Large language models are often praised for their linguistic fluency, but a growing area of focus is enhancing their reasoning ability—especially in contexts where complex problem-solving is required. These include mathematical equations and tasks involving spatial logic, pathfinding, and structured planning. In such domains, models must simulate human-like step-by-step thinking, where solutions are not immediately obvious. This type of structured reasoning makes inference-time behavior an important subject of study in machine learning research.
Despite the progress in model architecture and training datasets, many language models still falter when presented with multi-step or high-difficulty reasoning tasks. The challenge is that even if a model can access vast information, it might not know how to use it effectively across multiple steps. Tasks like selecting meeting times with constraints or solving NP-hard problems require sustained logical sequencing, which standard models find difficult. Adding more parameters or memory has helped in some areas, but such brute-force solutions often lead to diminishing returns when task complexity increases.
To handle these limitations, researchers have explored tools like chain-of-thought prompting and post-training fine-tuning to better align models with complex tasks. Some methods involve generating multiple independent answers and then using heuristics or voting mechanisms to pick the most likely correct one. Others experiment with self-refinement—having the model critique its answers and revise accordingly. These approaches have been implemented with varying success in conventional models such as GPT-4o, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, and Gemini 2.0 Pro, but these models still show variability depending on the benchmark. In some instances, longer output did not translate into better accuracy, and token efficiency remained inconsistent.
Researchers at Microsoft introduced a rigorous evaluation framework for inference-time scaling that covers nine models and eight complex task benchmarks. This included comparing conventional models against reasoning-optimized ones such as DeepSeek R1, O1, and O3-mini. Their method involved parallel scaling, where multiple outputs are generated and aggregated, and sequential scaling, where the model is prompted to revise its output based on structured feedback iteratively. Benchmarks were sourced from domains like calendar planning, math Olympiads, and spatial reasoning, and the team introduced two new datasets for NP-hard problems: 3SAT and TSP.
The methodology relied on two core strategies: sampling multiple generations to evaluate result variability and using critics to simulate feedback-enhanced reasoning. In parallel scaling, the model outputs several answers that are evaluated using aggregators such as majority vote or best-of-n. In sequential scaling, the model receives feedback after each attempt and is prompted to try again. This allowed researchers to estimate current performance and the potential ceiling for improvement if computational resources were scaled up. Aggregators like average and worst-of-n helped identify where models consistently failed or succeeded. This dual approach provided insight into how models use additional inference steps and whether feedback mechanisms improve answer quality.
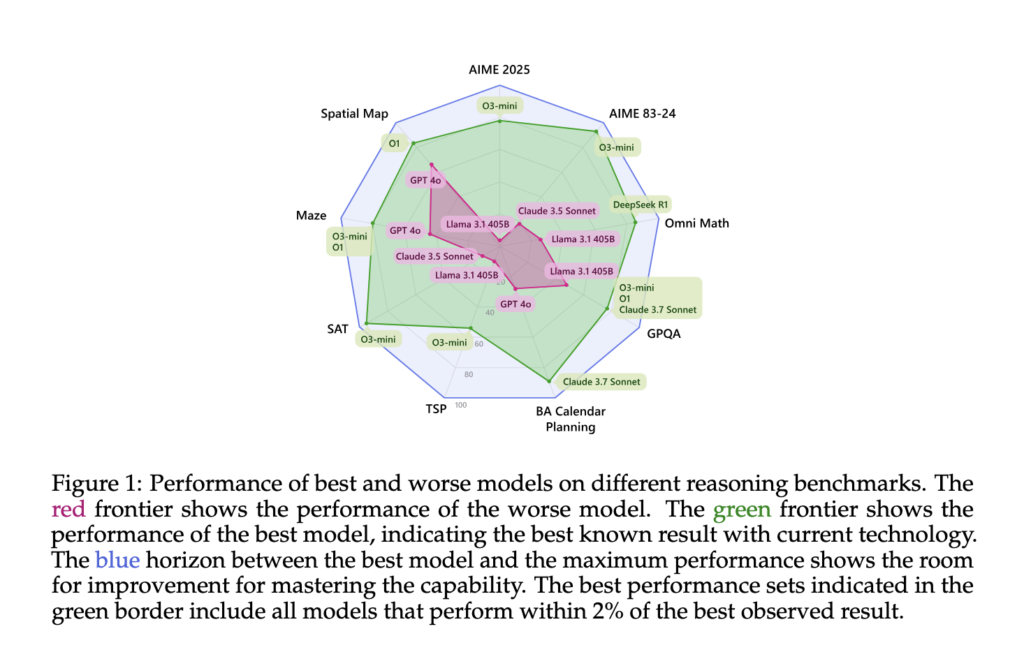
The performance analysis showed significant differences between models and task types. On the GPQA benchmark, the top-performing model, O1, reached 90.9% accuracy, while GPT-4o reached 77.7%. On the TSP dataset, O1 maintained accuracy above 80% across most levels, while GPT-4o’s performance peaked only when superscaled with over 20 inference calls. In BA Calendar, DeepSeek R1 achieved 88.5% accuracy, outperforming Claude 3.7 Sonnet and Gemini 2.0 Pro. However, results also revealed that increased token usage did not guarantee higher accuracy. For example, DeepSeek R1 consumed significantly more tokens than Claude 3.7 Sonnet but only marginally outperformed it in some math tasks. Even within a single model, repeated attempts on the same question showed high variation in token counts, raising concerns about cost predictability for real-world applications.
This study underscores the gap between traditional and reasoning-enhanced models and highlights that intelligent scaling—not just more tokens—can improve complex task performance. The researchers showed that feedback loops and strong verifiers offer substantial gains in model accuracy, even in difficult domains. Their findings suggest that reasoning models still have headroom for improvement, especially when guided by structured inference strategies and cost-efficient token management.
Check out the Paper and GitHub. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 85k+ ML SubReddit.
The post This AI Paper Introduces Inference-Time Scaling Techniques: Microsoft’s Deep Evaluation of Reasoning Models on Complex Tasks appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ
 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on OPEN SOURCE AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 3 Hour Short Event (April 12, 9 am- 12 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop [Sponsored]
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on OPEN SOURCE AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 3 Hour Short Event (April 12, 9 am- 12 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop [Sponsored]
