Large language mdoels LLMs have shown remarkable performance across diverse text and multimodal tasks. However, many applications, such as document and video understanding, in-context learning, and inference-time scaling, demand the ability to process and reason over long sequences of tokens. The limited context window of LLMs poses a significant challenge in these situations, as critical information spread over lengthy documents may be overlooked. Models often miss vital information when processing extensive documents or videos, falling outside their fixed-context windows. This limitation creates a need for models that can efficiently handle ultra-long contexts without sacrificing performance on standard tasks.
Existing context extension strategies for long-context language models fall into three categories: exact attention methods, approximate attention methods, and approaches incorporating additional modules. Methods like Position Interpolation, NTK-aware, Dynamic NTK, YaRN, and CLEX enhance attention mechanisms through redesigned position embeddings. Recent advancements include models like GPT-4o, Gemini, and Claude that support extensive context windows of hundreds of thousands of tokens, but their closed-source nature limits reproducibility. Open-source efforts like ProLong use NTK-aware scaling but require expensive computation, while Gradient uses continued pretraining that contains standard task performance.
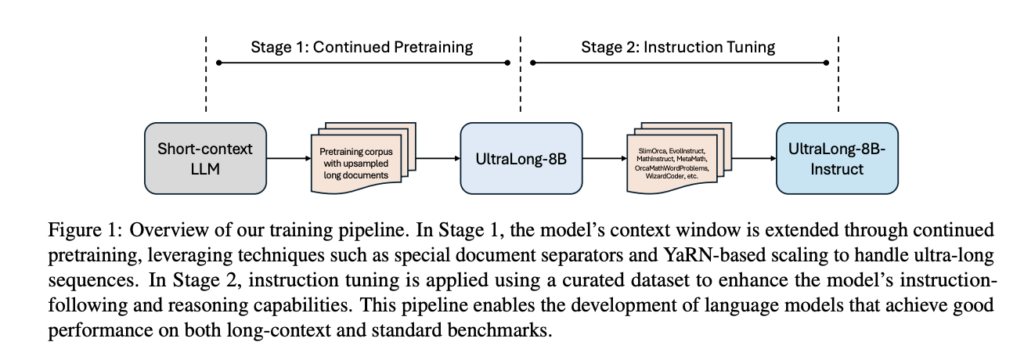
Researchers from UIUC and NVIDIA have proposed an efficient training recipe for building ultra-long context LLMs from aligned instruct models, pushing the boundaries of context lengths from 128K to 1M, 2M, and 4M tokens. The method utilizes efficient, continued pretraining strategies to extend the context window while using instruction tuning to maintain instruction-following and reasoning abilities. Moreover, their UltraLong-8B model achieves state-of-the-art performance across diverse long-context benchmarks. Models trained with this approach maintain competitive performance on standard benchmarks, showing balanced improvements for long and short context tasks. The research provides an in-depth analysis of key design choices, highlighting impacts of scaling strategies and data composition.
The proposed method consists of two key stages: continued pretraining and instruction tuning. Together, these stages enable the effective processing of ultra-long inputs while maintaining strong performance across tasks. A YaRN-based scaling approach is adopted for context extension with fixed hyperparameters as α = 1 and β = 4 rather than NTK-aware scaling strategies. The scale factors are computed based on target context length and employ larger scaling factors for RoPE embeddings to accommodate extended sequences and mitigate performance degradation at maximum lengths. Researchers subsample high-quality SFT datasets spanning general, mathematics, and code domains for training data and further utilize GPT-4o and GPT-4o-mini to refine responses and perform rigorous data decontamination.
The proposed models show superior long-context retrieval capabilities in the Needle in a Haystack passkey retrieval test. Baseline models like Llama-3-8B-Instruct-Gradient-1048k pass the test, but Llama3.1-8B-Instruct and Llama-3-8B-ProLong-512k-Instruct show errors. In contrast, the UltraLong models achieve 100% accuracy across all input lengths and depths, showing strong retrieval capability. The UltraLong achieves the highest average scores on RULER for inputs up to 512K and 1M tokens, the highest F1 scores on LV-Eval within 128K and 256K token lengths, and the best performance on InfiniteBench. Moreover, the models maintain strong performance across general, math, and code domains with average scores of 62.47, 61.06, and 60.95, exceeding the base model’s 61.45.
This research paper introduces an efficient and systematic training recipe for ultra-long context language models, extending context windows to 1M, 2M, and 4M tokens while maintaining competitive performance on standard benchmarks. The approach combines efficient continued pretraining with instruction tuning to enhance long-context understanding and instruction-following capabilities. However, this approach focuses only on SFT on instruction datasets during the instruction tuning stage without exploring reinforcement learning or preference optimization. Also, it does not address safety alignment. Future research includes integrating safety alignment mechanisms and exploring advanced tuning strategies, further enhancing performance and trustworthiness.
Check out Paper and Model on Hugging Face. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 85k+ ML SubReddit.
The post NVIDIA AI Releases Introduce UltraLong-8B: A Series of Ultra-Long Context Language Models Designed to Process Extensive Sequences of Text (up to 1M, 2M, and 4M tokens) appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ