V on most multidisciplinary knowledge and mathematical reasoning tasks like MMMU, MMMU-Pro, and MMStar, achieving a score of 60.1 on MMStar, close to Qwen2-VL’s 60.7, despite LLaDA-V using the weaker LLaDA-8B language tower. LLaDA-V also excelled in data efficiency, outperforming LLaMA3-V on MMMU-Pro with 1M samples against LLaMA3-V’s 9M. Although it lagged in chart and document understanding benchmarks, such as AI2D, and in real-world scene tasks, like RealworldQA, LLaDA-V’s results highlight its promise for multimodal tasks.
In summary, LLaDA-V addresses the challenges of building effective multimodal models by introducing a purely diffusion-based architecture that combines visual instruction tuning with masked diffusion. The approach offers strong multimodal reasoning capabilities while maintaining data efficiency. This work demonstrates the potential of diffusion models in multimodal AI, paving the way for further exploration of probabilistic approaches to complex AI tasks.
Check out the Paper and GitHub Page . All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 95k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post This AI Paper Introduces LLaDA-V: A Purely Diffusion-Based Multimodal Large Language Model for Visual Instruction Tuning and Multimodal Reasoning appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ