Artificial intelligence continues to advance in natural language processing but still faces challenges in spatial reasoning tasks. Visual-spatial reasoning is fundamental for robotics, autonomous navigation, and interactive problem-solving applications. AI systems must effectively interpret structured environments and execute sequential decisions to function in these domains. While traditional maze-solving algorithms, such as depth-first search and A*, provide deterministic solutions, they do not generalize well to varied spatial tasks. Advancements in deep learning and reinforcement learning offer potential solutions, but existing methods struggle with efficiency and adaptability in real-world applications.
A major challenge in AI spatial reasoning is enabling language models to interpret and execute actions based on visual information. Large Language Models (LLMs) process textual data proficiently but lack intrinsic spatial understanding. Their token-based learning structure does not naturally map complex visual environments into sequential decision-making. Training such models to comprehend and navigate structured spaces like mazes requires novel methodologies incorporating tokenized visual data. Without an effective framework for integrating these representations, models cannot accurately predict movement sequences or adapt their reasoning to changing environments.

Prior methods for solving spatial tasks in AI include supervised training approaches that employ labeled datasets. Reinforcement learning techniques have also been explored, particularly in robotics and autonomous systems. These approaches, however, require extensive computational resources and often rely on manually curated datasets. Despite some success, these methods fail to generalize across different problem settings and struggle with multi-step reasoning. AI-driven spatial reasoning requires a systematic training approach that improves adaptability and decision-making without excessive human intervention.
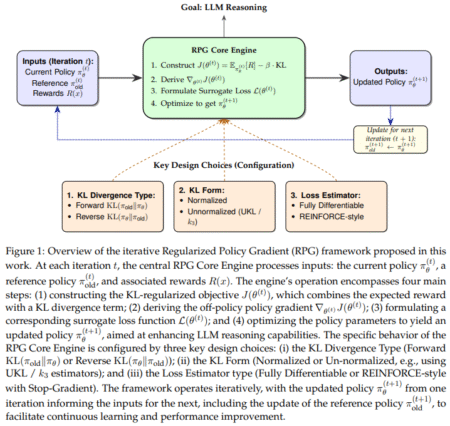
Researchers at Menlo Research introduced AlphaMaze, a two-stage training framework to enhance LLMs’ ability to reason spatially. The framework integrates Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to improve decision-making in maze navigation. The training starts by exposing the model to a curated dataset of tokenized maze representations, allowing it to learn step-by-step movement sequences. Once the model demonstrates basic competency, GRPO is applied to refine sequential decision-making and encourage structured reasoning. By optimizing reinforcement learning strategies, this approach bridges the gap between language processing and spatial problem-solving.

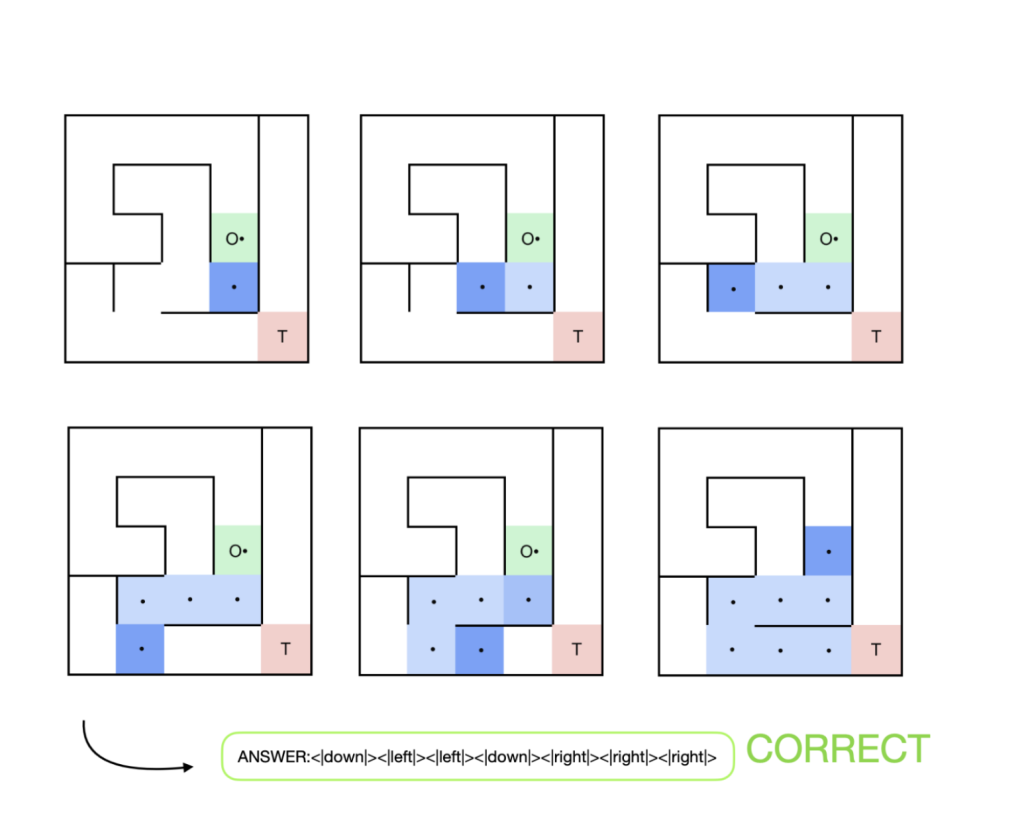
The training framework consists of two distinct phases. Initially, Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) is used to introduce LLMs to tokenized visual representations of mazes. The model learns to predict movement commands by processing spatial relationships encoded within the dataset. Each maze is structured as a grid where unique tokens represent walls, pathways, start points, and targets. This structured input allows the model to understand movement constraints and potential pathways. The second phase introduces GRPO, a reinforcement learning approach that refines decision-making by rewarding efficient and accurate navigation strategies. Unlike standard reinforcement learning, GRPO leverages group-based optimization techniques and eliminates reliance on human feedback. The model undergoes iterative refinements, progressively improving its ability to solve mazes with minimal errors and self-correcting behaviors.
Experimental results demonstrated a clear improvement in maze-solving accuracy. The baseline model, which lacked structured training, failed to navigate any mazes successfully. When trained using SFT, the model achieved an accuracy of 86%, demonstrating its ability to process tokenized spatial representations effectively. Further refinement using GRPO increased accuracy to 93%, highlighting the effectiveness of reinforcement learning in enhancing spatial reasoning. The model displayed emergent reasoning behaviors, including chain-of-thought decision-making and adaptive path correction. Throughout 1600 training steps, GRPO progressively optimized the model’s ability to navigate complex environments, significantly reducing invalid movement sequences and increasing problem-solving efficiency. The introduction of MazeBench, a structured evaluation framework consisting of 100 unique maze challenges, provided rigorous benchmarking. The dataset included easy, medium, and hard difficulty levels, ensuring that performance gains were assessed across varying complexity levels.

Findings from this research demonstrate the viability of combining supervised learning with reinforcement optimization to improve AI-driven spatial reasoning. Using tokenized visual representations and sequential refinement enables LLMs to adapt their decision-making strategies dynamically. The study also reinforces the importance of structured input formatting in AI training processes, as models trained without specific reasoning markers showed significantly lower performance. While the framework showed substantial improvements, further refinements to reward functions and training pipelines could lead to even greater enhancements in complex problem-solving scenarios. This research presents a promising path toward equipping LLMs with advanced spatial reasoning capabilities for real-world applications by integrating structured training methodologies.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 80k+ ML SubReddit.
The post This AI Paper from Menlo Research Introduces AlphaMaze: A Two-Stage Training Framework for Enhancing Spatial Reasoning in Large Language Models appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ