As estimates of the quantum computing power needed to crack current public key encryption algorithms continue to drop, a group of technology companies and organizations is urging users to begin migrating toward post-quantum cryptographic standards now.
To help organizations with the transition to post-quantum cryptography, the Post-Quantum Cryptography Coalition (PQCC) released a migration roadmap today to guide companies through the phases of that journey.
“As quantum computing technology continues to advance, organizations cannot afford to delay preparing for these transformative changes and threats to their security,” Wen Masters, MITRE’s vice president of cyber technologies, said in a statement.
MITRE is one of the founding members of PQCC, along with SandboxAQ, PQShield, IBM Quantum and Microsoft.
The roadmap’s release comes just days after the publication of a paper that reduced by more than 95% the estimated quantum computing power needed to crack RSA-2048 encryption keys.
Quantum Computing Power Needed to Crack RSA-2048 Lowered
That paper, by Craig Gidney of Google Quantum AI, updates a 2019 paper Gidney co-authored that estimated that 2048-bit RSA integers could be broken in eight hours by a quantum computer with 20 million noisy qubits.
“In this paper, I substantially reduce the number of qubits required,” Gidney wrote in the new paper published on arXiv. “I estimate that a 2048 bit RSA integer could be factored in less than a week by a quantum computer with less than a million noisy qubits.”
In a blog post on the paper, Gidney said that current quantum computers with relevant error rates “have on the order of only 100 to 1000 qubits,” and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is leading efforts to develop post-quantum cryptographic algorithms “that are expected to be resistant to future large-scale quantum computers. However, this new result does underscore the importance of migrating to these standards in line with NIST recommended timelines.”
In a November 2024 report, NIST said that “even if quantum computers are a decade away, organizations must begin the migration to postquantum cryptography today to avoid having their encrypted data exposed once quantum computers become operational in the future.”
While certain applications may require post-quantum cryptography (PQC) sooner, NIST and U.S. federal systems have set an “overall goal of achieving widespread PQC adoption by 2035.”
In an April update, PQCC noted that only three PQC standards have seen “some adoption” so far: SSH, TLS 1.3, and IKE/IPSec. Here is PQCC’s standards adoption heatmap:

Post-Quantum Cryptography Migration Roadmap
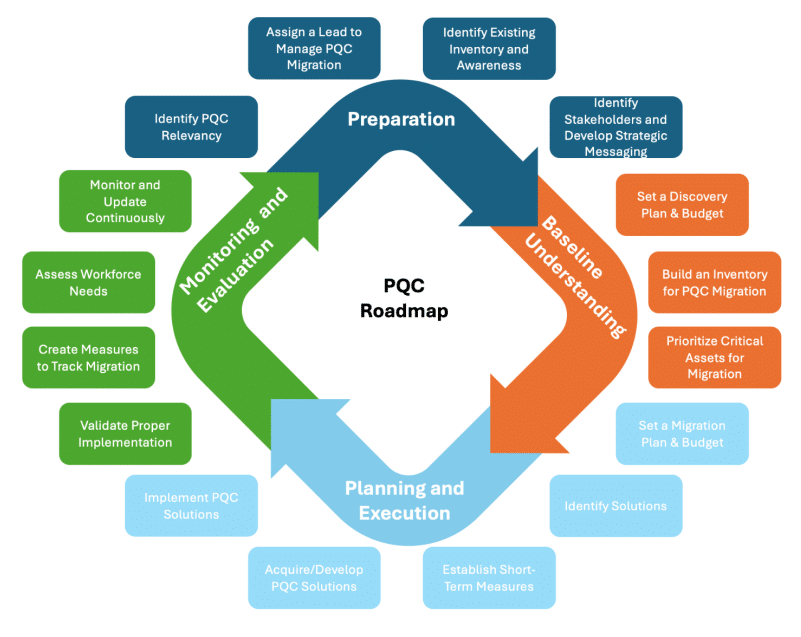
The 20-page PQCC migration roadmap details four migration phases to help CIOs and CISOs “act decisively, taking proactive steps to protect sensitive data now and in the future.”
Those migration phases are:
- Preparation: Starting with an overview of an organization’s PQC migration aims, assigning a migration lead, identifying stakeholders, “and aligning stakeholders through strategic messaging.”
- Baseline Understanding: Gathering a baseline understanding of an organization’s data inventory, prioritizing assets to be updated, and establishing required resources and available budget.
- Planning and Execution: Collaborating with system vendors and internal system owners “to ensure that post-quantum solutions are acquired externally or developed internally and implemented effectively.”
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Developing measures for tracking migration process and formulating a process “for reassessing cryptographic security as quantum capabilities evolve.”
“The process outlined in this roadmap underscores the importance of strategic planning, stakeholder alignment, and continuous monitoring and documentation to adapt to technological advancements and maintain robust security postures,” the migration document concludes. “As the quantum computing landscape continues to evolve, organizations must remain adaptable, tracking updates in guidance to maintain a secure PQC transition.”
Source: Read More