Adapting large language models for specialized domains remains challenging, especially in fields requiring spatial reasoning and structured problem-solving, even though they specialize in complex reasoning. Semiconductor layout design is a prime example, where AI tools must interpret geometric constraints and ensure precise component placement. Researchers are developing advanced AI architectures to enhance LLMs’ ability to process and apply domain-specific knowledge effectively.
A major limitation of general-purpose LLMs is their inability to convert theoretical knowledge into practical solutions. While these models can accurately define technical concepts, they often fail when solving real-world tasks that require spatial reasoning and structured logic. In semiconductor layout design, AI must go beyond text-based knowledge to ensure accurate placement of vias, metal layers, and circuit components. Without precise geometric relationships, layout designs may fail due to misalignment or incorrect spacing. Current models often require multiple rounds of human correction, making their deployment inefficient.
Several approaches have been developed to improve LLMs’ adaptability for domain-specific applications. Fine-tuning involves training LLMs with domain-specific data, but this process is time-intensive and requires significant computational resources. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) retrieves external knowledge to guide LLM outputs, but it does not fully address challenges related to structured problem-solving. In-context learning helps guide LLM reasoning by providing task-specific examples, yet it does not overcome spatial reasoning limitations. These methods offer incremental improvements but fail to deliver a comprehensive solution for applications requiring geometric logic.
Researchers at IBM T.J. Watson Research Center and MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab introduced SOLOMON, a neuro-inspired LLM reasoning network, to enhance domain-specific adaptability. Unlike conventional approaches, SOLOMON employs a multi-agent reasoning system that dynamically processes spatial constraints and geometric relationships. The framework integrates thought assessment mechanisms to refine outputs iteratively, improving problem-solving accuracy. SOLOMON leverages prompt engineering techniques to guide LLM-generated solutions, allowing it to adapt to semiconductor layout tasks with minimal retraining.
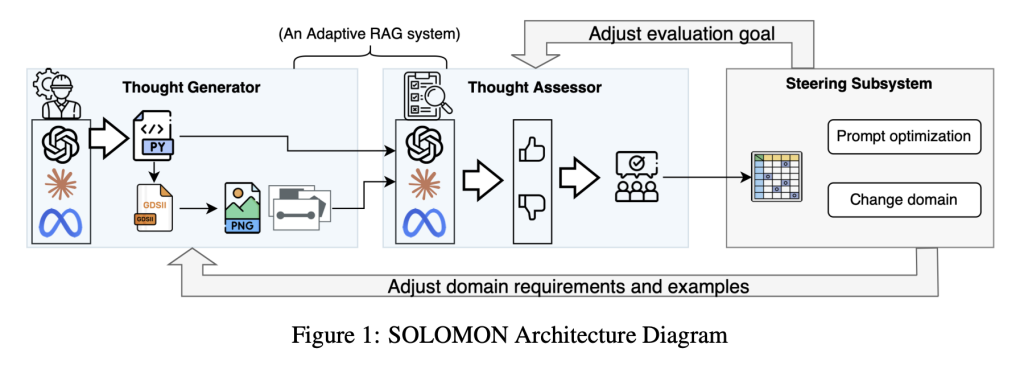
The architecture of SOLOMON is inspired by neuroscience and incorporates the Free Energy Principle, which optimizes reasoning by reducing discrepancies between expected and observed outcomes. The framework consists of three primary components: Thought Generators, Thought Assessors, and a Steering Subsystem. Thought Generators utilize diverse LLMs to produce multiple reasoning pathways, ensuring a broad range of solutions for complex tasks. The Thought Assessor evaluates these outputs, selecting the most logical and structured approach. The Steering Subsystem allows researchers to modify objectives dynamically, enabling more precise domain adaptation. Unlike fine-tuning, this architecture does not require continuous retraining, making it more efficient for specialized applications.
Researchers conducted experiments on 25 semiconductor layout tasks to evaluate SOLOMON’s effectiveness. The framework was compared to five baseline LLMs, including GPT-4o, Claude-3.5-Sonnet, and Llama-3 models. Each task assessed the models’ ability to generate geometric structures while maintaining spatial accuracy. SOLOMON demonstrated improvements in reducing runtime errors and scaling inaccuracies. The framework exhibited better spatial reasoning capabilities, improving placement precision and reducing mistakes in generated designs. SOLOMON instances also matched or exceeded the performance of o1-preview in multiple test categories, with the Claude-based SOLOMON performing strongly in certain complex tasks.
A key advantage of SOLOMON is its ability to correct logical inconsistencies and arithmetic errors in geometric designs. The Thought Assessor continuously refines generated layouts by analyzing previous iterations, mitigating common hallucination issues in traditional LLMs. The system effectively reduces misinterpretations and enhances the reliability of AI-generated designs. SOLOMON synchronizes reasoning across multiple LLMs when presented with ambiguous layout specifications, ensuring consistent and precise output. By incorporating hierarchical assessment mechanisms, the framework significantly improves AI-driven design accuracy.
This research highlights the importance of enhancing LLM reasoning capabilities rather than increasing model size. SOLOMON offers a structured and efficient approach for applying AI to domain-specific problem-solving, particularly in semiconductor layout design. Future research will focus on expanding the framework to other engineering applications, refining multimodal reasoning capabilities, and introducing iterative learning mechanisms to enhance AI decision-making. The introduction of SOLOMON represents a substantial advancement in making AI-driven tools more precise, adaptive, and effective for real-world industrial challenges.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 75k+ ML SubReddit.
The post This AI Paper from IBM and MIT Introduces SOLOMON: A Neuro-Inspired Reasoning Network for Enhancing LLM Adaptability in Semiconductor Layout Design appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 Recommended Open-Source AI Platform: ‘IntellAgent is a An Open-Source Multi-Agent Framework to Evaluate Complex Conversational AI System’ (Promoted)
Recommended Open-Source AI Platform: ‘IntellAgent is a An Open-Source Multi-Agent Framework to Evaluate Complex Conversational AI System’ (Promoted)