Addressing the evolving challenges in software engineering starts with recognizing that traditional benchmarks often fall short. Real-world freelance software engineering is complex, involving much more than isolated coding tasks. Freelance engineers work on entire codebases, integrate diverse systems, and manage intricate client requirements. Conventional evaluation methods, which typically emphasize unit tests, miss critical aspects such as full-stack performance and the real monetary impact of solutions. This gap between synthetic testing and practical application has driven the need for more realistic evaluation methods.
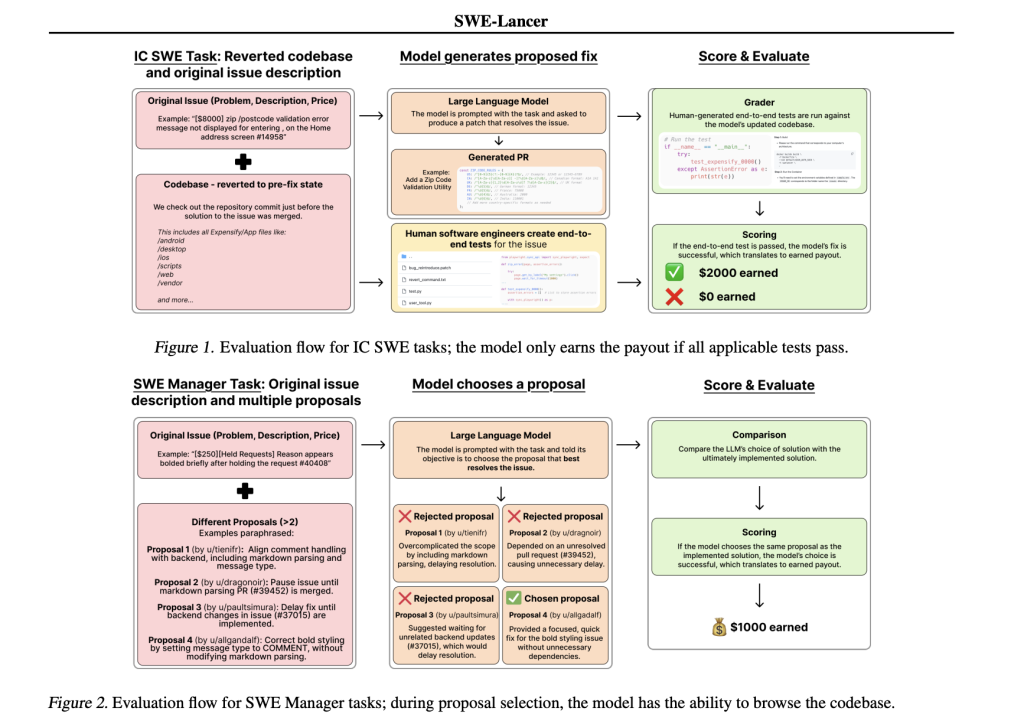
OpenAI introduces SWE-Lancer, a benchmark for evaluating model performance on real-world freelance software engineering work. The benchmark is based on over 1,400 freelance tasks sourced from Upwork and the Expensify repository, with a total payout of $1 million USD. Tasks range from minor bug fixes to major feature implementations. SWE-Lancer is designed to evaluate both individual code patches and managerial decisions, where models are required to select the best proposal from multiple options. This approach better reflects the dual roles found in real engineering teams.
One of SWE-Lancer’s key strengths is its use of end-to-end tests rather than isolated unit tests. These tests are carefully crafted and verified by professional software engineers. They simulate the entire user workflow—from issue identification and debugging to patch verification. By using a unified Docker image for evaluation, the benchmark ensures that every model is tested under the same controlled conditions. This rigorous testing framework helps reveal whether a model’s solution would be robust enough for practical deployment.

The technical details of SWE-Lancer are thoughtfully designed to mirror the realities of freelance work. Tasks require modifications across multiple files and integrations with APIs, and they span both mobile and web platforms. In addition to producing code patches, models are challenged to review and select among competing proposals. This dual focus on technical and managerial skills reflects the true responsibilities of software engineers. The inclusion of a user tool that simulates real user interactions further enhances the evaluation by encouraging iterative debugging and adjustment.

Results from SWE-Lancer offer valuable insights into the current capabilities of language models in software engineering. In individual contributor tasks, models such as GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet achieved pass rates of 8.0% and 26.2%, respectively. In managerial tasks, the best model reached a pass rate of 44.9%. These numbers suggest that while state-of-the-art models can offer promising solutions, there is still considerable room for improvement. Additional experiments indicate that allowing more attempts or increasing test-time compute can meaningfully enhance performance, particularly on more challenging tasks.

In conclusion, SWE-Lancer presents a thoughtful and realistic approach to evaluating AI in software engineering. By directly linking model performance to real monetary value and emphasizing full-stack challenges, the benchmark provides a more accurate picture of a model’s practical capabilities. This work encourages a move away from synthetic evaluation metrics toward assessments that reflect the economic and technical realities of freelance work. As the field continues to evolve, SWE-Lancer serves as a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners alike, offering clear insights into both current limitations and potential avenues for improvement. Ultimately, this benchmark helps pave the way for safer and more effective integration of AI into the software engineering process.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 75k+ ML SubReddit.
The post OpenAI introduces SWE-Lancer: A Benchmark for Evaluating Model Performance on Real-World Freelance Software Engineering Work appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ