Robots are increasingly being developed for home environments, specifically to enable them to perform daily activities like cooking. These tasks involve a combination of visual interpretation, manipulation, and decision-making across a series of actions. Cooking, in particular, is complex for robots due to the diversity in utensils, varying visual perspectives, and frequent omissions of intermediate steps in instructional materials like videos. For a robot to succeed in such tasks, a method is needed that ensures logical planning, flexible understanding, and adaptability to different environmental constraints.
One major problem in translating cooking demonstrations into robotic tasks is the lack of standardization in online content. Videos might skip steps, include irrelevant segments like introductions, or show arrangements that do not align with the robot’s operational layout. Robots must interpret visual data and textual cues, infer omitted steps, and translate this into a sequence of physical actions. However, when relying purely on generative models to produce these sequences, there is a high chance of logic failures or hallucinated outputs that render the plan infeasible for robotic execution.
Current tools supporting robotic planning often focus on logic-based models like PDDL or more recent data-driven approaches using Large Language Models (LLMs) or multimodal architectures. While LLMs are adept at reasoning from diverse inputs, they cannot often validate whether the generated plan makes sense in a robotic setting. Prompt-based feedback mechanisms have been tested, but they still fail to confirm the logical correctness of individual actions, especially for complex, multi-step tasks like those in cooking scenarios.
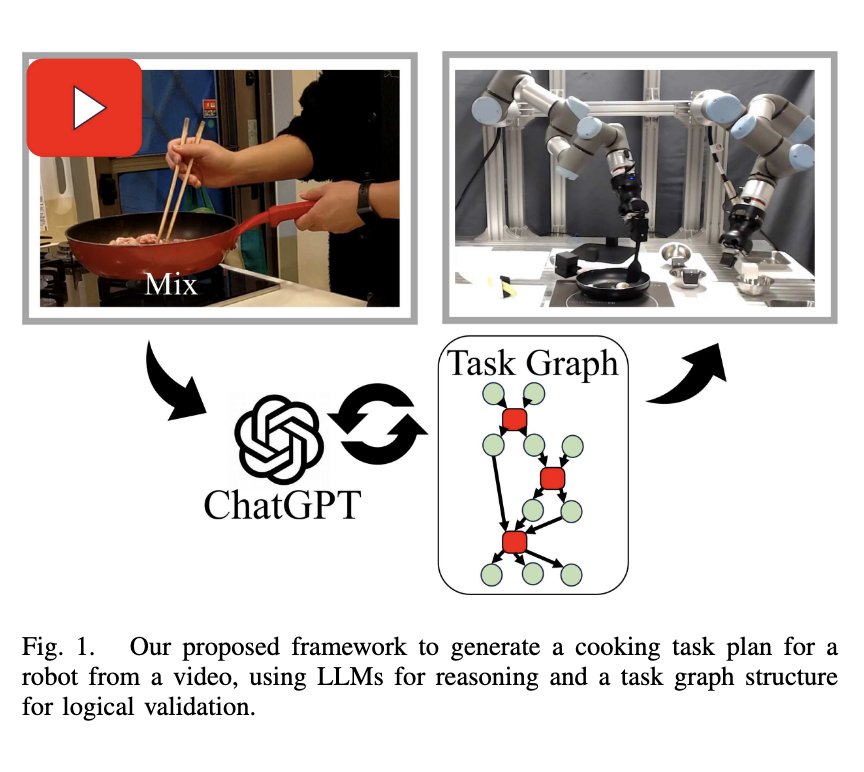
Researchers from the University of Osaka and the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Japan, introduced a new framework integrating an LLM with a Functional Object-Oriented Network (FOON) to develop cooking task plans from subtitle-enhanced videos. This hybrid system uses an LLM to interpret a video and generate task sequences. These sequences are then converted into FOON-based graphs, where each action is checked for feasibility against the robot’s current environment. If a step is deemed infeasible, feedback is generated so that the LLM can revise the plan accordingly, ensuring that only logically sound steps are retained.
This method involves several layers of processing. First, the cooking video is split into segments based on subtitles extracted using Optical Character Recognition. Key video frames are selected from each segment and arranged into a 3×3 grid to serve as input images. The LLM is prompted with structured details, including task descriptions, known constraints, and environment layouts. Using this data, it infers the target object states for each segment. These are cross-verified by FOON, a graph system where actions are represented as functional units containing input and output object states. If an inconsistency is found—for instance, if a hand is already holding an item when it’s supposed to pick something else—the task is flagged and revised. This loop continues until a complete and executable task graph is formed.
The researchers tested their method using five full cooking recipes from ten videos. Their experiments successfully generated complete and feasible task plans for four of the five recipes. In contrast, a baseline approach that used only the LLM without FOON validation succeeded in just one case. Specifically, the FOON-enhanced method had a success rate of 80% (4/5), while the baseline achieved only 20% (1/5). Moreover, in the component evaluation of target object node estimation, the system achieved an 86% success rate in accurately predicting object states. During the video preprocessing stage, the OCR process extracted 270 subtitle words compared to the ground truth of 230, resulting in a 17% error rate, which the LLM could still manage by filtering redundant instructions.
In a real-world trial using a dual-arm UR3e robot system, the team demonstrated their method on a gyudon (beef bowl) recipe. The robot could infer and insert a missing “cut” action that was absent in the video, showing the system’s ability to identify and compensate for incomplete instructions. The task graph for the recipe was generated after three re-planning attempts, and the robot completed the cooking sequence successfully. The LLM also correctly ignored non-essential scenes like the video introduction, identifying only 8 of 13 necessary segments for task execution.
This research clearly outlines the problem of hallucination and logical inconsistency in LLM-based robotic task planning. The proposed method offers a robust solution to generate actionable plans from unstructured cooking videos by incorporating FOON as a validation and correction mechanism. The methodology bridges reasoning and logical verification, enabling robots to execute complex tasks by adapting to environmental conditions while maintaining task accuracy.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 85k+ ML SubReddit.
The post This AI Paper Introduces an LLM+FOON Framework: A Graph-Validated Approach for Robotic Cooking Task Planning from Video Instructions appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ
 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on OPEN SOURCE AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 3 Hour Short Event (April 12, 9 am- 12 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop [Sponsored]
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on OPEN SOURCE AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 3 Hour Short Event (April 12, 9 am- 12 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop [Sponsored]
