In recent months, there has been growing interest in applying diffusion models—originally designed for continuous data, such as images—to natural language processing tasks. This has led to the development of Discrete Diffusion Language Models (DLMs), which treat text generation as a denoising process. Unlike traditional autoregressive models, DLMs enable parallel decoding and provide better control over structure, offering advantages such as flexible initialization of entire sequences, explicit control over output format, and improved infilling through bidirectional attention. Furthermore, their non-sequential nature opens the door to faster generation. Despite these benefits, most current multimodal large language models (MLLMs)—such as LLaMA, Qwen-VL, and InternVL—still rely solely on autoregressive methods.
Work in diffusion-based language models has explored both continuous and discrete diffusion spaces. Continuous approaches, such as DiffuSeq and SED, use embedding or relaxed categorical spaces for smoother generation. In contrast, discrete models like SDDM and RDM tailor the diffusion process to linguistic structures. Training techniques vary, but commonly use masked language modeling losses or entropy-based score matching. Some hybrid models, such as AR-Diffusion and SSD-LM, combine autoregressive and diffusion strategies to leverage the strengths of both approaches. Meanwhile, open-source MLLMs such as LLaVA and InternVL have advanced through visual instruction tuning and joint pretraining, yet still follow an autoregressive generation scheme.
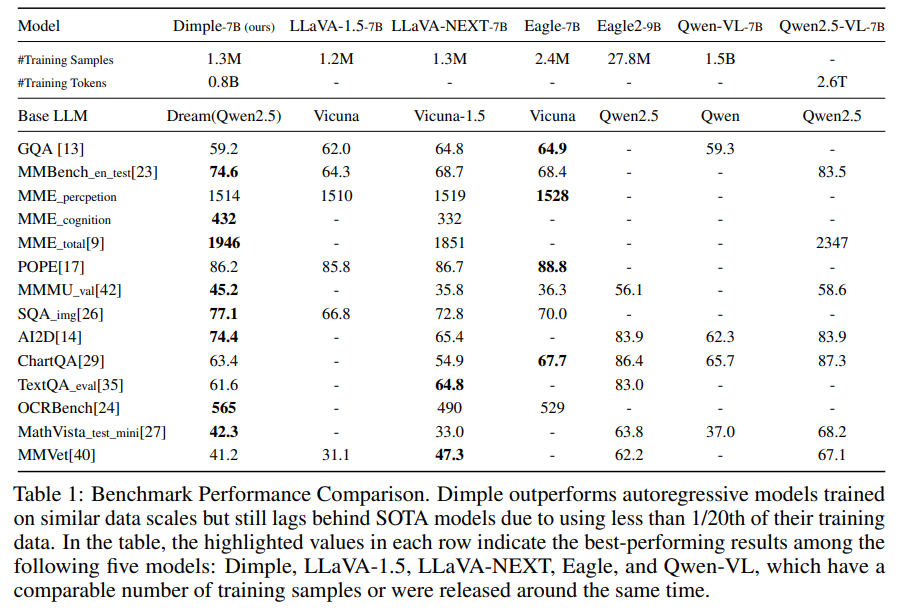
Researchers at the National University of Singapore present Dimple, the first Discrete DMLLM, which integrates a vision encoder with a discrete diffusion-based language model. To overcome the instability and performance issues of purely diffusion-based training, they introduce a two-phase training method—Autoregressive-then-Diffusion—combining initial autoregressive alignment with subsequent diffusion-based masked language modeling. Dimple-7B surpasses LLaVA-NEXT by 3.9% on benchmarks. The team also introduces Confident Decoding for dynamic token generation and explores Structure Priors for precise control over output. These innovations significantly improve inference efficiency, generation flexibility, and structural controllability without sacrificing performance.
Dimple is a Discrete Diffusion Multimodal LLM that integrates a vision encoder with a diffusion-based language model. To address inefficiencies in diffusion training, such as sparse supervision and limited generation coverage, the model is trained in two phases: first with autoregressive training using a causal attention mask for vision-language alignment, then with diffusion training to restore generation capabilities. During inference, a dynamic “Confident Decoding” strategy adapts token updates based on prediction confidence. Despite using significantly fewer training samples, Dimple exhibits competitive performance on multiple benchmarks, outperforming similar-scale autoregressive models, although it trails behind larger-scale state-of-the-art systems.
The experiments evaluate Dimple, a DMLLM, against autoregressive models on instruction-following tasks. Dimple, trained with a hybrid strategy that combines autoregressive and diffusion tuning, exhibits strong performance, surpassing models with similar training data on most benchmarks. Although it lags behind models trained on much larger datasets, Dimple benefits from a stronger base language model. Ablation studies reveal that combining autoregressive and diffusion tuning mitigates issues like length bias and improves consistency. Prefilling further boosts inference speed significantly, with only minor performance drops, making the model both efficient and competitive in multimodal understanding tasks.
In conclusion, Dimple, the first DMLLM, is designed to overcome the limitations of purely discrete diffusion training, such as instability and length bias. Dimple employs a hybrid training approach that starts with autoregressive learning, followed by diffusion tuning, yielding the Dimple-7B model, which outperforms LLaVA-NEXT by 3.9%. A decoding strategy, confident decoding, significantly reduces inference steps, while prefilling improves speed with minimal performance trade-offs. Dimple also enables structured and controllable outputs through structure priors, offering fine-grained control over format and length capabilities that autoregressive models struggle to provide.
Check out the Paper, Model on Hugging Face and GitHub Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 95k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post National University of Singapore Researchers Introduce Dimple: A Discrete Diffusion Multimodal Language Model for Efficient and Controllable Text Generation appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ