Blockchain systems face significant challenges in efficiently managing and updating state storage due to high write amplification (WA) and extensive I/O operations. In traditional architecture, such as Merkle Patricia Tries (MPT), frequent and expensive disk interactions incur inefficiencies that restrict throughput and scalability. Such problems are one of the biggest bottlenecks for decentralized applications requiring high transaction rates and low infrastructure costs. Overcoming these limitations is critical to supporting broader adoption and unlocking the full potential of blockchain technology.
Existing methods for blockchain state management, such as MPT, AVL Trees, and NOMT, suffer from inherent inefficiencies that limit their scalability and performance. MPTs are widely used because they can generate proofs efficiently, but they incur high write overhead and require substantial DRAM to mitigate excessive SSD reads. AVL Trees offer marginal improvements by relying on self-balancing structures, but they depend on path-based operations, making them resource-intensive and unsuitable for real-time demands. NOMT, a newer development, further improves flash storage performance for Merkle tree operations but suffers from high write amplification and poor sparsely distributed key handling. These limitations present significant impediments to achieving a balance between scalability, efficiency, and performance.
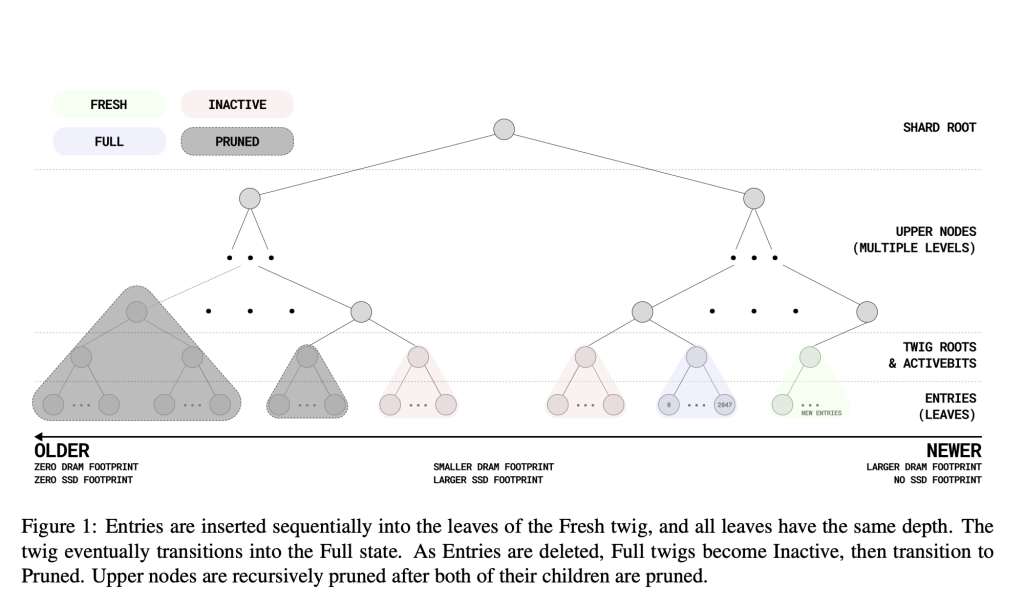
QMDB introduces a revolutionary approach to managing state across the blockchain by unifying key-value storage and Merkle tree functionality within one architecture. This design addresses the inefficiencies of earlier systems with a suite of novel features. A twig-based subtree compression mechanism significantly reduces memory requirements by compressing 2048 entries into a single hash and bitmap, achieving a 99.9% reduction in the DRAM footprint. By implementing in-memory Merkleization, QMDB eliminates the need for disk I/O during state updates, allowing the system to perform optimally even on consumer-grade hardware. Its append-only architecture for state updates minimizes write amplification while allowing efficient state modifications. In addition, including historical proof capabilities facilitates the efficient verification and reconstruction of blockchain states at any block height, thus improving the transparency and functionality of decentralized applications. These developments, therefore, put QMDB at the forefront as a high-performance and scalable alternative to traditional methods.
The system utilizes a binary Merkle tree design with fixed-size twigs and a modular indexer optimized for large-scale datasets. An indexer able to handle only 2.3 bytes of DRAM per entry enables the scaling of QMDB to billions of entries with the highest possible throughput. Sharding and a three-stage pipeline for prefetching, updating, and flushing have been used to make maximal use of available hardware resources and the parallel processing mechanism. It also provides CRUD operations with the least interaction with SSD to manage the state efficiently across the diversity of hardware configurations. The technological advancements support QMDB to deal with datasets much larger than the projected state size of Ethereum for 2024 while performing excellently on enterprise-grade as well as consumer hardware.
QMDB delivers remarkable improvements in blockchain state management, achieving up to 2.28 million updates per second and handling datasets with billions of entries. It consistently outperforms existing systems, delivering six times the throughput of RocksDB and eight times that of NOMT, even when tested under demanding conditions. It is flexible and efficient: it can attain 150,000 updates per second on a low-cost consumer setup while scaling to 280 billion entries on high-capacity servers. These results demonstrate the ability of QMDB to decrease hardware barriers to blockchain participation, maintaining exceptional scalability and throughput, hence a great achievement in decentralized system design.
By addressing critical inefficiencies in blockchain architectures, QMDB introduces a robust and scalable solution for managing state updates and storage. Its innovative approach, including twig-based compression, in-memory Merkleization, and append-only state updates, redefines the limits of performance and efficiency in blockchain systems. These innovations lower hardware requirements and enable broader participation in decentralized networks, paving the way for advanced applications requiring high transaction rates and efficient state management. Its unique capabilities make QMDB a landmark, pushing all the other benchmarks for scalability and performance in the state management system in blockchain.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 65k+ ML SubReddit.
 Recommend Open-Source Platform: Parlant is a framework that transforms how AI agents make decisions in customer-facing scenarios. (Promoted)
Recommend Open-Source Platform: Parlant is a framework that transforms how AI agents make decisions in customer-facing scenarios. (Promoted)
The post Efficient Blockchain State Management with Quick Merkle Database (QMDB) appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ