APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) have become the lifeblood of digital transformation. From mobile banking apps to enterprise SaaS platforms, APIs power the seamless flow of data between applications, services, and devices. However, with this power comes an equally significant risk: security vulnerabilities. A single exposed API can lead to massive data leaks, unauthorized access, and even complete system compromise. This is where API security testing steps in as a crucial practice. And while advanced security testing often requires specialized penetration testing tools, many teams underestimate the power of a tool they’re already familiar with, Postman. Known primarily as a functional testing and API development tool, Postman can also serve as an effective solution for basic API security testing. With its ability to manipulate requests, inject custom headers, and automate scripts, Postman provides development and QA teams with a practical way to catch vulnerabilities early in the lifecycle.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore:
- Why API security testing is essential
- The difference between general security testing and API-specific testing
- Common API vulnerabilities
- How to use Postman for API security testing
- Step-by-step examples of common tests (with mandatory screenshots/visuals)
- Best practices for integrating security testing into your workflow
- Compliance and regulatory considerations
By the end of this blog, you’ll understand how Postman can fit into your security toolkit, helping you protect sensitive data, ensure compliance, and build customer trust.
Key Highlights
- Postman as a Security Tool: Learn how Postman, beyond functional testing, can perform basic API security checks.
- Common Vulnerabilities: Explore API risks such as broken authentication, parameter tampering, and HTTP method misuse.
- Step-by-Step Testing Guide: Practical instructions for running security tests in Postman.
- Compliance Benefits: How Postman testing supports laws like the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA).
- Best Practices: Tips for integrating API security testing into CI/CD pipelines.
- Comparison Insights: Postman vs. specialized penetration testing tools.
- FAQs Section: Answers to top search queries around Postman API security testing.
Why API Security Testing Matters
The adoption of APIs has skyrocketed across industries. Unfortunately, APIs are now also the primary attack vector for hackers. According to OWASP, the OWASP API Security Top 10 highlights the most common vulnerabilities exploited today, including:
- Broken Authentication – Weak authentication mechanisms allow attackers to impersonate users.
- Excessive Data Exposure – APIs returning more data than necessary, enabling attackers to intercept sensitive information.
- Injection Attacks – Malicious input is inserted into requests that trick the server into executing harmful commands.
- Broken Object Level Authorization (BOLA) – Attackers are manipulating object IDs to access unauthorized data.
Real-life breaches underscore the importance of proactive API security testing. For example, the Twitter API breach exposed millions of users’ contact information simply due to a failure in properly validating API requests. Incidents like these demonstrate that API security is not just a technical necessity; it’s a business-critical priority.
Postman for API Security Testing
While Postman was originally designed for API development and functional validation, it has powerful features that make it suitable for basic security testing, especially during development. Postman allows testers and developers to:
- Modify Requests Easily: Change headers, tokens, and payloads on the fly.
- Test Authentication Flows: Simulate both valid and invalid tokens.
- Automate Tests: Use Postman collections and scripts for repeated checks.
- Visualize Responses: Quickly see how APIs behave with manipulated requests.
This makes Postman an ideal tool for catching vulnerabilities early, before APIs reach production.
Common Security Tests in Postman (with Examples)
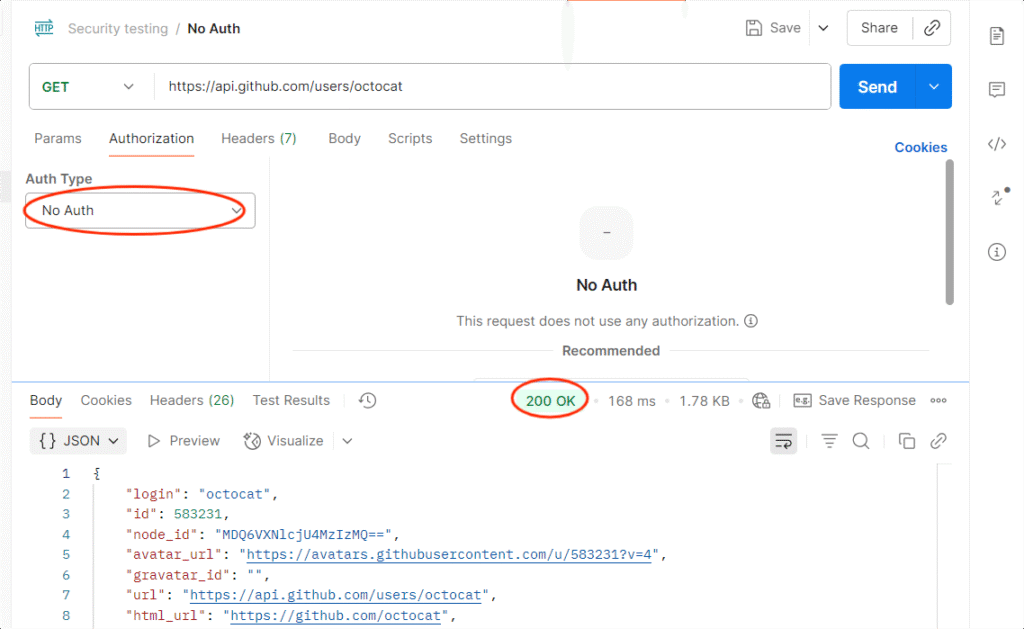
1. Missing Authentication
Objective: Ensure restricted endpoints reject unauthenticated requests.
How to Test in Postman:
- Select a protected endpoint (e.g., /user/profile).
- Remove the Authorization header/token.
- Send the request.
Expected: API should return 401 Unauthorized or 403 Forbidden.
Risk if Fails: Anyone could access sensitive data without logging in.
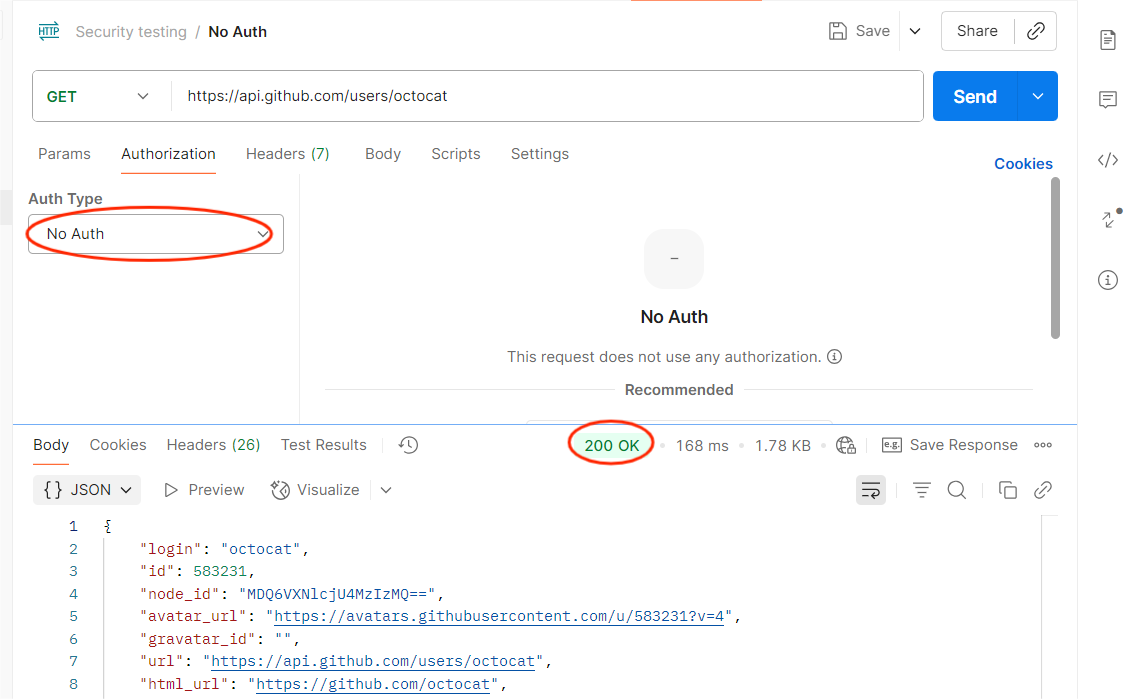
2. Broken Authentication
Objective: Check if the API validates tokens correctly.
How to Test in Postman:
- Replace a valid token with an expired or random token.
- Send the request.
Expected: API should deny access with 401 or 403.
Risk if Fails: Attackers could use stolen or fake tokens to impersonate users.
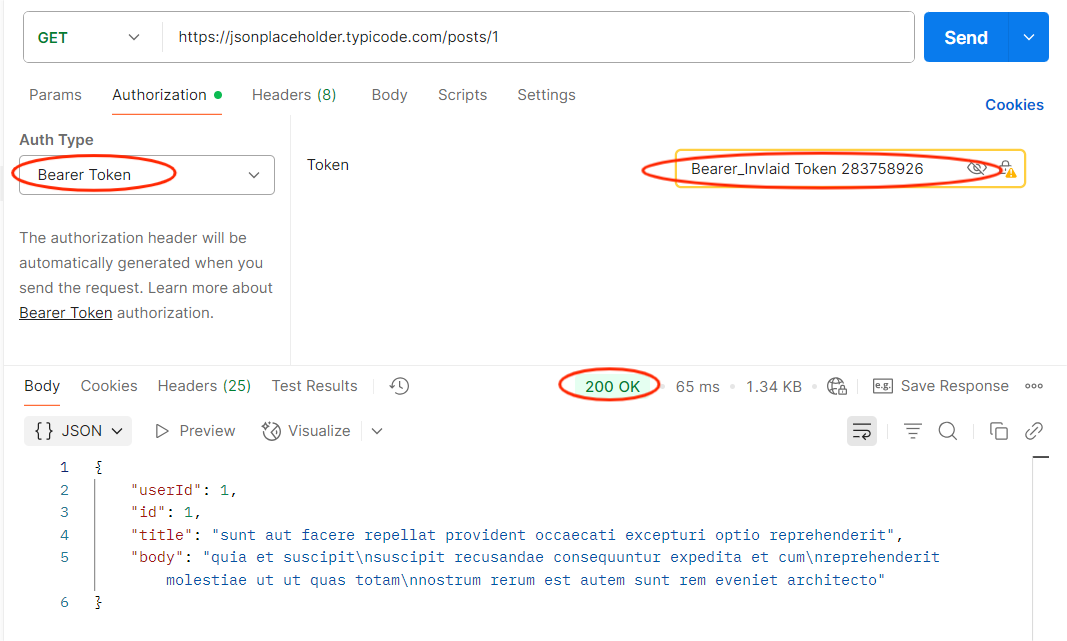
3. Parameter Tampering
Objective: Ensure unauthorized data access is blocked.
How to Test in Postman:
- Identify sensitive parameters (user_id, order_id).
- Change them to values you shouldn’t have access to.
- Send the request.
Expected: API should reject unauthorized parameter changes.
Risk if Fails: Attackers could access or modify other users’ data.
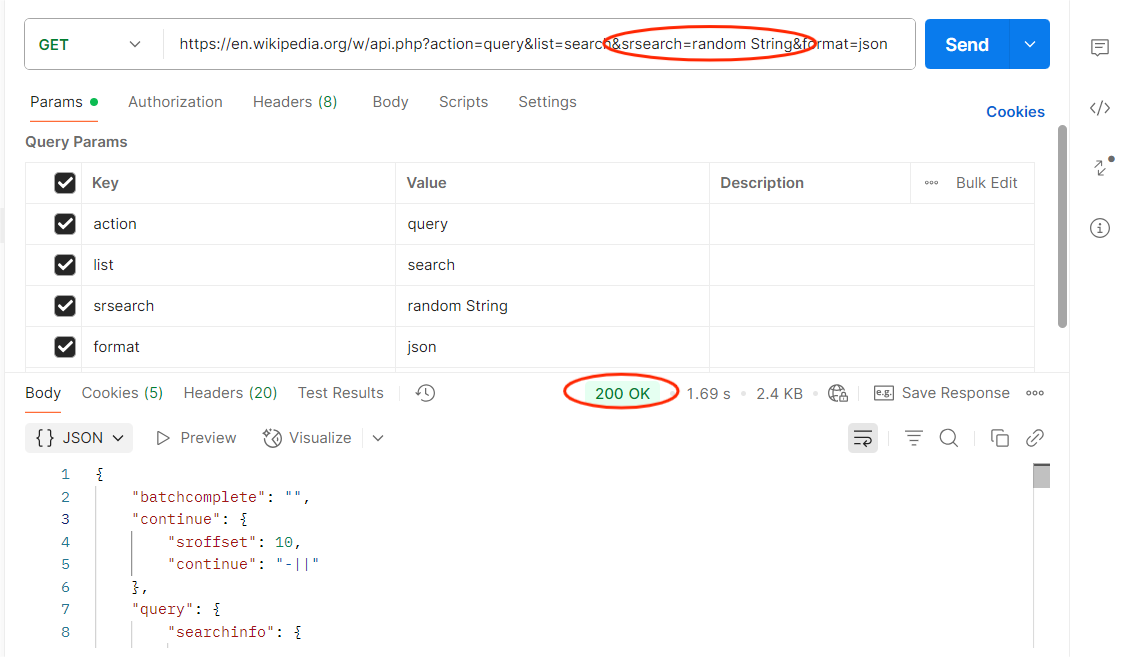
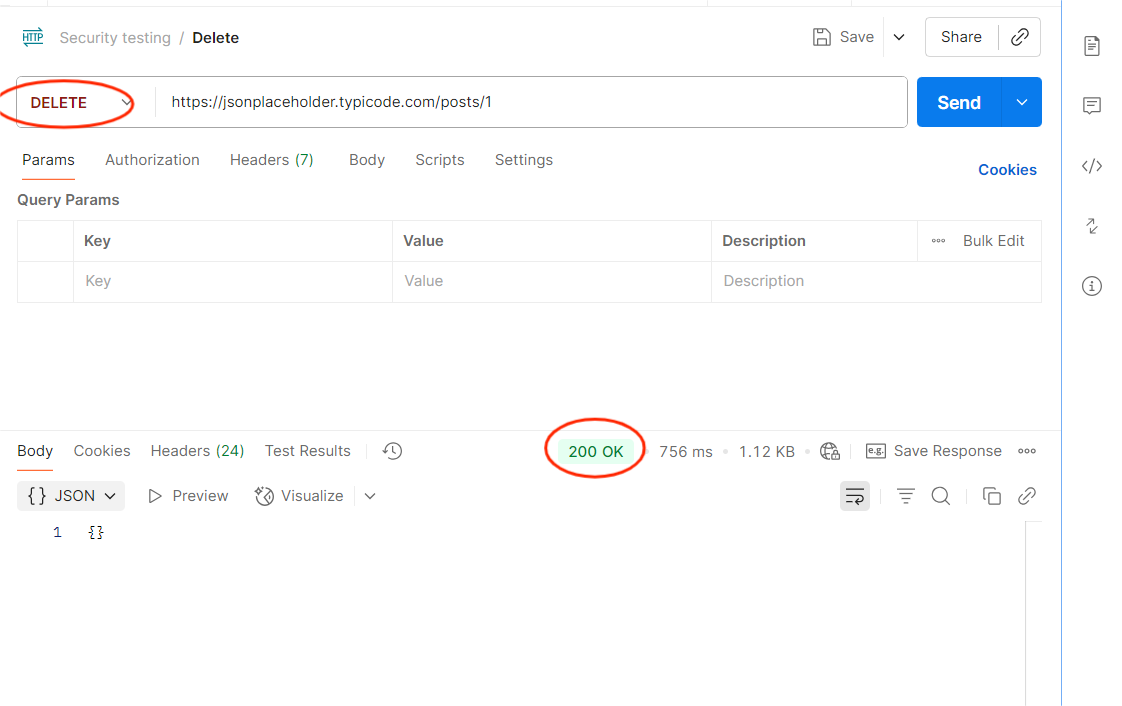
4. HTTP Method Misuse
Objective: Verify that APIs only allow intended methods.
How to Test in Postman:
- Take an endpoint (e.g., /user/profile).
- Change method from GET to DELETE.
- Send the request.
Expected: API should return 405 Method Not Allowed.
Risk if Fails: Attackers could perform unintended actions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting API Security Testing in Postman
- Preparation: Identify all API endpoints (documented and undocumented).
- Discovery: Use Postman collections to organize and catalog APIs.
- Testing: Apply common vulnerability tests (authentication, authorization, input validation).
- Automation: Set up test scripts for repeated validation in CI/CD.
- Remediation: Document vulnerabilities and share with development teams.
- Re-Validation: Fix and re-test before production deployment.
Best Practices for Secure API Testing with Postman
- Integrate with CI/CD: Automate basic checks in your pipeline.
- Use Environment Variables: Manage tokens and URLs securely.
- Adopt OWASP API Security Top 10: Align your Postman tests with industry best practices.
- Combine Manual + Automated Testing: Use Postman for basic checks, and penetration testing tools for deeper analysis.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
In regions like India, compliance with laws such as the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) is mandatory. Failing to secure APIs that handle personal data can result in heavy penalties. Postman testing helps organizations demonstrate due diligence in securing APIs, complementing more advanced security tools.
Comparison Table: Postman vs. Advanced Security Tools
| S. No | Feature | Postman (Basic Testing) | Specialized Tools (Advanced Testing) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ease of Use | High – user-friendly GUI | Moderate – requires expertise |
| 2 | Authentication Testing | Yes | Yes |
| 3 | Parameter Tampering Detection | Yes | Yes |
| 4 | Injection Attack Simulation | Limited | Extensive |
| 5 | Business Logic Testing | Limited | Strong (manual pen testing) |
| 6 | Automation in CI/CD | Yes | Yes |
| 7 | Cost | Free (basic) | High (license + expertise) |
Conclusion
API security testing is no longer optional. As APIs become central to digital experiences, ensuring their security is a business-critical responsibility. Postman, while not a full-fledged penetration testing tool, provides an accessible and practical starting point for teams to test APIs for common vulnerabilities. By using Postman for missing authentication, broken authentication, parameter tampering, and HTTP method misuse, you can catch security gaps early and avoid costly breaches. Combined with compliance benefits and ease of integration into CI/CD, Postman helps you shift security left into the development cycle.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Can Postman replace penetration testing tools?
No. Postman is excellent for basic security checks, but cannot fully replace penetration testing tools that identify complex vulnerabilities.
-
Is Postman suitable for enterprise-grade security?
It’s suitable for early-stage validation but should be complemented with advanced testing in enterprises.
-
Can Postman tests be automated?
Yes. Collections and Newman (Postman’s CLI tool) allow you to run automated tests in CI/CD pipelines.
-
What vulnerabilities can Postman NOT detect?
Postman struggles with advanced exploits like Race Conditions, Mass Assignment, and Chained Attacks. These require expert analysis.
-
How often should API security tests be performed?
Continuously, integrate into your development workflow, not just before production.
The post Postman API Security Testing: A Complete Guide appeared first on Codoid.
Source: Read More