In 2025, agentic AI is transforming the insurance industry, enabling autonomous systems to perceive, reason, and act independently to achieve complex objectives. Insurers are heavily investing in these technologies to overcome legacy system limitations, deliver hyper-personalized customer experiences, and to capitalize on the $79.86 billion AI insurance market projected by 2032.
Central to this transformation is efficient claim processing. AI tools like natural language processing, image classification, and vector embedding help insurers effectively manage claim-related data. These capabilities generate precise catastrophe impact assessments, expedite claim routing with richer metadata, prevent litigation through better analysis, and minimize financial losses using more accurate risk evaluations.
Because AI’s promises often sound compelling—but fall short when moving from experimentation to real-world production—this post explores how an AI agent can manage a multi-step claim processing workflow.
In this workflow, the agent manages accident photos, assesses damage, and verifies insurance coverage to enhance process efficiency and improve customer satisfaction. This system employs large language models (LLMs) to analyze policy information and related documents provided by MongoDB Atlas Vector Search, with the outcomes stored in the Atlas database.
Creating a work order for claim handlers
The defining characteristic of AI agents, which is what sets them apart from simply prompting an LLM, is autonomy. The ability to be goal-driven and to operate without precise instructions makes AI agents powerful allies for humans, who can now delegate tedious tasks like never before.
But each agent has a different degree of autonomy, and building such systems is a tradeoff between reliability and prescriptiveness. Since LLMs—which can be thought of as the agent’s brain—tend to hallucinate and behave nondeterministically, developers need to be very cautious. Too much “freedom” can lead to unexpected outcomes. On the other hand, including too many constraints, instructions, or hardcoded steps defeats the purpose of building agents.
To help agents understand their context, it is important to craft a prompt that describes their scope and goals. This is part of the prompt we’ve used for this exercise:
“You are a claims handler assistant for an insurance company. Your goal is to help claim handlers understand the scope of the current claim and provide relevant information to help them make an informed decision. In particular, based on the description of the accident, you need to fetch and summarize relevant insurance guidelines so that the handler can determine the coverage and process the claim accordingly. Present your findings in a clear and extremely concise manner.”
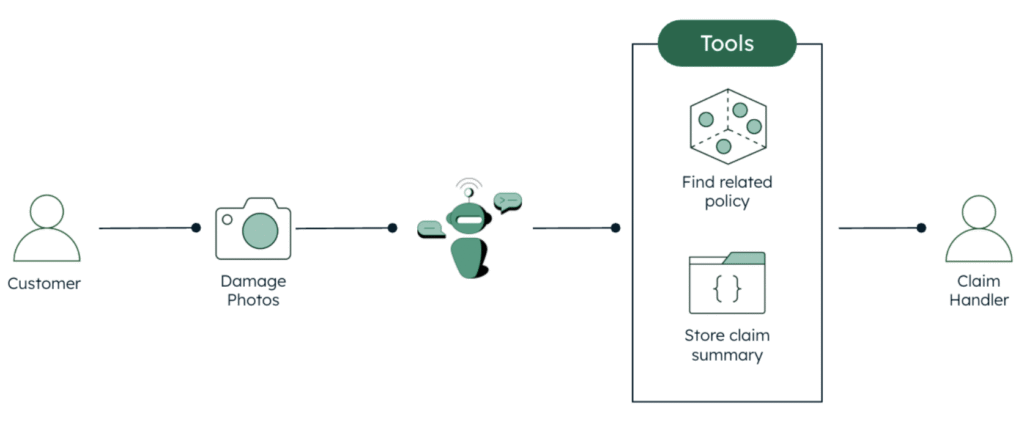
In addition to the definition of the tasks, it is also important to give instructions on the tools available to the agent and how to use them. Our system is pretty basic, featuring only two tools: Atlas Vector Search and write to the database (see Figure 1).
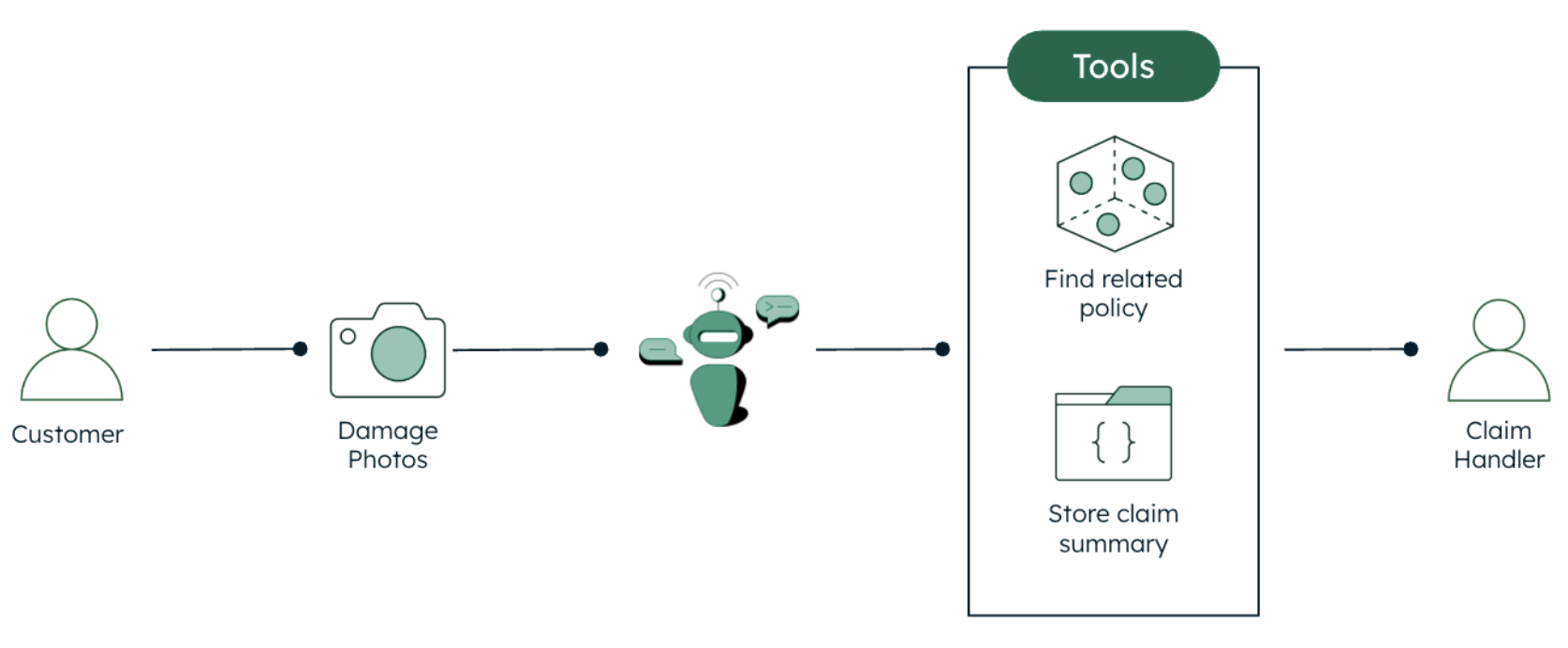
The Vector Search step maps the vectorized image description to the vectorized related policy, which also contains the description of the coverages for that class of accident.
The policy and the related coverages are used by the agent to figure out the recommended next actions and assign a work order to a claim handler. This information is persisted in the database using the second tool, write to the database.
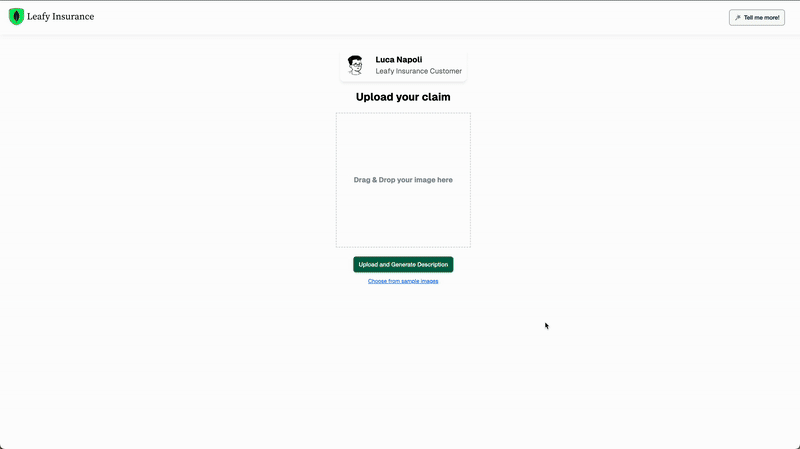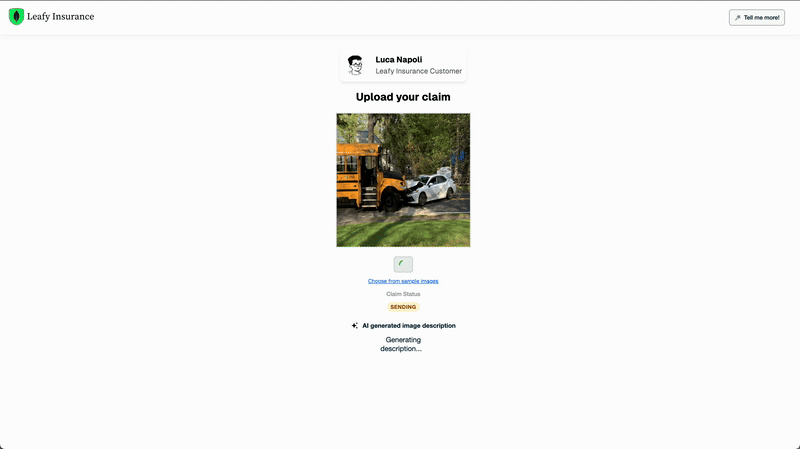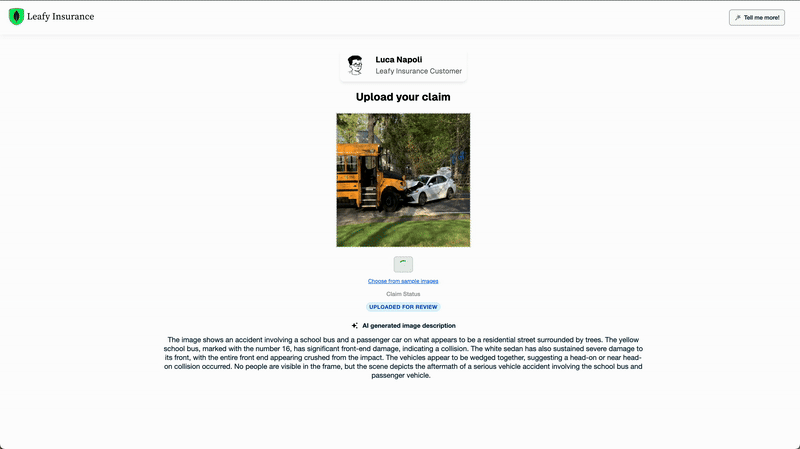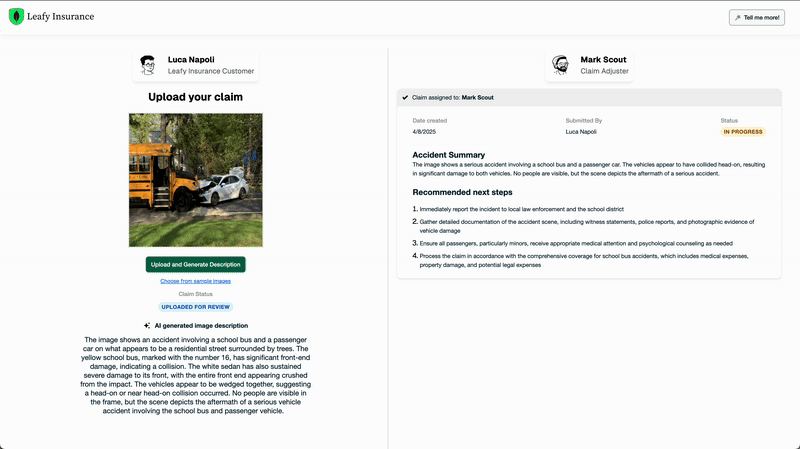
What does the future hold?
In our example, the degree of autonomy is quite low, and for the agent, it boils down to deciding when to use which tool. In real-life scenarios, such systems, even if simple, can save a lot of manual work. They eliminate the need for claim handlers to manually locate related policies and coverages, a cumbersome and error-prone process that involves searching multiple systems, reading lengthy PDFs, and summarizing all their findings.
Agents are still in their infancy and require handholding, but they have the potential to act with a degree of autonomy never before seen in software. AI agents can reason, perceive, and act—and their performance is improving at a breakneck pace.
The insurance industry (like everybody else!) needs to make sure it’s ready to start experimenting and to embrace change. This can only happen if systems and processes are aligned on one imperative: “make the data easier to work with.”
To learn more about integrating AI into insurance systems with MongoDB, check out the following resources:
-
The MongoDB Ebook: Innovate With AI: The Future Enterprise
-
The MongoDB Blog: AI-Powered Call Centers: A New Era of Customer Service
-
The MongoDB Youtube Channel: Unlock PDF Search in Insurance with MongoDB & SuperDuperDB
Source: Read More