Multi-agent AI systems utilizing LLMs are increasingly adept at tackling complex tasks across various domains. These systems comprise specialized agents that collaborate, leveraging their unique capabilities to achieve common objectives. Such collaboration has proven effective in complex reasoning, coding, drug discovery, and safety assurance through debate. The structured interactions among agents enhance problem-solving efficiency and provide a built-in self-correction mechanism, as agents can refine and verify each other’s outputs. This collaborative approach often surpasses single-agent performance, especially in tasks requiring rigorous reasoning or factual validation.
Despite these advancements, optimizing multi-agent systems presents significant challenges. A primary issue is acquiring appropriate training signals for each agent, as task-level reward feedback is available, but credit assignment across agents remains ambiguous. Determining how to attribute success or failure to specific decisions and reasoning steps each LLM agent makes is complex. This challenge parallels the multi-agent credit assignment problem in reinforcement learning. However, in language-based systems, reasoning unfolds through intricate and unstructured interactions, making attribution more difficult than in traditional reinforcement learning settings with well-defined action spaces.
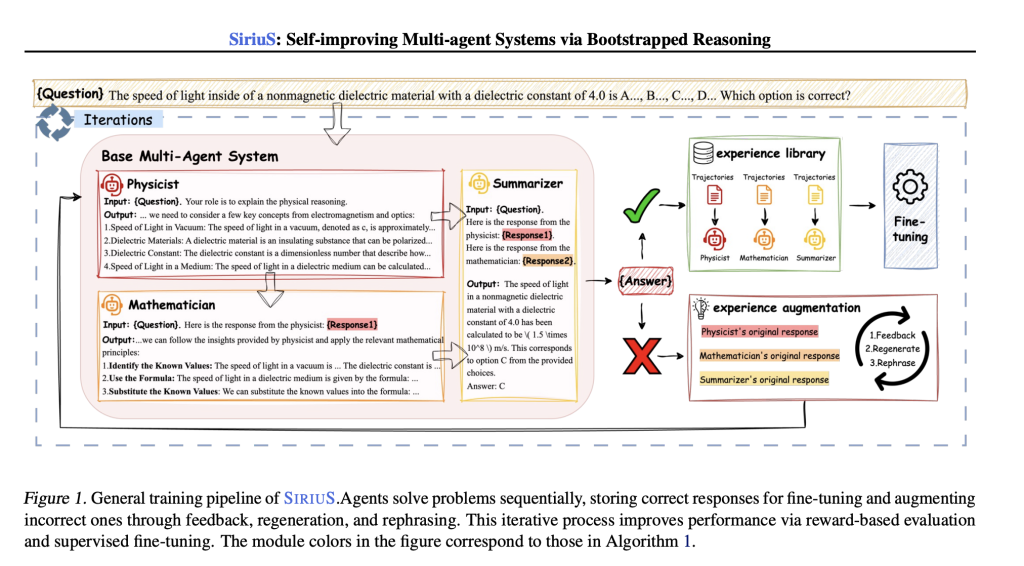
Stanford University researchers introduce SIRIUS, a self-improving optimization framework for multi-agent systems that leverages reasoning-driven learning. It constructs an experience library by retaining successful reasoning trajectories, providing a high-quality training set. Additionally, it refines unsuccessful attempts through augmentation, enriching the dataset. SIRIUS enhances reasoning and biomedical QA performance by 2.86% to 21.88% while improving agent negotiation in competitive settings. Agents iteratively refine their collaboration strategies by learning from successful interactions without direct supervision. This scalable approach enables self-generated data-driven optimization, fostering continuous improvement in multi-agent systems without relying on fine-grained human intervention.
A multi-agent system consists of agents interacting within a defined environment, where each agent follows a policy to optimize rewards. The environment primarily relies on natural language, with agents generating responses based on prior interactions. SIRIUS, a self-improving framework, enhances agent performance through iterative fine-tuning. The process includes generating responses, evaluating them using a reward function, refining low-quality outputs, and updating policies via supervised learning. By continuously optimizing responses through iterative training and augmentation, SIRIUS improves reasoning and decision-making in language-based multi-agent systems, leading to more effective and coherent interactions over time.
The experiments compare SIRIUS against various baselines, including Single-Agent, STaR, CoMM, and TextGrad. SIRIUS consistently outperforms other models, demonstrating improved problem-solving, task decomposition, and agent collaboration. Ablation studies reveal that specialized agent roles, multi-agent optimization, and experience augmentation are crucial for performance. SIRIUS also excels in actor-critic and competitive settings, outperforming other methods in tasks like PubMedQA and resource exchange games. Fine-tuning SIRIUS leads to improved win rates and payoffs, and it generalizes well across different game configurations, confirming its robustness and adaptability across various scenarios.
In conclusion, SIRIUS is a framework designed to optimize multi-agent systems powered by LLMs through learning from successful interactions and refining failed ones. It builds an experience library containing high-quality reasoning steps that lead to successful outcomes, which serves as a training set for system optimization. Additionally, SIRIUS augments the library by improving unsuccessful trajectories. The approach boosts reasoning, biomedical QA, and agent negotiation performance, with improvements ranging from 2.86% to 21.88%. SIRIUS also enables continuous self-improvement and generates reusable data for future enhancements in multi-agent collaboration.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 75k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Stanford Researchers Introduce SIRIUS: A Self-Improving Reasoning-Driven Optimization Framework for Multi-Agent Systems appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 Recommended Open-Source AI Platform: ‘IntellAgent is a An Open-Source Multi-Agent Framework to Evaluate Complex Conversational AI System’ (Promoted)
Recommended Open-Source AI Platform: ‘IntellAgent is a An Open-Source Multi-Agent Framework to Evaluate Complex Conversational AI System’ (Promoted)