The development of TTS systems has been pivotal in converting written content into spoken language, enabling users to interact with text audibly. This technology is particularly beneficial for understanding documents containing complex information, such as scientific papers and technical manuals, which often present significant challenges for individuals relying solely on auditory comprehension.
A persistent problem with existing TTS systems is their inability to process mathematical formulas accurately. These systems usually treat formulas as plain text, which results in unintelligible or incomplete speech. This problem is especially common in academic and technical documents that use LaTeX to represent mathematical content. Since formulas are rendered in distinctive formats, traditional TTS systems fail to recognize their mathematical meaning, leading to inaccurate or omitted speech output. This limitation presents a significant barrier for users, especially those in mathematics and science.
Current methods to address this problem involve OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technologies and basic TTS integration. However, these approaches have limitations. For instance, OCR systems convert formulas into text but fail to interpret their semantic structure, rendering them unsuitable for accurate vocalization. Popular TTS readers like Microsoft Edge and Adobe Acrobat skip or incorrectly read mathematical formulas, highlighting the need for a more sophisticated solution. Some tools attempt manual mapping of LaTeX codes to spoken English, but they struggle with exception cases and are impractical for widespread use.
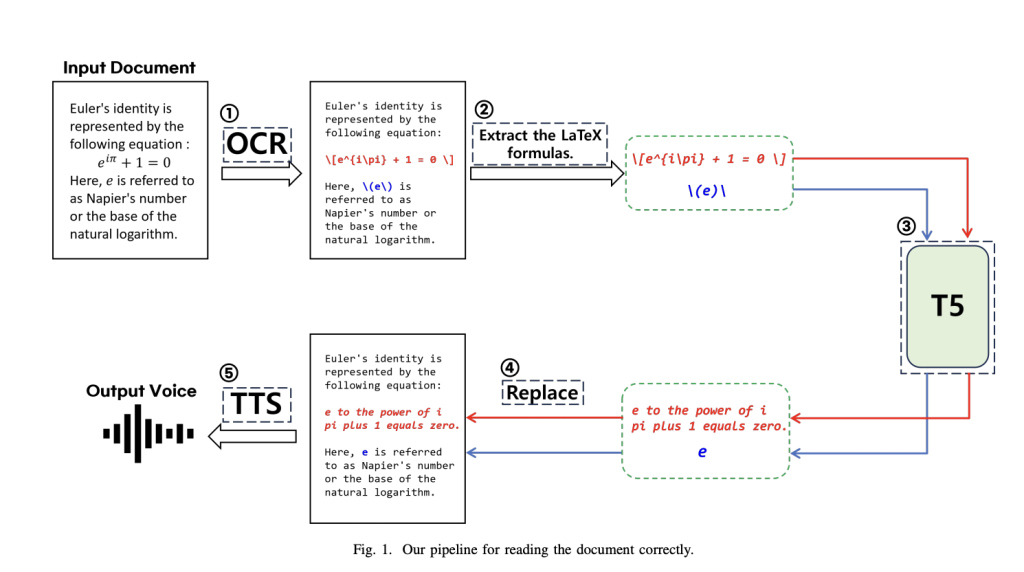
Researchers from Seoul National University, Chung-Ang University, and NVIDIA developed MathReader to bridge this gap between technology and users required to read mathematical text. MathReader mingles an OCR, a fine-tuned T5-small language model, and a TTS system to decode mathematical expressions without error. It overcomes the limited capabilities of the current technologies so that formulas in documents are precisely vocalized. A pipeline that asserts math content is turned into audio has significantly served visually impaired users.
MathReader employs a five-step methodology to process documents. First, OCR is used to extract text and formulas from documents. Based on hierarchical vision transformers, the Nougat-small OCR model converts PDFs into markup language files while distinguishing between text and LaTeX formulas. Next, formulas are identified using unique LaTeX markers. The fine-tuned T5-small language model then translates these formulas into spoken English, effectively interpreting mathematical expressions into audible language. Subsequently, the translated formulas replace their LaTeX counterparts in the text, ensuring compatibility with TTS systems. Finally, the VITS TTS model converts the updated text into high-quality speech. This pipeline ensures accuracy and efficiency, making MathReader a groundbreaking document-accessible tool.
Performance evaluation highlights MathReader’s effectiveness. It significantly outperforms existing TTS systems, achieving a Word Error Rate (WER) of 0.281 compared to 0.510 for Microsoft Edge and 0.617 for Adobe Acrobat. Similarly, its Character Error Rate (CER) is remarkably low at 0.148, compared to 0.341 and 0.454 for the other systems. This substantial improvement demonstrates MathReader’s ability to deliver accurate speech output, even for documents with low-resolution or complex mathematical content. For example, MathReader successfully vocalized formulas skipped by other systems, showcasing its robustness. Further, the time required for processing a single page averaged 23.62 seconds, including 12.54 seconds for OCR and 6.21 seconds for TTS conversion, indicating its practicality for real-time applications.
MathReader represents a significant advancement in TTS technology, addressing the critical challenge of accurately vocalizing mathematical content. Its integration of advanced OCR, a fine-tuned language model, and TTS ensures a comprehensive solution for users reliant on auditory access to documents. By delivering precise and efficient results, MathReader sets a new standard for accessibility tools, providing an indispensable resource for visually impaired individuals and paving the way for future innovations in the field.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 65k+ ML SubReddit.
The post This AI Paper Introduces MathReader: An Advanced TTS System for Accurate and Accessible Mathematical Document Vocalization appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ