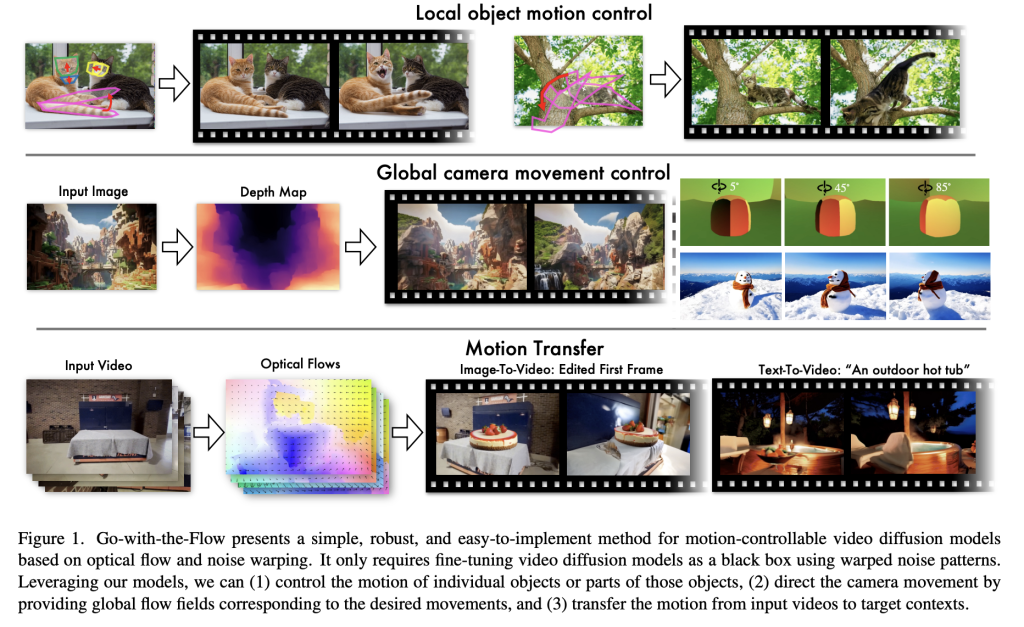
Generative modeling challenges in motion-controllable video generation present significant research hurdles. Current approaches in video generation struggle with precise motion control across diverse scenarios. The field uses three primary motion control techniques: local object motion control using bounding boxes or masks, global camera movement parameterization, and motion transfer from reference videos. Despite these approaches, researchers have identified critical limitations including complex model modifications, difficulties in acquiring accurate motion parameters, and the fundamental trade-off between motion control precision and spatiotemporal visual quality. The existing methods often require technical interventions that restrict their generalizability and practical applicability across different video generation contexts.
Existing research on motion-controllable video generation has explored multiple methodological approaches to address motion control challenges. Image and video diffusion models have used techniques like noise warping and temporal attention fine-tuning to improve video generation capabilities. Noise-warping methods like HIWYN attempt to create temporally correlated latent noise, though they suffer from spatial Gaussianity preservation and computational complexity issues. Advanced video diffusion models such as AnimateDiff and CogVideoX have made significant progress by fine-tuning temporal attention layers and combining spatial and temporal encoding strategies. Further, Motion control approaches have focused on local object motion control, global camera movement parameterization, and motion transfer from reference videos.
Researchers from Netflix Eyeline Studios, Netflix, Stony Brook University, University of Maryland, and Stanford University have proposed a novel approach to enhance motion control in video diffusion models. Their method introduces a structured latent noise sampling technique that transforms video generation by preprocessing training videos to yield structured noise. Unlike existing approaches, this technique requires no modifications to model architectures or training pipelines, making it uniquely adaptable across different diffusion models. This innovative approach provides a solution for motion control, including local object motion, global camera movement, and motion transfer with improved temporal coherence and per-frame pixel quality.
The proposed method consists of two primary components: a noise-warping algorithm and video diffusion fine-tuning. The noise warping algorithm operates independently from the diffusion model training process, generating noise patterns used to train the diffusion model without introducing additional parameters to the video diffusion model. Inspired by existing noise warping techniques, the researchers use warped noise as a motion conditioning mechanism for video generation models. The method fine-tunes state-of-the-art video diffusion models like CogVideoX-5B, utilizing a massive general-purpose video dataset of 4 million videos with resolutions of 720×480 or higher. Moreover, the approach is both data and model-agnostic, allowing motion control adaptation across various video diffusion models.
Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed method across multiple evaluation metrics. Statistical analysis using Moran’s I index reveals the method achieved an exceptionally low spatial cross-correlation value of 0.00014, with a high p-value of 0.84, indicating excellent spatial Gaussianity preservation. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K-S) test further validates the method’s performance, obtaining a K-S statistic of 0.060 and a p-value of 0.44, suggesting the warped noise closely follows a standard normal distribution. Performance efficiency tests conducted on an NVIDIA A100 40GB GPU show the proposed method outperforms existing baselines, running 26 times faster than the most recently published approach.
In conclusion, the proposed method represents a significant advancement in motion-controllable video generation, addressing critical challenges in generative modeling. Researchers have developed a seamless approach to incorporating motion control into video diffusion noise sampling. This innovative technique transforms the landscape of video generation by providing a unified paradigm for user-friendly motion control across various applications. The method bridges the gap between random noise and structured outputs, enabling precise manipulation of video motion without compromising visual quality or computational efficiency. Moreover, this method excels in motion controllability, temporal consistency, and visual fidelity, positioning itself as a robust and versatile solution for next-generation video diffusion models.
Check out the Paper and Project Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 70k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Netflix Introduces Go-with-the-Flow: Motion-Controllable Video Diffusion Models Using Real-Time Warped Noise appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ