Text-to-SQL translation, the task of transforming natural language queries into structured SQL statements, is essential for facilitating user-friendly database interactions. However, the task involves significant complexities, notably schema linking, handling compositional SQL syntax, and resolving ambiguities in user queries. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown robust capabilities across various domains, the efficacy of structured reasoning techniques such as Chain-of-Thought (CoT) within text-to-SQL contexts remains limited. Prior attempts employing zero-shot CoT or Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) without structured reasoning yielded marginal improvements, indicating the necessity for more rigorous methodologies.
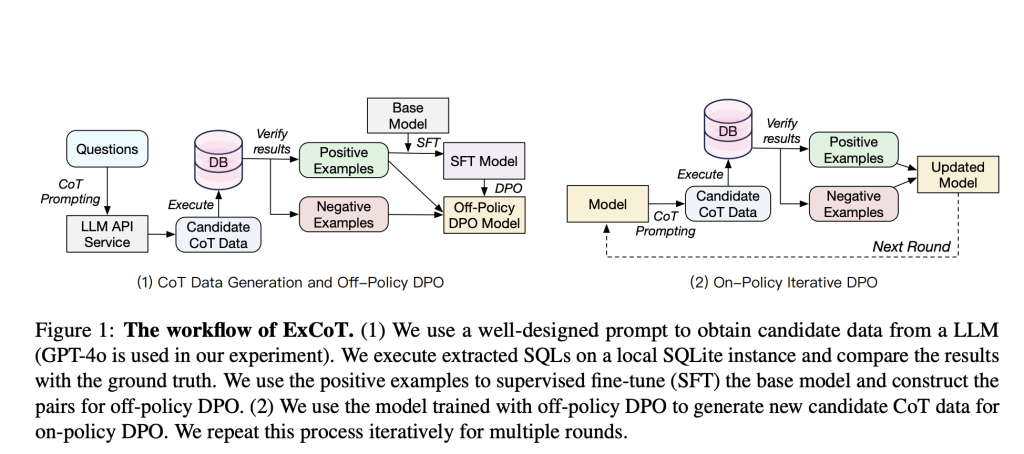
Snowflake introduces ExCoT, a structured framework designed to optimize open-source LLMs through the combination of CoT reasoning and iterative preference optimization, specifically utilizing off-policy and on-policy DPO guided exclusively by execution accuracy feedback. ExCoT dispenses with external reward models and human annotations, relying instead on internally generated reasoning steps and execution results. The method operates in two principal phases: initially, it generates candidate CoT data validated through off-policy DPO, forming the basis for supervised fine-tuning. Subsequently, the model iteratively generates and refines CoT data via on-policy DPO, incrementally improving accuracy through feedback derived from execution correctness.

ExCoT employs detailed CoT reasoning, particularly adopting a divide-and-conquer strategy wherein complex queries are decomposed into simpler sub-queries. Each sub-query is analyzed and independently resolved before being integrated into a coherent final query. This structured decomposition enables the model to manage the complexity and nested structures common in SQL operations more effectively. Execution-based verification serves as the core mechanism for correctness evaluation, where generated queries are validated by comparing their execution outputs against ground-truth results. Incorrect and correct queries are systematically paired, providing explicit signals for preference-based learning. The iterative refinement in the on-policy DPO phase progressively enhances the model’s reasoning accuracy.
Experimental evaluation of ExCoT demonstrated significant improvements in execution accuracy. Specifically, with the LLaMA-3.1 70B model, ExCoT elevated execution accuracy on the BIRD development set from 57.37% to 68.51%, and increased Spider test set performance from 78.81% to 86.59%. Comparable performance enhancements were recorded with the Qwen-2.5-Coder 32B model. These results position ExCoT as a leading approach in single-model evaluations for these benchmarks, surpassing established methods such as XiYanSQL and proprietary models including OpenAI variants. Notably, the improvements consistently maintained high query validity rates (exceeding 98%), confirming enhancements in semantic correctness alongside syntactic precision.

In conclusion, ExCoT represents a methodical advancement in structured reasoning optimization for open-source LLMs applied to text-to-SQL tasks. By integrating structured CoT reasoning with preference optimization, guided solely by execution-based feedback, ExCoT effectively addresses limitations identified in previous methods. Its iterative refinement capability ensures continuous improvement without dependence on external reward structures or manual annotations. Further research might explore extending this framework to more intricate schema environments and additional structured reasoning tasks, thus broadening the applicability and reliability of LLMs in structured query generation contexts.
Check out the Paper, GitHub Page and Details. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 85k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Snowflake Proposes ExCoT: A Novel AI Framework that Iteratively Optimizes Open-Source LLMs by Combining CoT Reasoning with off-Policy and on-Policy DPO, Relying Solely on Execution Accuracy as Feedback appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ
 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on OPEN SOURCE AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 3 Hour Short Event (April 12, 9 am- 12 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop [Sponsored]
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on OPEN SOURCE AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 3 Hour Short Event (April 12, 9 am- 12 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop [Sponsored]
