Have you ever wondered why some software teams are consistently great at handling unexpected issues, while others scramble whenever a bug pops up? It comes down to preparation and more specifically, software testing technique known as bebugging. You’re probably already familiar with traditional debugging, where developers identify and fix bugs that naturally occur during software execution. But bebugging takes this a step further by deliberately adding bugs into the software. Why would anyone intentionally introduce errors, you ask? Simply put, bebugging is like having a fire drill for your software. It prepares your team to recognize and resolve issues quickly and effectively. Imagine you’re about to launch a new app or software update. Wouldn’t it be comforting to know that your team has already handled many of the potential issues before they even arose?
Related Blogs
In this detailed guide, you’ll discover exactly what bebugging is, why it’s essential for your development process, and how you can implement it successfully. Whether you’re a QA engineer, software developer, or tech lead, mastering bebugging will transform your team’s approach to troubleshooting and significantly boost your software’s reliability.
What Exactly Is Bebugging, and How Is It Different from Debugging?
Though they sound similar, bebugging and debugging have very different purposes:
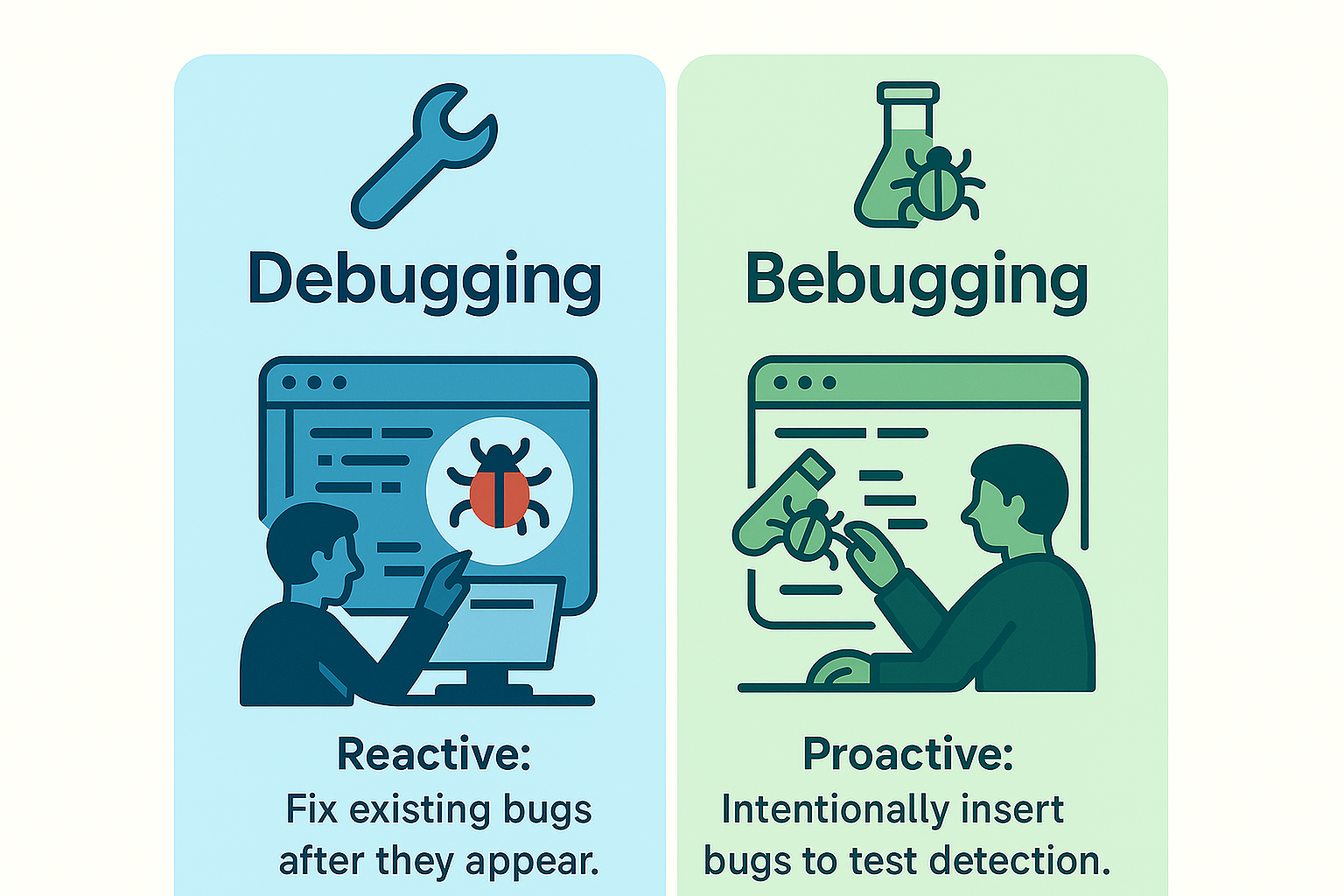
- Debugging is reactive. It involves locating and fixing existing software errors.
- Bebugging is proactive. It means intentionally inserting bugs to test how effectively your team identifies and resolves issues.
Think about it this way: debugging is like fixing leaks as you discover them in your roof. Bebugging, on the other hand, involves deliberately making controlled leaks to test whether your waterproofing measures are strong enough to handle real storms. This proactive practice encourages a problem-solving culture in your team, making them better prepared for real-world software challenges.
A Brief History: Where Did Bebugging Come From?
The term “debugging” famously originated with Admiral Grace Hopper in the 1940s when she literally removed a moth from a malfunctioning computer. Over the years, as software became increasingly complex, engineers realized that simply reacting to bugs wasn’t enough. In response, the concept of “bebugging” emerged, where teams began intentionally inserting errors to test their software’s reliability and their team’s readiness.
By the 1970s and 1980s, the practice gained traction, especially in large-scale projects where even minor errors could lead to significant disruptions. With modern development practices like Agile and CI/CD, bebugging has become a critical component in ensuring software quality.
Why Should Your Team Use Bebugging?
Bebugging isn’t just a quirky testing technique; it brings substantial benefits:
- Enhanced Troubleshooting Skills: Regularly handling intentional bugs improves your team’s ability to quickly diagnose and fix complex real-world issues.
- Better Preparedness: Your team will be better equipped to deal with unexpected problems, significantly reducing panic and downtime during critical periods.
- Improved Software Reliability: Regular bebugging ensures your software remains robust, reducing the likelihood of major issues slipping through to customers.
- Sharper Error Detection: It refines your team’s ability to spot subtle errors, enhancing overall testing effectiveness.
Key Techniques for Successful Bebugging
Error Seeding
Error seeding involves strategically placing known bugs within critical software components. It helps teams practice identifying and fixing errors in controlled scenarios, just like rehearsing emergency drills. For example, introducing bugs in authentication or payment processing modules can greatly enhance your team’s readiness for high-risk situations.
Automated Error Injection
Automation is a powerful tool in bebugging, particularly for larger or continuously evolving projects. AI-driven automated tools systematically introduce errors, allowing for consistent, repeatable testing without overwhelming your team. These tools often integrate with robust error tracking systems to monitor anomalies and improve detection accuracy.
Stress Testing Combined with Bebugging
Stress testing pushes your software to its limits to observe its behavior under extreme conditions. When combined with bebugging, intentionally adding bugs during these stressful scenarios, you’ll gain insight into potential vulnerabilities, allowing your team to proactively address issues before users encounter them.
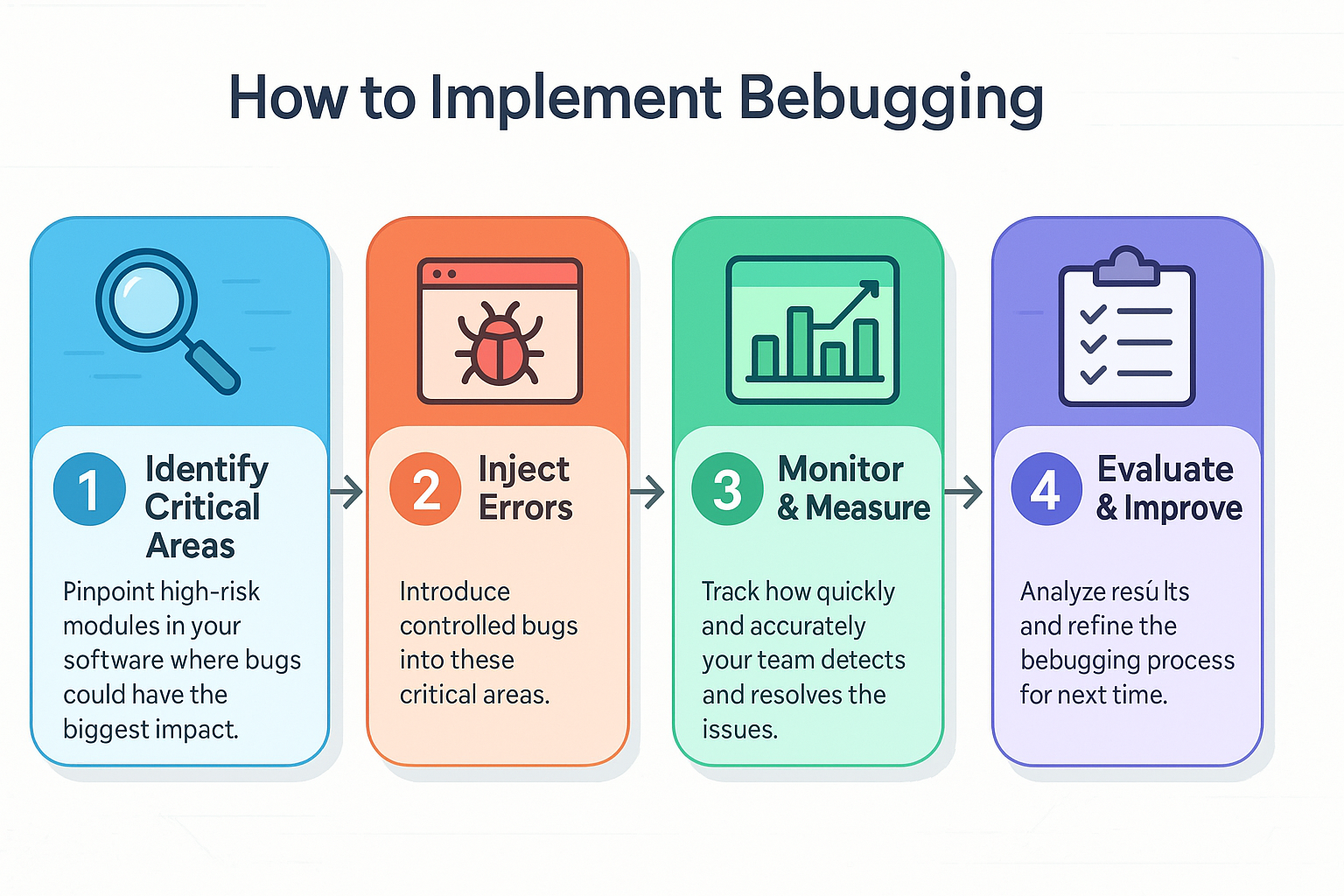
How to Implement Bebugging Step-by-Step
- Identify Critical Areas: Pinpoint areas within your software most susceptible to significant impacts if bugs arise.
- Plan and Inject Errors: Decide on the types of intentional errors, syntax errors, logical bugs, and runtime issues, and introduce them systematically.
- Monitor and Measure: Observe how effectively and swiftly your team identifies and fixes these injected bugs. Capture metrics like detection time and accuracy.
- Evaluate and Improve: Analyze your team’s performance, identify strengths and weaknesses, and refine your error-handling procedures accordingly.
Bebugging in Action: A Real-World Example
Consider a fintech company that adopted bebugging in their agile workflow. They intentionally placed logic and security errors in their payment processing software. Because they regularly practiced handling these issues, the team quickly spotted and resolved them. This proactive strategy significantly reduced future debugging time and helped prevent potential security threats, increasing customer trust and regulatory compliance.
Traditional Debugging vs. Bebugging
| Aspect | Traditional Debugging | Bebugging |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reactive error fixing | Proactive error detection |
| Implementation | Fixing existing errors | Introducing intentional errors |
| Benefits | Immediate bug resolution | Enhanced long-term reliability |
| Suitability | Post-development phase | Throughout software development |
Why Rapid Bug Detection Matters to Your Business
Rapid bug detection is critical because unresolved issues harm your software’s performance, disrupt user experience, and damage your brand reputation. Quick detection helps you avoid:
- User Frustration: Slower software performance or crashes lead to dissatisfied customers.
- Data Loss Risks: Bugs can cause significant data issues, potentially costing your business heavily.
- Brand Damage: Persistent issues weaken customer trust and loyalty, negatively impacting your business.
Common Types of Bugs to Look Out For:
- Syntax Errors: Basic code mistakes, like typos or missing punctuation.
- Semantic Errors: Logic errors where the software works incorrectly despite being syntactically correct.
- Runtime Errors: Issues arising during the software’s actual execution, often due to unexpected scenarios.
- Concurrency Errors: Bugs related to improper interactions between parallel processes or threads, causing unpredictable results or crashes.
Conclusion
Bebugging isn’t just another testing practice, it’s a strategic move toward building reliable and robust software. It empowers your team to handle problems confidently, proactively ensuring your software meets the highest quality standards. At Codoid Innovations, we are committed to staying ahead of software testing challenges by continuously embracing innovative methods like bebugging. With our dedicated expertise in quality assurance and advanced testing strategies, we ensure your software is not just error-free but future-proof.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What’s the key difference between debugging and bebugging?
Debugging reacts to errors after they appear, while bebugging proactively inserts errors to prepare teams for future issues.
-
Can we automate bebugging for large projects?
Absolutely! Automation tools using AI are perfect for systematic bebugging, especially in extensive or continuously evolving software projects.
-
Is bebugging good for all software?
While helpful in most cases, bebugging is especially beneficial in agile environments or complex software systems where rapid, continuous improvement is essential.
-
What tools are best for bebugging?
Integrated Development Environment (IDE) debuggers like GDB, combined with error-tracking tools like Sentry, Bugzilla, or JIRA, work effectively for bebugging practices.
The post Master Bebugging: Fix Bugs Quickly and Confidently appeared first on Codoid.
Source: Read More