The ability to search high-dimensional vector representations has become a core requirement for modern data systems. These vector representations, generated by deep learning models, encapsulate data’s semantic and contextual meanings. This enables systems to retrieve results not based on exact matches, but on relevance and similarity. Such semantic capabilities are essential in large-scale applications such as web search, AI-powered assistants, and content recommendations, where users and agents alike need access to information in a meaningful way rather than through structured queries alone.
One of the main issues faced in vector-based retrieval is the high cost and complexity of operating separate systems for transactional data and vector indexes. Traditionally, vector databases are optimized solely for semantic search performance, but they require users to duplicate data from their primary databases, introducing latency, storage overhead, and risk of inconsistencies. Developers are also burdened with synchronizing two distinct systems, which can limit scalability, flexibility, and data integrity when updates occur rapidly.
Some popular tools for vector search, like Zilliz and Pinecone, operate as standalone services that offer efficient similarity search. However, these platforms rely on segment-based or fully in-memory architectures. They often require repeated rebuilding of indices and can suffer from latency spikes and significant memory usage. This makes them inefficient in scenarios that involve large-scale or constantly changing data. The issue worsens when dealing with updates, filtering queries, or managing multiple tenants, as these systems lack deep integration with transactional operations and structured indexing.
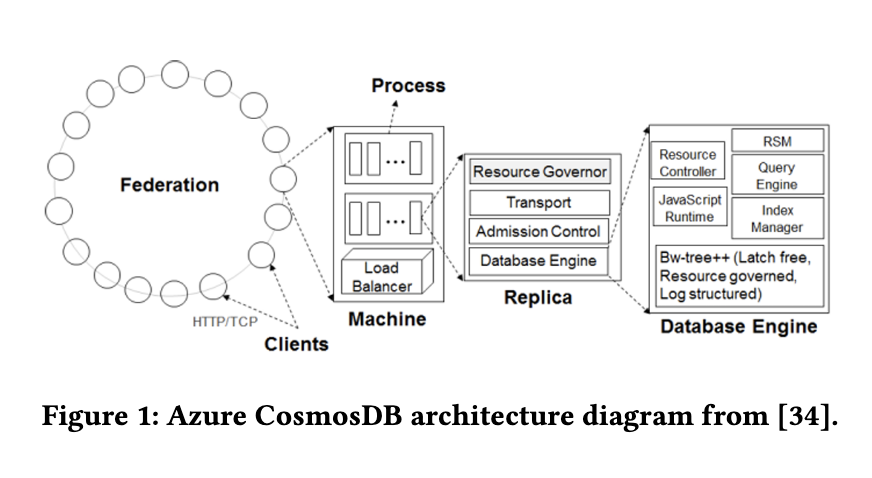
Researchers at Microsoft introduced an approach that integrates vector indexing directly into Azure Cosmos DB’s NoSQL engine. They used DiskANN, a graph-based indexing library already known for its performance in large-scale semantic search, and re-engineered it to work within Cosmos DB’s infrastructure. This design eliminates the need for a separate vector database. Cosmos DB’s built-in capabilities—such as high availability, elasticity, multi-tenancy, and automatic partitioning—are fully utilized, making the solution both cost-efficient and scalable. Each collection maintains a single vector index per partition, which is synchronized with the main document data using the existing Bw-Tree index structure.
The rewritten DiskANN library uses Rust and introduces asynchronous operations to ensure compatibility with database environments. It allows the database to retrieve or update only necessary vector components, such as quantized versions or neighbor lists, reducing memory usage. Vector insertions and queries are managed using a hybrid approach, with most computations occurring in quantized space. This design supports paginated searches and filter-aware traversal, which means queries can efficiently handle complex predicates and scale across billions of vectors. The methodology also includes a sharded indexing mode, allowing separate indices based on defined keys, such as tenant ID or time period.
In experiments, the system demonstrated strong performance. For a dataset of 10 million 768-dimensional vectors, query latency remained below 20 milliseconds (p50), and the system achieved a recall@10 of 94.64%. Compared to enterprise-tier offerings, Azure Cosmos DB provided query costs that were 15× lower than Zilliz and 41× lower than Pinecone. Cost-efficiency was maintained even as the index increased from 100,000 to 10 million vectors, with less than a 2× rise in latency or Request Units (RUs). On ingestion, Cosmos DB charged about $162.5 for 10 million vector inserts, which was lower than Pinecone and DataStax, though higher than Zilliz. Furthermore, recall remained stable even during heavy update cycles, with in-place deletions significantly improving accuracy in shifting data distributions.
The study presents a compelling solution to unifying vector search with transactional databases. The research team from Microsoft designed a system that simplifies operations and achieves considerable performance in cost, latency, and scalability. By embedding vector search within Cosmos DB, they offer a practical template for integrating semantic capabilities directly into operational workloads.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
The post This AI Paper from Microsoft Introduces a DiskANN-Integrated System: A Cost-Effective and Low-Latency Vector Search Using Azure Cosmos DB appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ