Biophysical modeling serves as a valuable tool for understanding brain function by linking neural dynamics at the cellular level with large-scale brain activity. These models are governed by biologically interpretable parameters, many of which can be directly measured through experiments. However, some parameters remain unknown and must be tuned to align simulations with empirical data, such as resting-state fMRI. Traditional optimization approaches—including exhaustive search, gradient descent, evolutionary algorithms, and Bayesian optimization—require repeated numerical integration of complex differential equations, making them computationally intensive and difficult to scale for models involving numerous parameters or brain regions. As a result, many studies simplify the problem by tuning only a few parameters or assuming uniform properties across regions, which limits biological realism.
More recent efforts aim to enhance biological plausibility by accounting for spatial heterogeneity in cortical properties, using advanced optimization techniques like Bayesian or evolutionary strategies. These methods improve the match between simulated and real brain activity and can generate interpretable metrics such as the excitation/inhibition ratio, validated through pharmacological and PET imaging. Despite these advancements, a significant bottleneck remains: the high computational cost of integrating differential equations during optimization. Deep neural networks (DNNs) have been proposed in other scientific fields to approximate this process by learning the relationship between model parameters and resulting outputs, significantly speeding up computation. However, applying DNNs to brain models is more challenging due to the stochastic nature of the equations and the vast number of integration steps required, which makes current DNN-based methods insufficient without substantial adaptation.
Researchers from institutions including the National University of Singapore, the University of Pennsylvania, and Universitat Pompeu Fabra have introduced DELSSOME (Deep Learning for Surrogate Statistics Optimization in Mean Field Modeling). This framework replaces costly numerical integration with a deep learning model that predicts whether specific parameters yield biologically realistic brain dynamics. Applied to the feedback inhibition control (FIC) model, DELSSOME offers a 2000× speedup and maintains accuracy. Integrated with evolutionary optimization, it generalizes across datasets, such as HCP and PNC, without additional tuning, achieving a 50× speedup. This approach enables large-scale, biologically grounded modeling in population-level neuroscience studies.
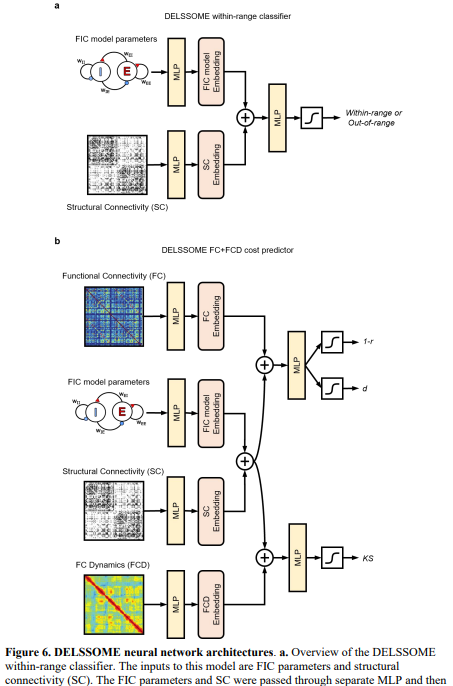
The study utilized neuroimaging data from the HCP and PNC datasets, processing resting-state fMRI and diffusion MRI scans to compute functional connectivity (FC), functional connectivity dynamics (FCD), and structural connectivity (SC) matrices. A deep learning model, DELSSOME, was developed with two components: a within-range classifier to predict if firing rates fall within a biological range, and a cost predictor to estimate discrepancies between simulated and empirical FC/FCD data. Training used CMA-ES optimization, generating over 900,000 data points across training, validation, and test sets. Separate MLPs embedded inputs like FIC parameters, SC, and empirical FC/FCD to support accurate prediction.
The FIC model simulates the activity of excitatory and inhibitory neurons in cortical regions using a system of differential equations. The model was optimized using the CMA-ES algorithm to make it more accurate, which evaluates numerous parameter sets through computationally expensive numerical integration. To reduce this cost, the researchers introduced DELSSOME, a deep learning-based surrogate that predicts whether model parameters will yield biologically plausible firing rates and realistic FCD. DELSSOME achieved a 2000× speed-up in evaluation and a 50× speed-up in optimization, while maintaining comparable accuracy to the original method.
In conclusion, the study introduces DELSSOME, a deep learning framework that significantly accelerates the estimation of parameters in biophysical brain models, achieving a 2000× speedup over traditional Euler integration and a 50× boost when combined with CMA-ES optimization. DELSSOME comprises two neural networks that predict firing rate validity and FC+FCD cost using shared embeddings of model parameters and empirical data. The framework generalizes across datasets without additional tuning and maintains model accuracy. Although retraining is required for different models or parameters, DELSSOME’s core approach—predicting surrogate statistics rather than time series—offers a scalable solution for population-level brain modeling.
Here is the Paper. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Biophysical Brain Models Get a 2000× Speed Boost: Researchers from NUS, UPenn, and UPF Introduce DELSSOME to Replace Numerical Integration with Deep Learning Without Sacrificing Accuracy appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ
 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
