Reasoning language models, or RLMs, are increasingly used to simulate step-by-step problem-solving by generating long, structured reasoning chains. These models break down complex questions into simpler parts and build logical steps to reach answers. This chain-of-thought (CoT) approach has proven effective in improving output quality, especially in mathematical and logical tasks. Despite multilingual capabilities in many modern large models, the focus of research and training has remained largely centered on English, leaving a gap in understanding how well these reasoning skills translate to other languages.
One major challenge is that most RLMs are fine-tuned on English data, which limits their ability to reason effectively in other languages. This becomes especially problematic for low-resource languages that have limited training examples. The models may default to English thinking patterns, producing lower-quality outputs when prompted in another language. Furthermore, differences in language structure can cause reasoning errors, particularly when a model trained in one language is expected to infer logic in another without adequate linguistic alignment.
Current techniques employ zero-shot or few-shot prompting strategies to manage these limitations, often using English as a pivot language. Some efforts involve presenting prompts in the same language as the query to preserve linguistic consistency. However, small models have minimal benefits due to limited capacity, and even large models show inconsistent performance when reasoning in low-resource languages. Despite multilingual pretraining, the gap between the training and reasoning language continues to hinder accurate multilingual reasoning.
The Brown University and MBZUAI research team focused on evaluating how increasing test-time computation, particularly through extended reasoning chains, can affect the multilingual reasoning abilities of English-centric RLMs. They investigated using s1 models based on the Qwen2.5-Instruct architecture and fine-tuned on 1,000 English STEM reasoning samples. These models were tested across various languages using benchmarks like MGSM and Global-MMLU to answer four core questions: the effectiveness of crosslingual test-time scaling, language-mixing behaviors, performance under language-forcing, and cross-domain generalization.
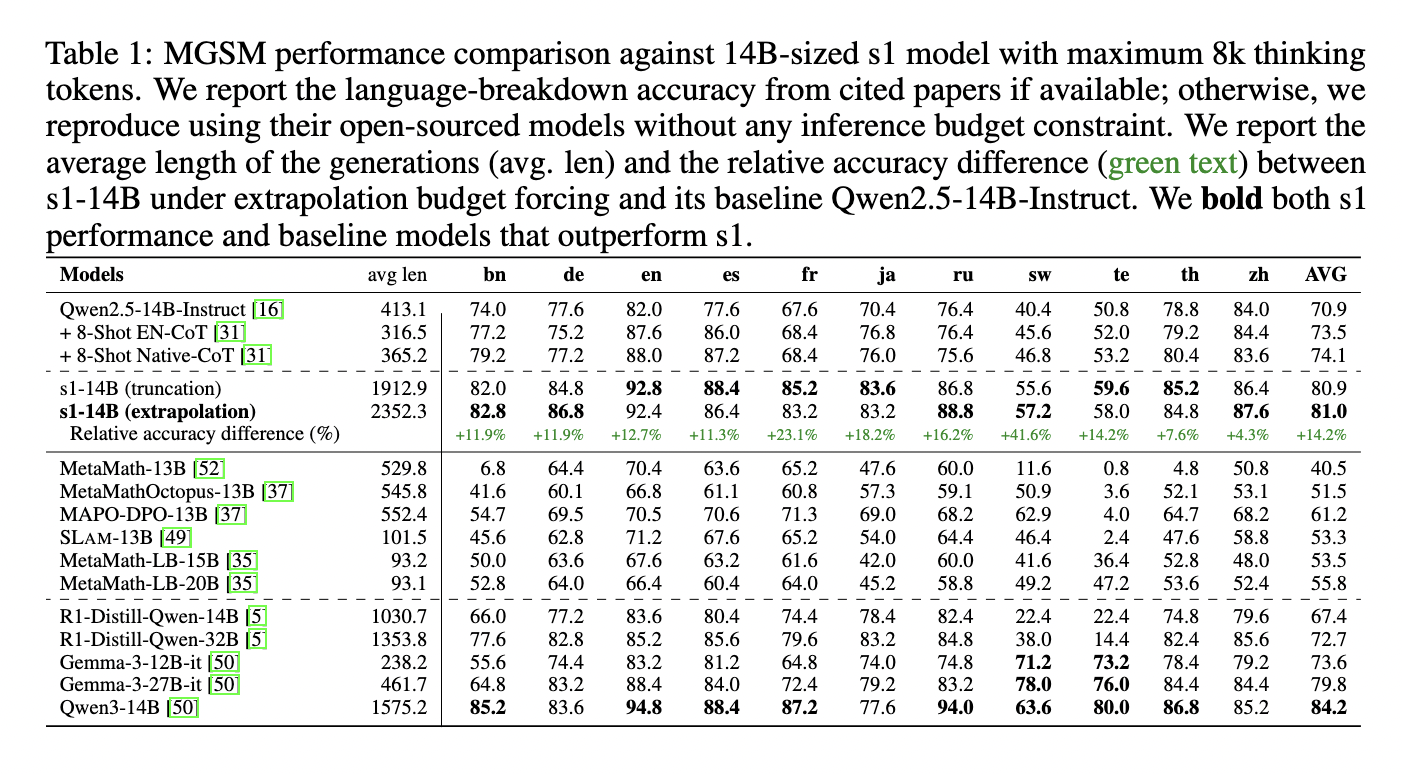
In-depth experiments showed that models with more parameters significantly benefited from increased test-time thinking tokens. The 14B s1 model, when scaled to 8,000 thinking tokens, achieved an average accuracy of 81% across non-English languages in MGSM. It outperformed models like Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct by +23.1% in French and +41.6% in Swahili. Even though the model was trained only in English, its performance surpassed that of larger models such as DeepSeek’s R1-Distill-Qwen-32B in several high-resource languages. The study also found that reasoning in high-resource languages like Chinese and English is more efficient, requiring fewer tokens and delivering better results than in low-resource languages like Swahili or Telugu.
A key observation was the “quote-and-think” behavior, where the model quoted non-English phrases from prompts and reasoned in English. This consistent pattern across languages like Japanese and Russian suggested that the model used its multilingual understanding to interpret non-English input without direct translation. Language-forcing experiments further confirmed that forcing reasoning in high-resource languages yielded better results, while strict reasoning in low-resource languages led to significant accuracy drops and computational inefficiencies.
Despite strong results in STEM-related tasks, performance gains did not transfer to domains like cultural commonsense or humanities. In benchmarks like FORK, increasing thinking tokens sometimes reduced performance, indicating overthinking. The study concludes that while test-time scaling enhances multilingual reasoning in high-resource languages, it does not generalize effectively to out-of-domain tasks or low-resource languages, indicating the need for further research on balanced multilingual training and domain adaptation.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
Here’s a brief overview of what we’re building at Marktechpost:
- ML News Community – r/machinelearningnews (92k+ members)
- Newsletter– airesearchinsights.com/(30k+ subscribers)
- miniCON AI Events – minicon.marktechpost.com
- AI Reports & Magazines – magazine.marktechpost.com
- AI Dev & Research News – marktechpost.com (1M+ monthly readers)
- Partner with us
The post This AI Paper Investigates Test-Time Scaling of English-Centric RLMs for Enhanced Multilingual Reasoning and Domain Generalization appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ