Reasoning with LLMs can benefit from utilizing more test compute, which depends on high-quality process reward models (PRMs) to select promising paths for search or ranking. PRMs score problem-solution pairs to indicate whether the solution is correct, and have been implemented as discriminative classifiers. However, these models require extensive resources, including human annotation, gold step-by-step solutions, or computationally intensive rollouts. LLM-as-a-judge approaches offer advantages in data efficiency and interpretability, but they perform poorly compared to specialized reward models for complex reasoning tasks, failing to recognize incorrect reasoning. This creates a challenge to maintain data-efficiency and interpretability advantages while achieving the superior performance of discriminative PRMs.
Research approaches to solve process verification challenges have followed three main paths. Discriminative PRMs function as classifiers that predict numerical correctness scores for each reasoning step, requiring extensive step-level annotations. Generative PRMs frame verification as a language-generation task, producing correctness decisions as natural language tokens accompanied by verification chain-of-thought (CoT). These models compute correctness scores through conditional token probabilities like P(“correct”), making them inherently interpretable and scalable. Test-time scaling techniques like Best-of-N selection and tree-based search improve reasoning performance using additional inference-time compute. The effectiveness of these approaches depends heavily on verifier quality for scoring solutions.
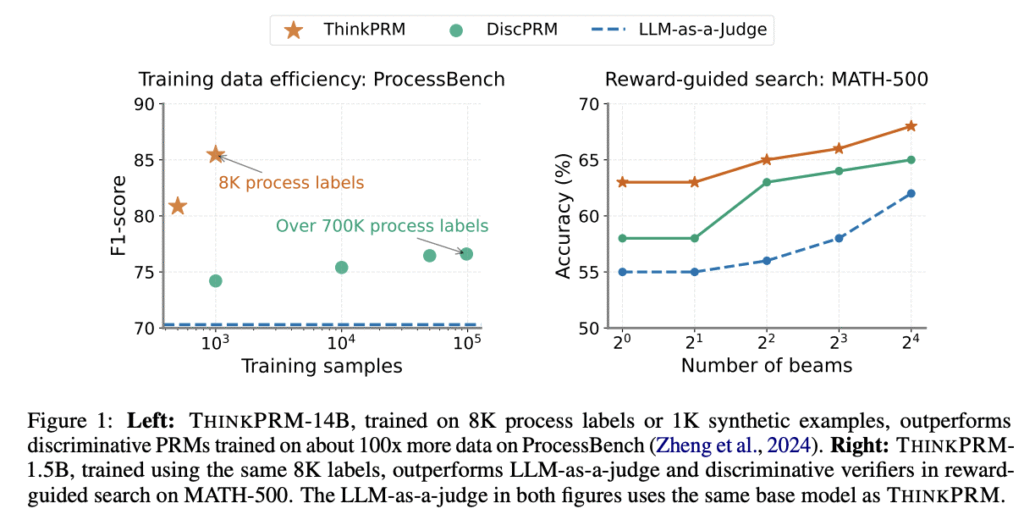
Researchers from the University of Michigan, Mila, LG AI Research, and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have proposed THINKPRM, a long CoT verifier fine-tuned on significantly fewer process labels than those required by discriminative PRMs. It uses the inherent reasoning abilities of long CoT models to outperform both LLM-as-a-Judge and discriminative verifiers while using only 1% of process labels in PRM800K across several challenging benchmarks. Under equal token budgets, THINKPRM scales verification compute more effectively than LLM-as-a-Judge, outperforming it by 7.2% on a ProcessBench subset, highlighting the value of generative, long CoT PRMs for scaling test-time verification compute with minimal supervision.
The THINKPRM is evaluated against DiscPRM, the same base model finetuned with binary cross-entropy on the entire PRM800K dataset containing 712K process labels from 98K problem-solution pairs. Additional comparisons include unweighted majority voting and verifier-weighted majority for best-of-N experiments. The results are shown on three math reasoning tasks: 100 problems from MATH-500 covering all difficulty levels, 2024 American Invitational Mathematics Examination (AIME) problems, and out-of-domain tasks including physics problems from GPQA-Diamond and a 200-problem subset from LiveCodeBench v5. For MATH-500, researchers used THINKPRM-1.5B and THINKPRM-14B with two different generator models.
On best-of-N selection with MATH500, THINKPRM achieves higher or comparable reasoning accuracy to DiscPRM across all sampling budgets. Under verifier-guided search on MATH-500, THINKPRM-1.5B outperforms discPRM by approximately 5 percentage points and surpasses LLM-as-a-judge using the same base model (R1-Qwen-1.5B). THINKPRM-1.5B’s scaling curve exceeds all baselines when compared to strong off-the-shelf PRMs like RLHFFlow-Deepseek-PRM and MATH-Shepherd-PRM, outperforming RLHFFlow-Deepseek-PRM by over 7% at 16 beams. For out-of-domain evaluation, THINKPRM shows better scaling than DiscPRM on GPQA-physics, outperforming it by 8%, while on LiveCodeBench, THINKPRM surpasses DiscPRM by 4.5%.
In conclusion, researchers introduced THINKPRM, a generative process reward model trained with minimal supervision on synthetic data, allowing efficient and scalable verification of step-by-step reasoning. Researchers show that lightweight fine-tuning of generative PRMs on as few as 8K process labels can improve upon zero-shot LLM-as-a-judge baselines. THINKPRM also surpasses discriminative PRMs trained with orders of magnitude more process labels, highlighting the advantages of utilizing generative language-modeling objectives for interpretability, scalability, and data efficiency. The results underscore the potential of generative PRMs to scale verification compute at test-time effectively, benefiting challenging domains such as mathematical and scientific reasoning.
Check out the Paper. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
The post ThinkPRM: A Generative Process Reward Models for Scalable Reasoning Verification appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ
 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
