Human behavior research strives to comprehend how individuals and groups act in social contexts, forming a foundational social science element. Traditional methodologies like surveys, interviews, and observations face significant challenges, including high costs, limited sample sizes, and ethical concerns. These challenges have pushed researchers toward alternative approaches for studying human behavior. For example, Social simulation is an effective method to solve the problem of studying human behaviour. This method utilizes agents to model human behavior, observe reactions, and translate findings into meaningful insights.
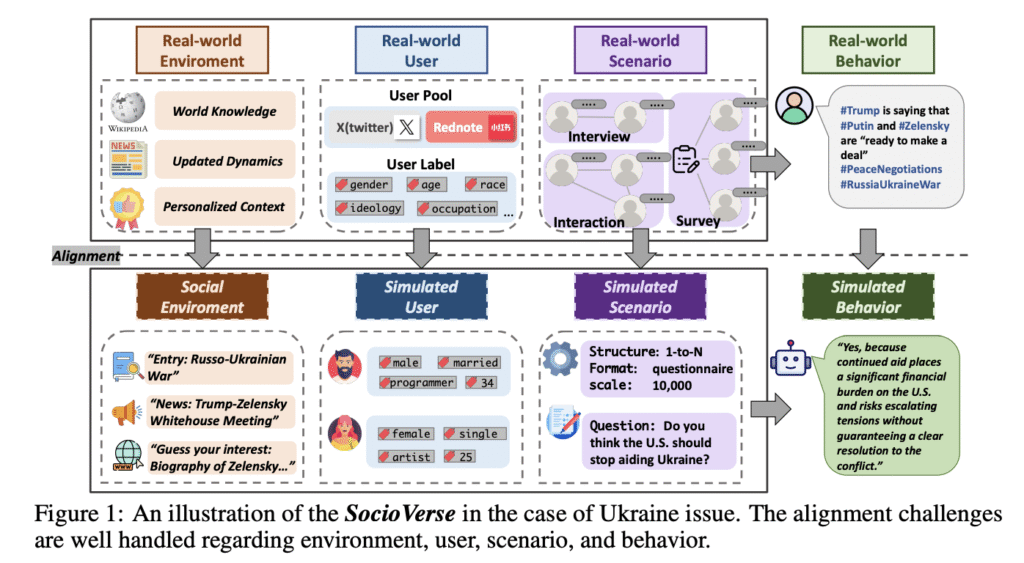
Recent studies have explored social simulation across various levels, from mimicking specific individuals to modeling large-scale social dynamics. However, these simulations consistently face a critical challenge of maintaining alignment between the simulated environment and the real world. This alignment issue manifests across multiple dimensions and raises the following questions:
- How should the simulated environment be aligned with the real world?
- How should the simulated agents be aligned with target users, precisely?
- How should the interaction mechanism be aligned with the real world among different scenarios?
- How should the behavioral pattern be aligned with the real-world groups?
Researchers from Fudan University, Shanghai Innovation Institute, University of Rochester, Indiana University, and Xiaohongshu Inc. have proposed SocioVerse, a world model for social simulation powered by LLM-based agents built upon a large-scale real-world user pool. Modular components are designed to address the above four questions. The Social Environment component incorporates up-to-date external real-world information into simulations, while the User Engine and Scenario Engine reconstruct realistic user contexts and arrange simulation processes to align with reality. Based on this rich contextual setup, the Behavior Engine drives agents to reproduce human behaviors. To support this framework, researchers have constructed a massive user pool containing 10 million individuals based on real social media data, comparable to the entire populations of Hungary or Greece.
The SocioVerse is validated through three simulations: presidential election prediction, breaking news feedback, and national economic survey. Researchers designed a questionnaire based on established polls from various media and research institutes for the presidential election prediction in America. Its evaluation metrics are Accuracy rate and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE). The breaking news feedback simulation utilizes the ABC attitude model (Affect, Behavior, Cognition) combined with a 5-point Likert scale, and its evaluation metrics are Normalized RMSE and KL-divergence. For the national economic survey of China, spending details from the China Statistical Yearbook 2024 are categorized into eight parts, including food, clothing, housing, etc. The evaluation metrics are NRMSE and KL-divergence.
For the presidential election prediction, GPT-4o-mini and Qwen2.5-72b show competitive performance in the Accuracy and RMSE metrics. Following the winner-takes-all rule, over 90% of state voting results are predicted correctly, achieving high-precision macroscopic alignment with real-world election outcomes. In the breaking news feedback scenario, GPT-4o and Qwen2.5-72b most closely aligned with real-world perspectives in KL-Divergence and NRMSE, successfully capturing public trends and opinions. For the national economic survey, Llama3-70b shows superior performance. Models generally perform better in developed regions (top 10 GDP regions) than overall, showing SocioVerse’s ability to reproduce individual spending habits accurately.
In conclusion, researchers introduce a generalized social simulation framework called SocioVerse and evaluate its performance across three distinct real-world scenarios. Their findings indicate that state-of-the-art LLMs show a notable ability to simulate human responses in complex social contexts. Future research needs to incorporate a broader range of scenarios and develop more fine-grained evaluations built upon the current analytic engine to explore and expand the boundaries of LLMs’ simulation capabilities further. Such efforts could pave the way for establishing LLMs as reliable tools for large-scale social simulation, transforming how researchers approach the study of human behavior in diverse social environments.
Check out the Paper and GitHub Page. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
The post LLMs Can Now Simulate Massive Societies: Researchers from Fudan University Introduce SocioVerse, an LLM-Agent-Driven World Model for Social Simulation with a User Pool of 10 Million Real Individuals appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ
 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
