If you’re starting your journey into penetration testing, you’ve likely heard of Metasploit.
Metasploit is one of the most versatile tools in cybersecurity. It helps simplify vulnerability testing and exploitation.
Metasploit helps us find and fix weaknesses before malicious actors exploit them. In this tutorial, you’ll learn what Metasploit is, why it’s useful, and how to use it.
What is Metasploit?
Metasploit is an open-source framework for penetration testing.
You can use it to find vulnerabilities, exploit them, and get access to the target.
Metasploit provides a collection of exploits, payloads, and helper tools. It’s often called the “Swiss army knife” for pen testers.
Instead of writing your own scripts to exploit vulnerabilities, Metasploit gives you pre-built modules to automate a lot of your work.
A module is a piece of code that performs an action. These actions can include scanning, exploitation, or anything that helps to simplify a pen-test.
Why is Metasploit Useful for Penetration Testers?
Pentesters try to attack networks, applications, and systems to check their security. Metasploit helps make this job easier in several ways.
First, it simplifies exploitation. Metasploit has a large library of exploits that allows us to attack known weaknesses in software and systems quickly.
Next, it helps with reconnaissance and scanning. Metasploit’s scanning tools gather information about a target, such as open ports, running services, and likely vulnerabilities.
After breaking in, Metasploit provides post-exploitation features. Tools like Meterpreter let pentesters keep access, collect data, and test defenses further.
Metasploit is also very flexible. We can build or change modules to fit our specific needs.
In short, Metasploit lets us do complete security tests, from finding vulnerabilities to exploiting them.
What Are Metasploit Auxiliaries?
Auxiliary modules are helper tools within Metasploit that perform tasks other than exploitation.
They’re used for reconnaissance, scanning, brute-forcing and more. These flexible modules can help you gather valuable information about a target.
For example, an auxiliary module can scan a network for open ports, check for vulnerable services, or attempt a brute-force login on an application.
Here is a sample list of auxiliaries from metasploit.
You can see that Metasploit has a range of auxiliaries from scanners to
What Are Metasploit Exploits?
Exploits are scripts or programs that take advantage of vulnerabilities in systems.
They help an attacker gain access or perform malicious activities. Metasploit’s library includes hundreds of exploits, covering a wide range of platforms and services.
For example, if a target system is running an outdated version of Samba, Metasploit may have an exploit specifically designed to exploit that vulnerability.
What Are Metasploit Payloads?
Payloads are scripts that run on the target system after an exploit has been successfully executed.
They determine what happens next — whether you open a reverse shell, add a backdoor, or perform another post-exploitation task.
There are two main types of payloads:
-
Single Payloads: These perform one task, such as creating a user account on the target.
-
Staged Payloads: These download a larger payload in stages, allowing for more complex actions.
One of the most commonly used payloads is windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp, which gives you a command shell on the target system.
What is Metasploit Meterpreter?
Meterpreter is an advanced, interactive payload within Metasploit. It allows you to interact with the target system after exploiting it.
Meterpreter is loaded directly into the target’s memory, making it stealthier than traditional payloads.
Using Meterpreter, you can gather details about the operating system, transfer files between the attacker and target, and even execute commands directly on the target machine.
You can also set up a persistent backdoor to maintain access even after a system reboot.
Meterpreter is a powerful tool for post-exploitation activities, giving you complete control over the compromised system.
How to Work with msfconsole
Let’s get some hands-on experience with Metasploit.
msfconsole is the command-line interface (CLI) for Metasploit. It’s the main way to interact with the framework.
Metasploit is pre-installed in Kali Linux. If you are using Kali Linux, you can find the installation instructions here.
After installing Metasploit, launch the console by typing:
msfconsole
Once it loads, you’ll see a prompt like this
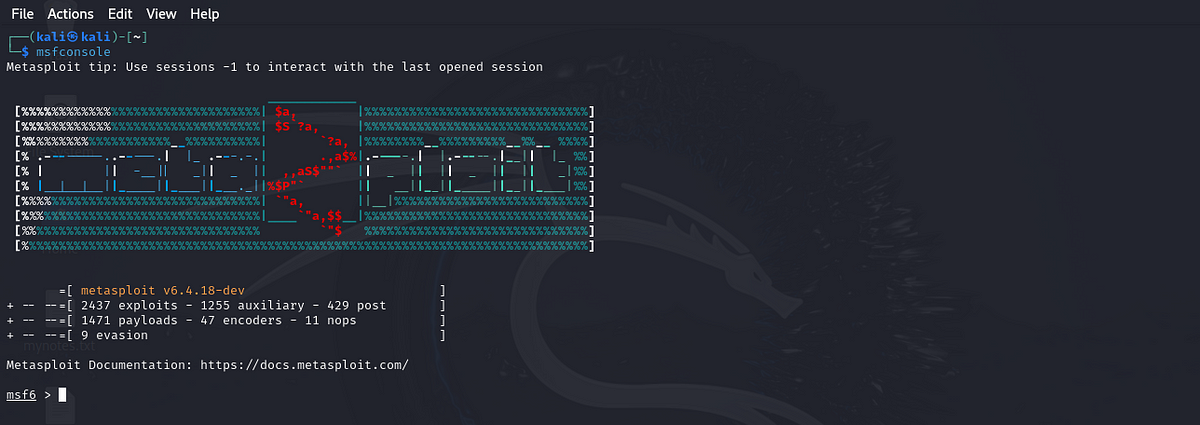
This is where you’ll type commands to interact with Metasploit. Let’s try some basic commands to get you started.
Metasploit commands
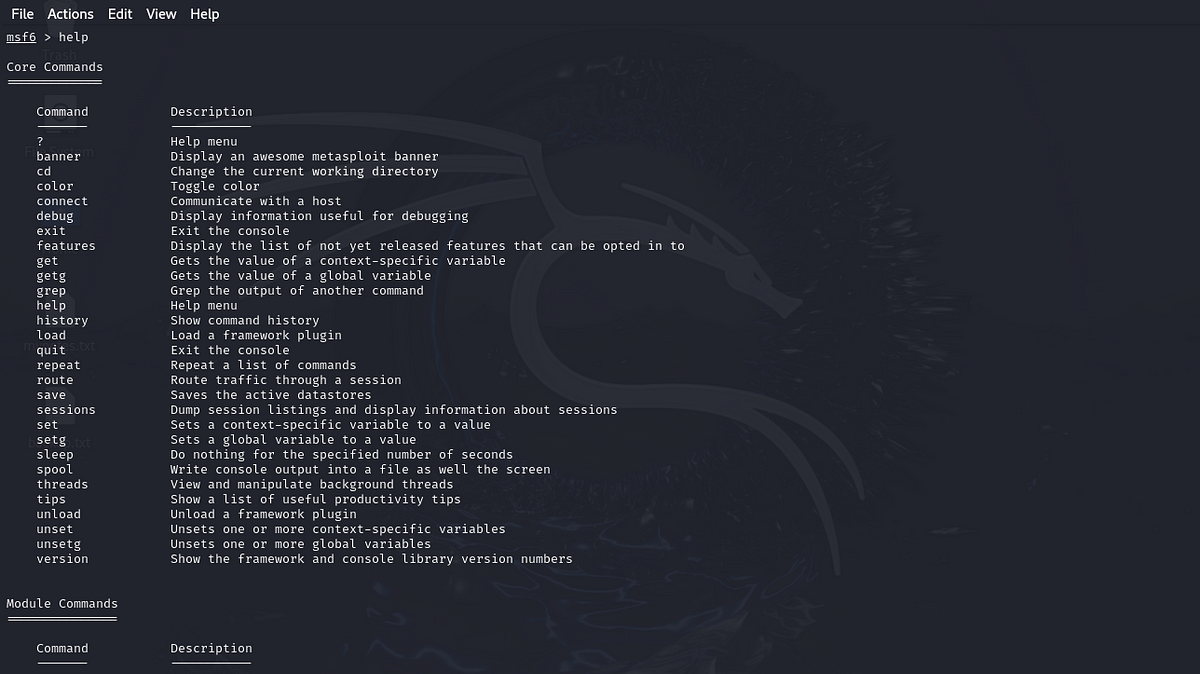
help: If you’re unsure about what to do, start by typinghelp. This displays a list of available commands along with brief descriptions. For example:
search: The search command helps us to find specific modules, such as exploits or auxiliaries (helper modules). For example, if you’re looking for modules related to scanning, you’d type:
msf6 > search scanner
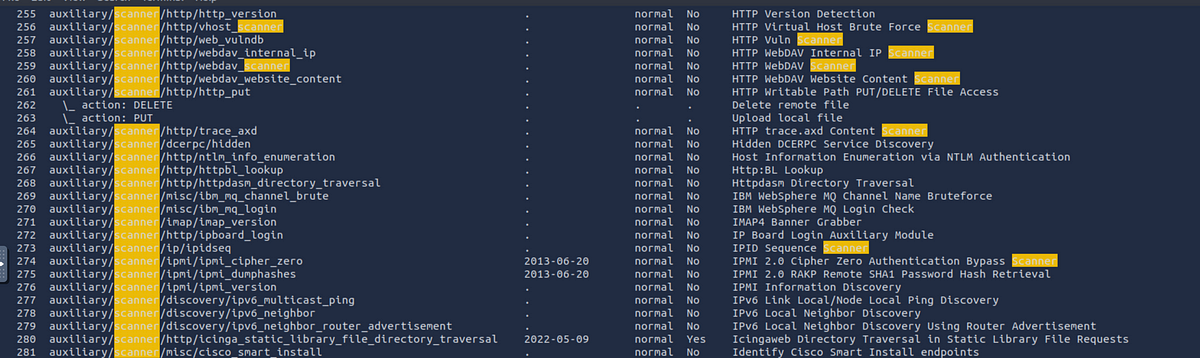
Metasploit will display all modules that match the keyword scanner.
info: You can use theinfocommand to learn more about a module, including its options and how it works. For example:
msf6 > info auxiliary/scanner/portscan/tcp
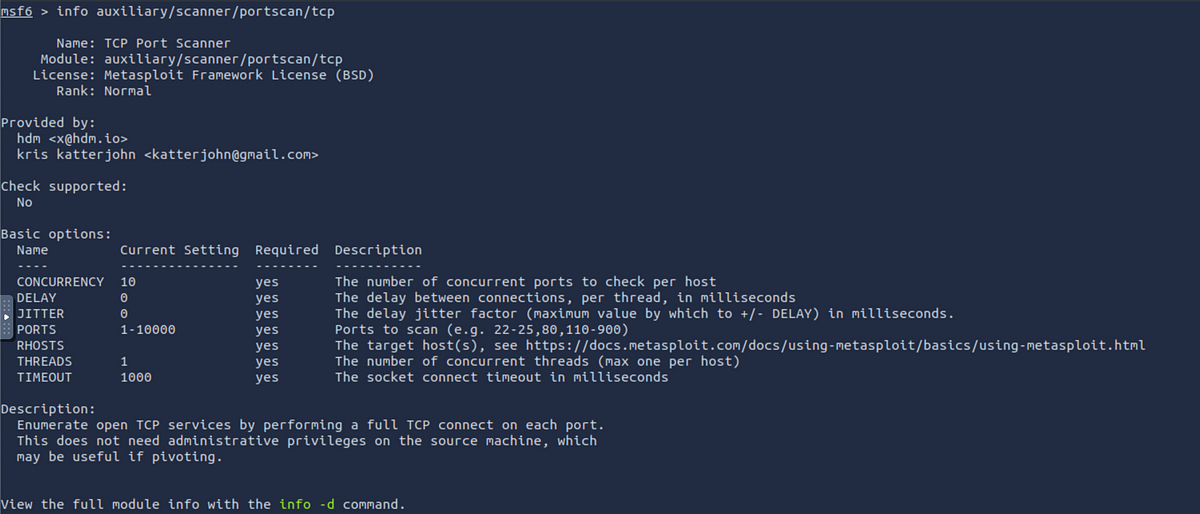
use: To use an exploit or an auxiliary, we can simply typeusealong with the module name. Let’s use the scanning moduleauxiliary/scanner/portscan/tcpwhich will scan for open TCP ports in a server.
msf6> use auxiliary/scanner/portscan/tcp
options: Once you have loaded a module with theusecommand, you can see the list of options using theoptionscommand. it will give you the list of options you can set for that module.
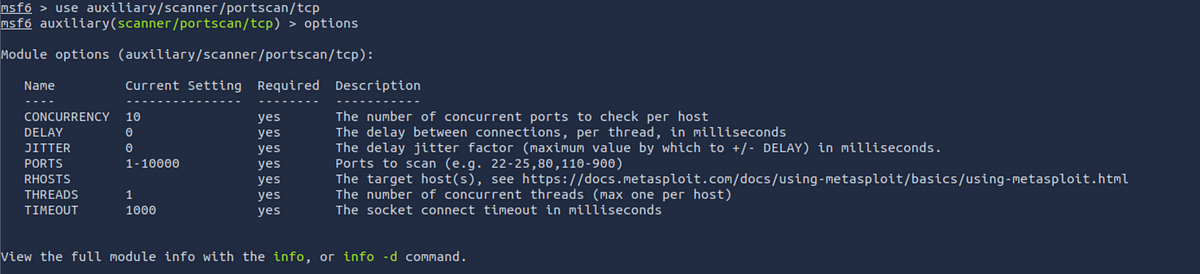
For example, the RHOSTS parameter is used to set the target IP address for scanning. scanme.nmap.org lets us run port scans on that server, so let’s use that to run a scan.
Let’s grab the IP address of the server. We will issue a simple ping command to get the IP address of the server.
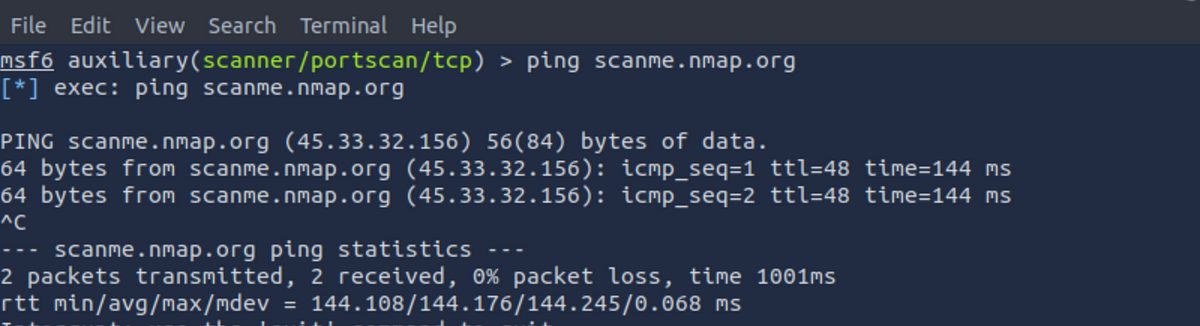
We can see that the IP address of the server is 45.33.32.156 (it can change when you run the ping command). Now let’s use this IP as our input for RHOSTS parameter. We will use the set command to set the IP address.
msf6 auxiliary(scanner/portscan/tcp)> set RHOSTS 45.33.32.156
run: To run a module, we use theruncommand. Now that we have set the target IP address, let’s run the module to see if any ports are open.
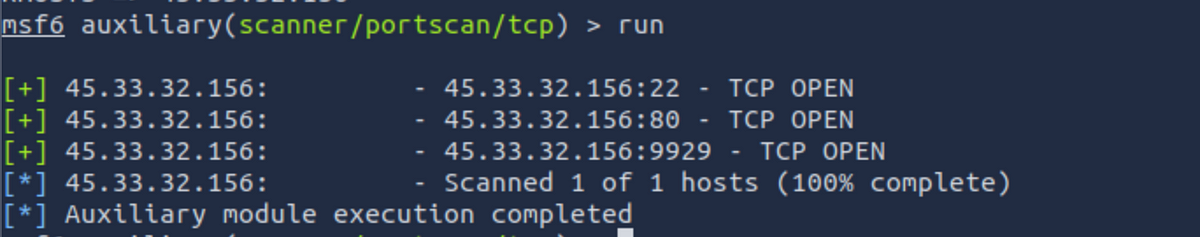
As you can see, we have found 3 ports — 22,80 and 9929. Tools like Nmap are better for in-depth port scanning, but Metasploit offers modules for almost every segment of a cybersecurity audit.
exit: When you’re done using Metasploit, simply typeexitto leave the console.
The msfconsole is user-friendly once you get the hang of these basic commands. Take your time exploring and experimenting with the help of the help command.
Conclusion
Metasploit is one of the most powerful tools in a penetration tester’s toolkit.
As you grow more familiar with Metasploit, you’ll unlock its full potential and gain deeper insights into how attackers exploit systems — and how you can defend against them. Keep learning, stay curious, and always use Metasploit responsibly!
Join our Weekly Newsletter for more tutorials on Ethical Hacking. For video tutorials on cybersecurity, check out our Youtube Channel.
Source: freeCodeCamp Programming Tutorials: Python, JavaScript, Git & MoreÂ