Have you ever wondered who’s behind the groundbreaking technologies like ChatGPT from OpenAI, Tesla’s autonomous vehicles, or the humanoid robots redefining our perception of artificial intelligence? What does it take to be one of those innovators driving the next wave of technological evolution?
If you’ve ever been curious, you’re about to find out. Welcome to this AI Engineering handbook. The field of AI Engineering is where innovation meets industry, where cutting-edge research transforms into world-changing products.
In this handbook, I’ll share proven strategies and actionable insights that have empowered countless developers to break into the highly competitive field of AI engineering.
You’ll find a step-by-step roadmap to mastering the skills and tools required to thrive in the transformative world of AI in 2025, enabling you to secure high-impact roles and achieve your career goals.
We’ll also discuss some of the many fields that have started successfully incorporating AI into their processes and workflows. And we’ll look at many examples of companies who are using AI in innovating and interesting ways.
This handbook is your ultimate guide to embracing the future of technology. Dive into comprehensive insights, actionable strategies, and expert perspectives that will empower you to excel in the transformative field of AI engineering. Whether you’re an aspiring engineer or a seasoned professional, this handbook offers the tools and knowledge to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving industry.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
I’ve recorded a podcast to supplement this book. You can listen to it here:
And if you’d like to have this handbook in a convenient PDF format, you can download it here.
Introduction to AI Engineering
As one of the most in-demand fields today, AI engineering sits at the heart of technological progress. Industry leaders are hunting for top-tier AI engineers across the globe. These engineers are being offered salaries ranging from $300,000 to $700,000 annually, with some even earning in the millions. The demand for AI engineers has never been higher, and the opportunities are vast for those ready to take the leap.
The global artificial intelligence market is projected to grow from $184 billion in 2024 to over $826 billion by 2030. This exponential growth is driven by AI engineers who are developing these products and solutions, transforming many industries and driving economic expansion.
My name is Tatev Aslanyan**,** and I’m from LunarTech, a deep tech innovation company specializing in teaching cutting-edge technologies like data science and AI through courses, bootcamps, and corporate training. In this comprehensive handbook, I will guide you step-by-step through what it takes to become a world-class AI engineer. You will learn:
-
What AI Engineering Is: Gain clarity on the role and its significance in the broader tech ecosystem.
-
Step-by-Step Skills Development: Learn exactly what skills you need and how to acquire them in detail to become world class AI Engineer.
-
Learning Resources: Discover the best tools and materials for self-study.
-
Career Opportunities: Understand what to expect from a career in AI engineering, including the roles, industries, and exceptional earning potential.
-
Modern Applications of AI Engineering: Discover how AI engineers are transforming industries worldwide.
Whether you’re an aspiring AI Engineer or looking to take your passion for AI to the next level, this handbook has been designed with you in mind. It’ll give you everything in one place so you can start and excel in your AI Engineering Career.
Why AI Engineering Matters
AI engineering is one of the most in-demand and fastest-growing professions today, sitting at the intersection of machine learning, data science, and software engineering. From autonomous vehicles to generative AI tools like ChatGPT, DALL-E, and Sora, AI engineering drives transformative solutions across industries. It is a field where creativity meets technical prowess, providing countless opportunities to shape the future of technology.
As AI continues to evolve, its applications are becoming increasingly pervasive. From diagnosing diseases to crafting personalized user experiences, AI is the backbone of modern innovation.
What Is AI Engineering?
AI engineering is the practice of designing, building, and deploying AI models and systems to solve real-world problems. It combines the principles of software engineering with advanced data science techniques to build reliable, scalable systems. AI engineering is exciting because it bridges the gap between cutting-edge research and practical implementation, ensuring AI solutions deliver value in real-world settings.
Unlike data scientists, who focus on model development and deployment of traditional Machine Learning models, AI engineers integrate these models as well as more complex Deep Learning and Generative AI models into scalable, reliable, and efficient systems.
For example, while a data scientist might develop an algorithm to detect tumors in X-rays, an AI engineer ensures the model operates in real-time within hospital systems under diverse conditions. This unique blend of skills makes AI engineers indispensable in translating theoretical models into impactful solutions.
Key areas of focus for AI engineers include:
-
System Design: Building infrastructure for data processing and model deployment.
-
Optimization: Ensuring performance, scalability, and reliability.
-
Advanced Models: Working with deep learning, generative AI, and neural networks.
-
Integration: Bridging the gap between AI models and enterprise-level systems.
Must-Have Skills to Start a Career in AI
To succeed as an AI engineer, you must master a diverse set of skills, each contributing to your ability to innovate and implement cutting-edge solutions. Below, we’ll delve into the essential skill sets that form the foundation for a career in AI engineering.
Later on in this guide, I’ll list and link to a bunch of helpful resources that can help you learn and polish these key skills.
Mathematics: The Backbone of AI
Mathematics is the fuel that powers all AI models, from traditional machine learning to cutting-edge generative AI. Without a strong mathematical foundation, understanding and building AI systems is nearly impossible.
-
Linear Algebra: Grasp vectors, matrices, eigenvalues, and transformations. These concepts underpin neural networks and deep learning architectures.
-
Calculus: Learn about gradients, derivatives, and integrals to understand optimization techniques used in training models.
-
Game Theory: Understand concepts like Nash equilibrium and the min-max strategy, which are fundamental for algorithms like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs).
Statistics: Making Sense of Data
Statistics is a cornerstone for any AI engineer, providing the tools to analyze data and extract meaningful insights. A strong foundation in statistics is critical for understanding machine learning models and making data-driven decisions.
-
Probability: Master fundamental concepts such as random variables, probability distributions, and independence. Learn how to calculate conditional probabilities and apply Bayes’ theorem.
-
Descriptive Statistics: Understand measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and dispersion (variance, standard deviation) to summarize data effectively.
-
Inferential Statistics: Gain expertise in hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and significance levels to draw conclusions from data samples.
-
Probability Distributions: Familiarize yourself with common distributions such as normal, binomial, and Poisson distributions, and their applications in AI modeling.
-
Regression Analysis: Study linear and logistic regression to understand relationships between variables and make predictions.
-
Dimensionality Reduction: Learn techniques like Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to reduce data complexity while retaining essential information.
-
Statistical Tests: Understand t-tests, ANOVA, chi-square tests, and non-parametric methods for analyzing data and validating hypotheses.
Programming: The Craft of AI Implementation
Programming is the cornerstone of AI engineering. A deep understanding of coding ensures that theoretical knowledge can be applied to solve real-world problems.
-
Python: The go-to language for AI development. Familiarize yourself with libraries like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and NumPy.
-
Data Structures and Algorithms: Essential for efficient problem-solving and implementing optimized AI solutions.
-
Version Control Systems: Use tools like Git for managing code, collaborating, and maintaining robust development workflows.
Machine Learning: The Foundation of AI
Machine learning (ML) equips engineers with the tools to create intelligent systems capable of learning from data. To excel in ML, you must understand the underlying mathematics and statistics that power these models. This includes grasping how algorithms work, how to train machine learning models, and how to evaluate their performance using appropriate metrics.
Mastery of ML involves not just theoretical knowledge but also practical implementation in programming languages like Python, using libraries such as scikit-learn or TensorFlow.
Each field of ML has its applications: supervised learning is key in fraud detection and predictive analytics, while unsupervised learning is vital in clustering for customer segmentation and anomaly detection. Boosting algorithms are widely used in areas such as recommendation systems and ranking tasks, making it crucial to understand their nuances and optimization techniques.
-
Supervised Learning: Focus on labeled data tasks, like regression and classification, and learn models such as linear regression, logistic regression, and support vector machines (SVMs).
-
Unsupervised Learning: Master clustering techniques such as k-means and hierarchical clustering, and dimensionality reduction methods like PCA.
-
Reinforcement Learning: Explore reward-based learning frameworks, widely used in robotics, gaming, and resource optimization.
-
Boosting and Ensemble Methods: Study algorithms like XGBoost, LightGBM, and Random Forest to improve model accuracy and robustness.
-
Evaluation Metrics: Understand precision, recall, F1-score, and area under the ROC curve to evaluate model performance effectively.
-
Feature Selection: Learn methods like mutual information and recursive feature elimination to optimize model input.
Deep Learning: Solving Complex Problems
Deep learning is essential for handling complex tasks like image recognition, language processing, and autonomous driving.
To truly master deep learning, you must have a strong grasp of the mathematics and statistics underpinning neural networks. This includes understanding the architecture and operations of different types of neural networks, such as feedforward networks, convolutional neural networks (CNNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), gated recurrent units (GRUs), and long short-term memory networks (LSTMs).
Each of these networks has specific benefits and disadvantages, making it crucial to know when to use which type based on the problem at hand.
You’ll also need to learn how to train these networks effectively, manage issues like overfitting and vanishing gradients, and evaluate their performance using appropriate metrics. Practical skills in frameworks like PyTorch or TensorFlow are essential for implementing these networks and applying them to real-world tasks.
-
Feedforward Neural Networks (FNNs): Study their structure and applications in simple pattern recognition and regression tasks.
-
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Learn about convolutional layers, pooling, and their applications in image and video processing.
-
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Understand sequence modeling and their use in time-series predictions and natural language processing.
-
Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) and LSTMs: Delve into their architecture to handle long-term dependencies in sequential data.
-
Optimization Techniques: Master Adam optimizer, RMSprop, and learning rate scheduling to improve model convergence.
-
Regularization Methods: Study dropout, batch normalization, and L2 regularization to mitigate overfitting.
-
Hyperparameter Tuning: Learn techniques like grid search and Bayesian optimization to fine-tune model performance.
-
Evaluation Metrics for Deep Learning: Understand metrics such as cross-entropy loss and accuracy for classification tasks, and mean squared error for regression.
Data Science: Preparing and Analyzing Data
Data science skills are vital for cleaning, analyzing, and visualizing data—the fuel of AI systems.
-
Data Cleaning: Learn how to clean dirty data and make it ready for ingesting into Machine Learning or AI model.
-
Data Preprocessing: Learn techniques for handling missing data, normalization, and data augmentation.
-
Feature Engineering: Master creating meaningful features from raw data to improve model performance.
-
Visualization: Use Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib for exploratory data analysis and storytelling.
Generative AI: Creative AI Revolution
Generative AI represents one of the most transformative areas in modern AI, enabling systems to produce content such as text, images, and music.
-
Foundational Models: Study foundational models like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs). Learn how these models are designed and trained to generate new data.
-
Applications: Explore applications in creative industries, including content generation, art creation, and video synthesis. Tools like DALL-E, Runway, and Artbreeder demonstrate the potential of generative AI.
-
Challenges and Ethical Considerations: Understand challenges such as mode collapse in GANs, data bias, and ethical concerns in AI-generated content.
-
Techniques for Improvement: Dive into advanced topics like attention mechanisms in generative models and integrating reinforcement learning to improve output quality.
Large Language Models (LLMs): Transforming Communication
LLMs have revolutionized how machines understand and generate human language. These models are critical for tasks in natural language processing (NLP) and beyond.
-
Key Architectures: Study transformer-based architectures, including GPT, BERT, and Llama. Understand how they leverage self-attention mechanisms to process language.
-
Fine-Tuning: Learn how to fine-tune pre-trained LLMs for specific tasks like sentiment analysis, summarization, and conversational AI.
-
Applications: Explore diverse applications, such as chatbots, code generation, and real-time translation. Familiarize yourself with platforms like OpenAI GPT, Hugging Face, and Google’s BERT.
-
Training and Scaling: Understand the computational demands of training LLMs and the techniques to scale these models efficiently.
-
Evaluation Metrics: Learn how to evaluate LLMs using metrics such as BLEU, ROUGE, and perplexity, ensuring robust performance in various tasks.
Prompt Engineering
Prompt engineering is a critical skill for effectively leveraging large language models (LLMs). It involves crafting precise and creative prompts to guide LLMs like GPT in producing accurate and relevant outputs.
-
Understanding Prompt Templates: Learn how to create structured templates to elicit specific responses from models.
-
Iterative Optimization: Refine prompts through iterative testing and feedback to achieve the desired level of output quality.
-
Practical Applications: Apply prompt engineering in areas like conversational AI, automated content generation, and customer support.
Optimization and Production of Large-Language Models (LLMs)
Large-language models have become pivotal in modern AI, and optimizing them for efficiency and deploying them in production are essential skills.
-
Optimization Techniques: Master quantization, pruning, and knowledge distillation to reduce model size and improve performance without sacrificing accuracy.
-
Productionization Tools: Familiarize yourself with frameworks like Hugging Face, LangChain, and Flask to deploy models in scalable environments.
-
Real-World Applications: Understand how to fine-tune and deploy LLMs for real-world use cases, such as chatbots, document summarization, and sentiment analysis.
-
Monitoring and Maintenance: Learn how to monitor deployed models, collect feedback, and implement updates to maintain relevance and accuracy.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG is an advanced technique that combines the power of LLMs with external knowledge sources to improve accuracy and relevance.
-
Core Principles: Understand how RAG integrates retrieval systems and generative models to fetch and incorporate relevant data into outputs.
-
Applications: Explore use cases like document summarization, question answering, and knowledge base enhancements.
-
Tools and Frameworks: Work with open-source tools such as Hugging Face RAG, Pinecone, and LangChain to build and deploy RAG systems.
-
Optimization: Learn strategies for improving retrieval accuracy and model integration for seamless performance.
Deployment and Optimization: Bringing AI to Life
An AI system’s value lies in its real-world application, which requires efficient deployment and optimization.
-
Deployment Tools: Master platforms like Flask, Docker, and Kubernetes for scalable deployments.
-
Model Optimization: Explore techniques such as quantization, pruning, and knowledge distillation to make models efficient.
-
Monitoring: Set up systems to evaluate and improve models continuously in production environments.
Ethics and Governance in AI
As an AI engineer, you bear the responsibility of building ethical and fair AI systems.
-
Bias and Fairness: Understand and mitigate biases in data and algorithms.
-
Data Privacy: Implement GDPR-compliant data handling practices.
-
AI Regulations: Stay updated on global laws and best practices to ensure responsible AI development.
By learning these skills, you will position yourself as a world-class AI engineer ready to tackle the challenges of the future. These competencies not only provide the technical know-how but also equip you with the ability to innovate and lead in this transformative field.
Career Tips for Aspiring AI Engineers
Building a successful career in AI engineering requires strategic effort, consistent learning, and proactive networking. Here are detailed tips to guide you on your journey:
1. Build a Portfolio
A strong portfolio is your ticket to showcasing your technical skills and creativity to potential employers and collaborators. A well-curated portfolio not only demonstrates your abilities but also provides tangible proof of your expertise.
Many things go into creating an attention-grabbing portfolio. First, you’ll want to include projects that demonstrate a range of skills—machine learning models, neural network implementations, data preprocessing pipelines, and generative AI experiments.
Second, make sure you host your projects on GitHub to make your work accessible to recruiters and collaborators. Use detailed README files to explain the project goals, methodology, and results.
It’s also helpful to engage in open-source projects to show your ability to collaborate and contribute to the community. Highlight projects on your portfolio that solve real-world problems, such as sentiment analysis for social media, automated text generation tools, or predictive models for industries like healthcare or finance.
Finally, you should develop a website that serves as a central hub for your portfolio, resume, and contact information. Use platforms like GitHub Pages or WordPress to create a professional presence.
2. Network Strategically
Networking is vital for gaining insights, finding mentors, and exploring job opportunities. Building relationships within the AI community can open doors to collaborations and mentorship.
To do this, there are a number of things you can do and activities you can engage in. For example, you can attend conferences and meetups. Participate in industry events like NeurIPS, ICML, CVPR, and AI Summit to meet professionals and learn about cutting-edge advancements.
You can also join online communities and engage in forums like Reddit r/MachineLearning, AI Stack Exchange, and Kaggle for discussions and advice.
Make sure you use LinkedIn effectively as it contains a wealth of resources and potential contacts. Regularly update your profile, share your work, and connect with professionals in the AI field. Join LinkedIn groups focused on AI engineering.
You can also collaborate with other budding or more experienced AI engineers at events like hackathons. Search out AI and machine learning hackathons where you can work on innovative problems, build projects quickly, and meet like-minded individuals.
And don’t forget to seek out mentorship opportunities. You can reach out to industry leaders or academics for mentorship. A mentor can guide your learning path and career decisions.
3. Stay Resilient
The AI field evolves at a breakneck pace, and staying relevant requires dedication and adaptability. Resilience is key to navigating challenges and leveraging them as growth opportunities.
To really succeed in this field, you’ll need to commit to a lifetime of learning. Make sure you regularly update your skill set by taking advanced courses in trending topics like generative AI, autonomous systems, or explainable AI.
And it won’t always be easy, so you’ll need to learn to embrace failure. Projects may not always work as expected, but each failure is a learning opportunity. Document your challenges and solutions to demonstrate your problem-solving process.
Also, try to stay curious. Read the latest AI research papers, follow industry blogs, and explore how AI is being applied across various domains.
You’ll also want to invest in popular and well-established tools. Try to familiarize yourself with the latest tools and platforms, such as Hugging Face, LangChain, and cloud computing services like AWS and Google Cloud.
4. Specialize to Stand Out
Specialization allows you to focus your skills on a specific niche, making you a go-to expert in that area. Employers value individuals who can bring deep expertise to solve complex problems.
There are various areas within AI engineering that you can explore, and one of them might be a better fit for you than the others. You can consider Generative AI and learn about GANs, VAEs, and tools like DALL-E or Runway to specialize in creative AI applications.
There’s also Autonomous Systems, where you’ll explore areas like robotics, computer vision for navigation, and sensor integration to work on self-driving cars or drones.
AI Ethics and Governance is another important area of specialization. You can dive into topics like bias detection, fairness algorithms, and compliance with global AI regulations to lead ethical AI initiatives. Here’s a full course on the topic on freeCodeCamp’s YouTube channel if you want to learn more.
You can also dig into AI applications for specific industries based on some of what you read above. Consider specializing in healthcare AI, financial modeling, or supply chain optimization, depending on your interests and the market demand.
5. Stay Updated with Industry Trends
AI is one of the fastest-evolving fields, and staying informed is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
You’ll want to stay up on current research, especially in your area(s) of interest. Regularly check platforms like arXiv for the latest AI research papers. You can also subscribe to AI newsletters like DeepLearning.AI, The Batch, and Import AI to receive updates on the latest trends.
Make sure you keep track of what industry leaders are doing in the space. Learn about innovations from organizations like OpenAI, DeepMind, Google AI, and Meta AI.
And finally, engage with blogs and podcasts that focus on AI engineering. Start following influential blogs like Towards Data Science and listen to podcasts like the Lex Fridman Podcast to gain insights into the AI ecosystem.
6. Gain Hands-On Experience
Employers value practical experience, and the best way to build it is by working on real-world applications.
There are a number of practical and more approachable ways to do this, whether you’re new to the field or just want to gain more or different experience.
One way to gain experience is by freelancing. You can offer your skills on platforms like Upwork or Toptal to gain experience in solving diverse AI challenges.
Internships are another popular option. Try to pursue internships at leading AI companies to learn industry practices and build a professional network.
You can also participate in challenges on Kaggle or DrivenData to test your skills against global talent. These are all things you can put on your résumé when you’re job hunting, and will be especially valuable if you’re newer to the field and don’t have a ton of (or any) work experience yet.
7. Develop Communication and Presentation Skills
AI engineers often collaborate with cross-functional teams and need to explain technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders.
You’ll need to know how to tell stories with data, for example. So learn to create compelling visualizations and narratives around your findings.
Public speaking will also likely be important for you as an AI engineer. Make sure you practice presenting your projects at meetups, conferences, or internal team meetings whenever you get the chance.
You’ll also need to learn various collaboration tools like Jupyter Notebooks, Google Colab, and project management platforms.
By following these detailed career tips, you can navigate the competitive world of AI engineering with confidence and build a rewarding career in one of the most transformative fields of our time.
The Future of AI Engineering
The field of artificial intelligence is witnessing an unprecedented surge, marking it as one of the most transformative industries of the 21st century. With applications spanning healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and entertainment, AI is reshaping how societies operate and thrive. This growth is underscored by an ever-increasing demand for skilled AI engineers, who play a pivotal role in developing innovative solutions and driving this global transformation.
The global artificial intelligence market is expected to exceed $1.8 trillion by 2030, growing at an impressive compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 37.3% from 2023 to 2030. As of 2022, the AI market was valued at $328 billion, a testament to its rapid adoption across industries.
Investments in AI are accelerating worldwide, with private and public sectors recognizing its transformative potential. From improving efficiencies in business operations to enabling groundbreaking discoveries in healthcare, AI is driving growth across domains.
Advancements in AI Technologies
AI technologies continue to evolve at a breakneck pace, opening up new possibilities for innovation:
-
Generative AI is transforming creative industries, with tools like DALL-E, Runway, and ChatGPT redefining how we produce content, art, and designs.
-
Large Language Models (LLMs), such as GPT, BERT, and LLaMA, have revolutionized natural language processing, enhancing tasks like sentiment analysis, translation, and conversational AI.
-
Autonomous Systems powered by AI are enabling self-driving cars, drones, and robotics, improving industries like logistics, agriculture, and healthcare.
-
Healthcare AI systems are projected to drive a market worth $187 billion by 2030, offering innovative solutions in diagnostics, drug discovery, and personalized medicine.
Regional Initiatives Driving AI Growth
Countries and regions across the globe are vying for leadership in AI, each contributing unique advancements and initiatives to the global AI landscape.
1. United States
As a global leader in AI, the United States continues to spearhead innovation through initiatives like the National AI Initiative Act, which has allocated over $2 billion to AI research and workforce development.
Industry giants such as OpenAI, Google, and Meta are investing heavily in generative AI, large language models, and reinforcement learning. In 2022 alone, the U.S. accounted for a significant portion of the $52.1 billion invested globally in AI startups.
2. European Union
The EU is shaping itself as a global hub for ethical AI innovation, with significant investments aimed at bolstering AI infrastructure and research.
The Digital Europe Programme has pledged €9.2 billion toward AI education and technological advancements, while the Horizon Europe Program allocates over €1 billion annually to AI projects.
The establishment of AI research centers such as the European Laboratory for Learning and Intelligent Systems (ELLIS) and NAVER LABS Europe underscores Europe’s commitment to advancing machine learning and AI technologies.
3. Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
The GCC, led by Saudi Arabia and the UAE, is rapidly becoming a powerhouse in AI innovation. Saudi Arabia has announced investments of over $40 billion through the National Strategy for Data and AI (NSDAI) and aims to train 25,000 AI and data science professionals by 2030. Initiatives like the NEOM Project and the establishment of the Saudi Data and AI Authority (SDAIA) highlight the Kingdom’s commitment to leveraging AI for economic diversification. Meanwhile, the UAE’s National AI Strategy 2031 emphasizes AI-driven government services and industrial transformation.
4. China
China is a powerful force in AI, with its market projected to reach $200 billion by 2030. The government’s Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan commits over $15 billion by 2025, focusing on smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and AI-enabled healthcare.
Companies like Baidu, Tencent, and Alibaba are leading the charge in advancing AI technologies for both domestic and global markets.
5. Russia
Russia is leveraging its National Strategy for the Development of Artificial Intelligence, committing $12.5 billion through 2030 to develop AI technologies across sectors such as defense, agriculture, and healthcare. These efforts underscore Russia’s ambition to be a key player in the global AI landscape.
Role of AI Engineers in Shaping the Future
AI engineers are the architects of tomorrow, transforming research into actionable solutions that drive industry and societal advancements. Their contributions include:
-
Innovating Across Industries: AI engineers develop tools and systems that revolutionize sectors from autonomous vehicles and smart cities to personalized healthcare and financial analytics.
-
Addressing Global Challenges: They are instrumental in tackling pressing issues such as climate change, resource optimization, and global health crises.
-
Ethical AI Leadership: Engineers ensure that AI systems are fair, unbiased, and compliant with global standards, contributing to the creation of trustworthy AI.
Opportunities for AI Engineers
The demand for AI engineers is growing exponentially across the globe. And opportunities are not just limited to established tech hubs like the U.S. and EU but are also expanding rapidly in regions like the GCC, China, and Russia.
The global AI market is on an impressive growth trajectory, fueled by significant investments, technological advancements, and regional initiatives.
As AI applications diversify, AI engineers are increasingly required in industries such as creative arts, autonomous systems, and financial technology.
AI Engineers are the architects of future technologies. And they’re at the forefront of reshaping industries, solving global challenges, and building a smarter, more connected world. Now is the time to acquire the skills, seize the opportunities, and become a driving force in the AI revolution.
Recommended Resources for Becoming AI Engineer
Becoming a world-class AI engineer requires access to top-notch learning materials and platforms. Below are recommended resources tailored to each skill area:
Resources for Mathematics
-
Fundamentals of Linear Algebra by LunarTech: Comprehensive course covering vectors, matrices, and their applications in AI (Paid Course)
-
Linear Algebra Crash Course by LunarTech (Free Course)
-
Calculus 1 and Calculus 2 by freeCodeCamp (Free Courses)
-
Math Course by Khan Academy: Beginner-friendly lessons on calculus and algebra (Free Course)
-
OpenCourseWare Mathematics by MIT: Advanced lectures on mathematics for in-depth theoretical understanding.(Free Course)
Resources for Statistics
-
Statistics for AI Professionals by LunarTech: Covers probability, hypothesis testing, and regression analysis, with real-world AI applications and all fundamental Stats topics in one place. (Paid Course)
-
Ultimate Data Science Bootcamp by LunarTech: Offers bigginner to advanced Statistics as well Python, Machine Learning and other topics to help you become Data Scientist. (Paid Bootcamp)
-
Learn Statistics for Data Science and AI Engineering by Tatev Aslanyan: Covers key statistical concepts you’ll need to get into the AI field. (Free Handbook)
-
Data Science Specialization by Coursera: Offers foundational and statistics courses. (Paid Course)
-
The Elements of Statistical Learning: A deeper dive into statistics tailored for AI engineers. (Book)
Resources for Programming
-
Python for Data Science by LunarTech: Focused course on Python for Data Science and AI. (Paid Course)
-
Python for Data Science and Analytics Crash Course by LunarTech (Free Course)
-
Automate the Boring Stuff with Python: Beginner-friendly book for foundational Python skills. (Book)
-
How to Use Git and GitHub: Teaches you everything you need to know to confidently use version control (Free Book)
-
GitHub Guides: Practical version control tutorials.
Resources for Machine Learning
-
Fundamentals of Machine Learning by LunarTech: Detailed course covering all essential Traditional ML topics in one place. (Paid Course)
-
Machine Learning Crash Course by LunarTech: Crash Course teaching basics in ML for beginners. (Free Course)
-
Machine Learning for AI by Tatev and Vahe Aslanyan: Teaches you ML basics, key algorithms to know, and examines various case studies.
-
Andrew Ng’s Machine Learning Course by Coursera: Popular beginner course with foundational ML algorithms. (Paid Course)
-
Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow: Practical applications of ML algorithms. (Book)
Resources for Deep Learning
-
Deep Learning Foundations by LunarTech: Comprehensive training on neural networks, CNNs, RNNs, and optimization techniques. (Paid Course)
-
Deep Learning Specialization by Coursera: Includes advanced concepts such as LSTMs and GRUs.(Paid Course)
-
Deep Learning Interview Preparation – Crash Course by LunarTech (Free Course)
-
Deep Learning Course – Math and Applications on freeCodeCamp: Learn the math behind Deep Learning along with practical applications. (Free Course)
-
Deep Learning with Python: Practical guide for using TensorFlow and Keras. (Book)
Resources for Generative AI
-
Generative AI Essentials Crash Course by LunarTech: Dive into GANs, VAEs, and their applications in creative industries. (Paid Course)
-
AI Engineering Bootcamp by LunarTech: Get complete bootcamp in Generative AI from theory to practice with certification. (Paid Bootcamp)
-
Learn Generative AI in 23 Hours by Andrew Brown: Teaches key GenAI concepts like prompt engineering, model deployment, optimization, RAG, and AI Agents. (Free Course)
-
Runway ML Tutorials: Explore AI-powered tools for art and video creation.
-
GANs in Action: Understand the theory and implementation of GANs in various applications. (Book)
Resources for Large Language Models (LLMs)
-
AI Engineering Bootcamp by LunarTech: Get complete bootcamp in Generative AI including everything about LLMs from PRe-Training, Transformers Architecture, Fine-Tuning, Quantization, and Optimization of LLMs and more (Paid Bootcamp)
-
Hugging Face Tutorials: Practical guides for using pre-trained LLMs (Open Source LLMs)
-
Multi-Modal Data Analysis with LLMs and Python on freeCodeCamp: Teaches how to use LLMs to analyze multiple types of data using a few lines of Python code. (Free Course)
-
Transformer Models for Natural Language Processing: Detailed insights into LLM architectures. (Book)
-
LunarTech Model Deployment Workshop Learn tools like Flask, Docker, and Kubernetes for deploying scalable AI systems.
-
LangChain Documentation: For advanced retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems.(LangChain Documentation)
-
Efficient Deep Learning for AI Engineers: Practical techniques for optimizing large models. (Book)
Responsible AI
-
AI Now Institute Reports: Updates on AI ethics and global regulations.
-
The Ethics of AI and ML on freeCodeCamp: Tackles important questions about how to use AI responsibly and ethically. (Free Course)
-
Responsible AI Practices (Google): Guidelines for building ethical AI systems.
These resources provide a clear path to mastering the skills necessary to become a proficient AI engineer, with LunarTech courses offering comprehensive and practical insights across all domains.
Practical AI Engineering: Code Examples and Implementation
AI engineering is the bridge between theoretical concepts and real-world applications. It’s not enough to understand algorithms or frameworks in isolation – the true power of AI lies in its implementation. By working with code examples, you can gain hands-on experience, transforming your abstract ideas into functional, scalable solutions.
The field of AI is vast, encompassing everything from machine learning and natural language processing to computer vision and generative models. Each domain presents unique challenges and opportunities, but the common thread is the need for practical expertise.
In today’s rapidly evolving tech landscape, staying relevant requires more than just theoretical knowledge. Employers value candidates who can demonstrate proficiency in building and deploying AI systems. These code examples not only enhance technical skills but also serve as a portfolio of practical accomplishments, showcasing your ability to solve real-world challenges with AI.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for Image Classification
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) represent a cornerstone of modern computer vision, powering applications from facial recognition to autonomous vehicles. These networks are specifically designed to process and analyze visual data by mimicking the way the human brain interprets images.
Unlike traditional machine learning models, CNNs leverage convolutional layers to automatically detect patterns such as edges, textures, and shapes, making them highly effective for tasks like image classification and object detection.
By understanding and implementing CNNs, you can unlock the potential of machines to “see” and interpret the world around them.
How CNNs work:
The power of CNNs lies in their ability to learn hierarchical features from data. Early layers of a CNN identify basic patterns like edges or corners, while deeper layers capture more complex structures such as objects or scenes.
This hierarchical learning makes CNNs particularly adept at handling large-scale datasets like CIFAR-10, which contains thousands of labeled images across multiple categories. For AI engineers, mastering CNNs is not just about building models but also optimizing their architecture for accuracy and efficiency in real-world applications.
Implementing a CNN for image classification involves several critical steps: preprocessing the dataset, defining the network architecture, training the model, and evaluating its performance.
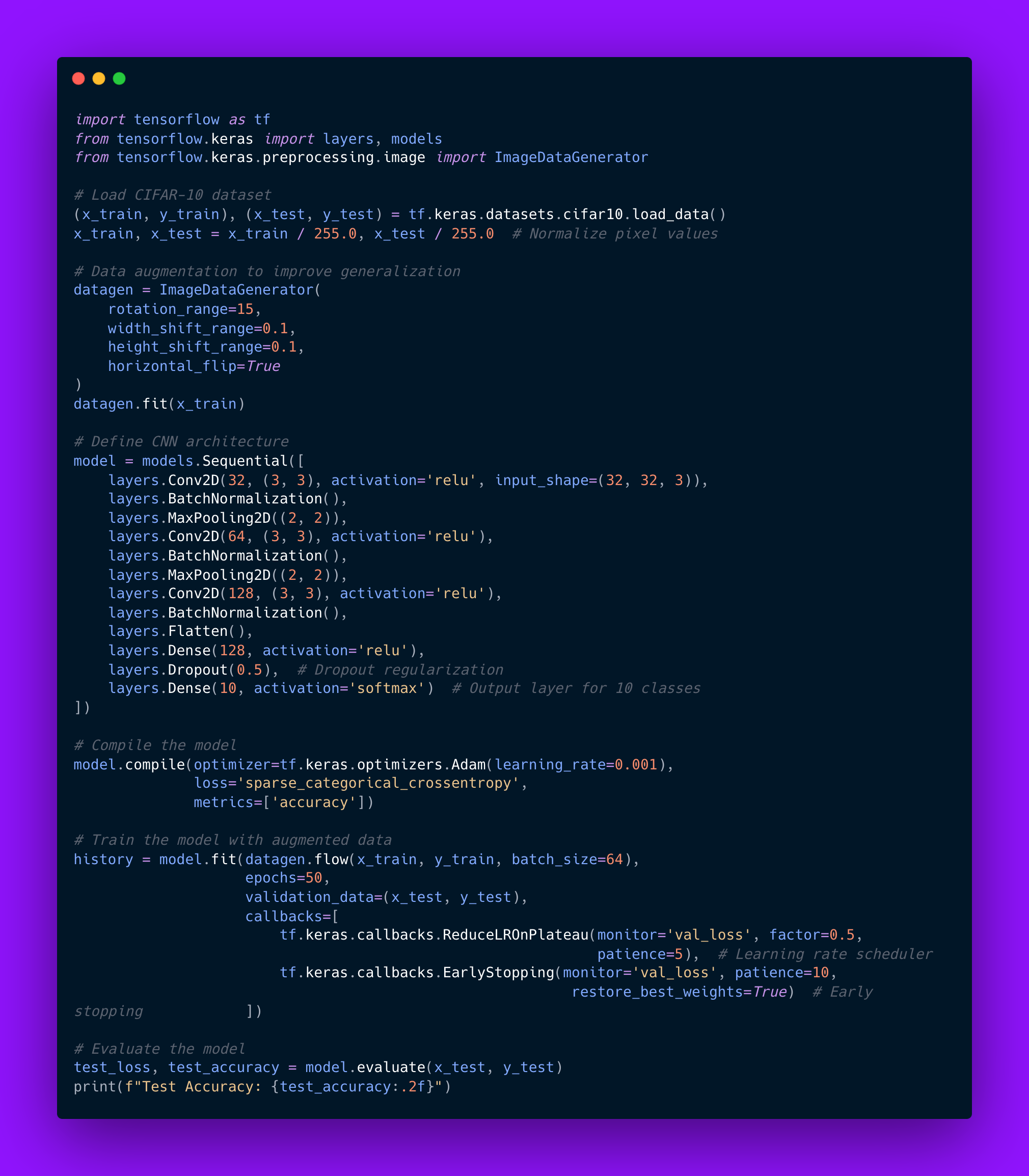
The following example demonstrates how to classify images from the CIFAR-10 dataset using TensorFlow. This example incorporates advanced techniques such as data augmentation, dropout regularization, and learning rate scheduling to enhance model performance and prevent overfitting.
Code example:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers, models
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
# Load CIFAR-10 dataset
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.cifar10.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0 # Normalize pixel values
# Data augmentation to improve generalization
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rotation_range=15,
width_shift_range=0.1,
height_shift_range=0.1,
horizontal_flip=True
)
datagen.fit(x_train)
# Define CNN architecture
model = models.Sequential([
layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(32, 32, 3)),
layers.BatchNormalization(),
layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'),
layers.BatchNormalization(),
layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu'),
layers.BatchNormalization(),
layers.Flatten(),
layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
layers.Dropout(0.5), # Dropout regularization
layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax') # Output layer for 10 classes
])
# Compile the model
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Train the model with augmented data
history = model.fit(datagen.flow(x_train, y_train, batch_size=64),
epochs=50,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test),
callbacks=[
tf.keras.callbacks.ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_loss', factor=0.5,
patience=5), # Learning rate scheduler
tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', patience=10,
restore_best_weights=True) # Early stopping
])
# Evaluate the model
test_loss, test_accuracy = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
print(f"Test Accuracy: {test_accuracy:.2f}")
This implementation highlights key practices in AI engineering: leveraging data augmentation to improve generalization, using dropout and batch normalization to prevent overfitting, and employing callbacks like learning rate scheduling and early stopping to optimize training.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) for Time-Series Forecasting
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are a fundamental tool for sequential data analysis, making them indispensable in applications like time-series forecasting, natural language processing, and speech recognition.
Unlike traditional neural networks, RNNs are designed to handle sequential dependencies by maintaining a memory of previous inputs, enabling them to model temporal patterns effectively. For AI engineers, mastering RNNs unlocks the ability to tackle complex problems where data evolves over time.
The architecture of RNNs allows them to process sequences of arbitrary length by looping through the input data while updating their hidden states. But standard RNNs often face challenges like vanishing gradients when dealing with long-term dependencies. Advanced variants such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks and Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) address these limitations by incorporating mechanisms to selectively retain or forget information over time.
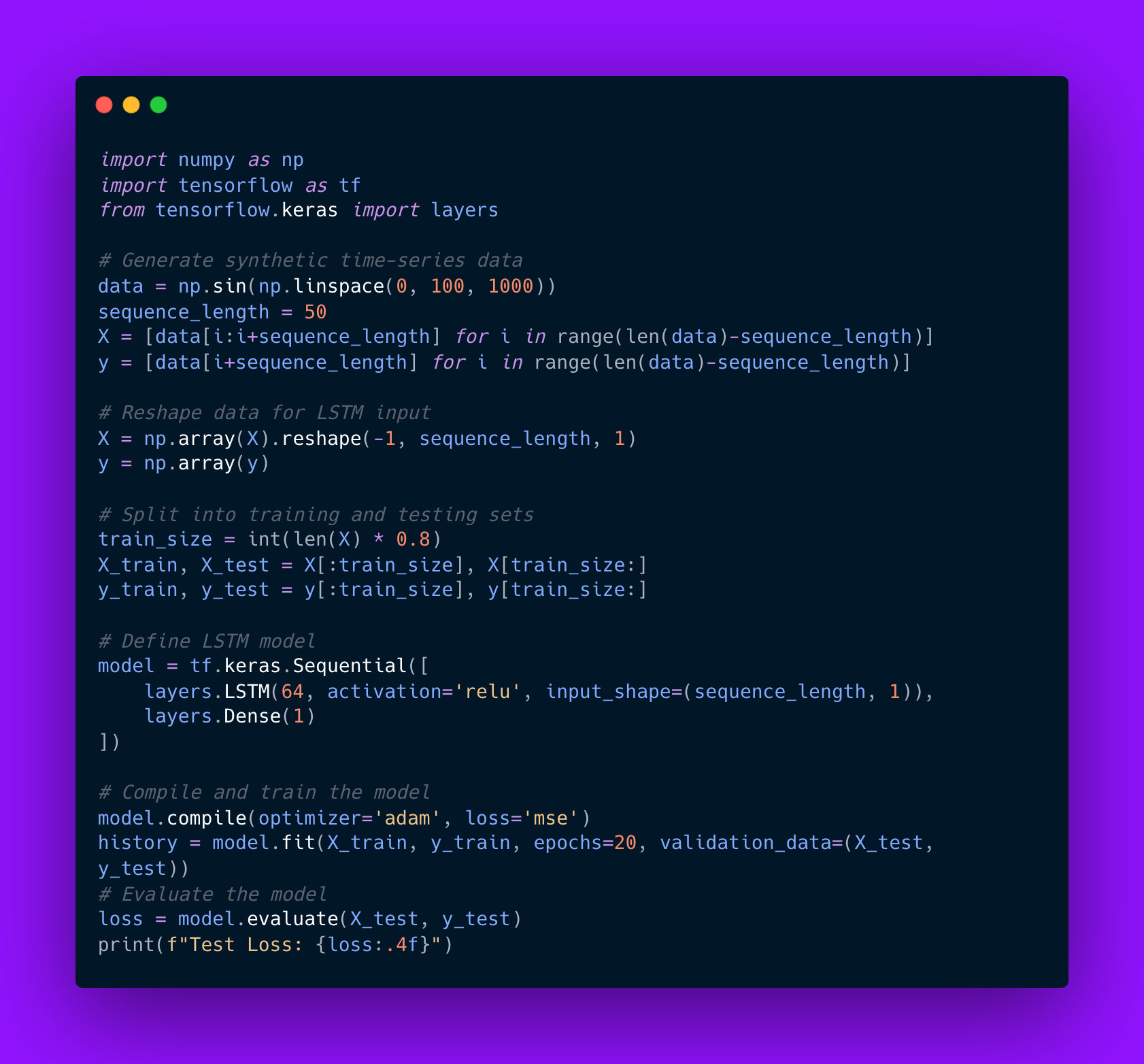
Implementing an RNN for time-series forecasting involves preprocessing the data, defining the network architecture, and training the model to predict future values based on historical patterns. The following example demonstrates how to use an LSTM network to forecast stock prices using TensorFlow.
Code example:
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
# Generate synthetic time-series data
data = np.sin(np.linspace(0, 100, 1000))
sequence_length = 50
X = [data[i:i+sequence_length] for i in range(len(data)-sequence_length)]
y = [data[i+sequence_length] for i in range(len(data)-sequence_length)]
# Reshape data for LSTM input
X = np.array(X).reshape(-1, sequence_length, 1)
y = np.array(y)
# Split into training and testing sets
train_size = int(len(X) * 0.8)
X_train, X_test = X[:train_size], X[train_size:]
y_train, y_test = y[:train_size], y[train_size:]
# Define LSTM model
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.LSTM(64, activation='relu', input_shape=(sequence_length, 1)),
layers.Dense(1)
])
# Compile and train the model
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mse')
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=20, validation_data=(X_test, y_test))
# Evaluate the model
loss = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test)
print(f"Test Loss: {loss:.4f}")
This implementation highlights the importance of preprocessing sequential data and using advanced architectures like LSTMs to capture long-term dependencies effectively. By mastering RNNs and their variants, AI engineers can build robust models for time-series forecasting and other sequential data tasks.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for Image Synthesis
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) represent a groundbreaking approach in AI for generating new data samples that resemble a given dataset.
Introduced by Ian Goodfellow in 2014, GANs consist of two neural networks—a generator and a discriminator—that compete against each other in a zero-sum game. The generator creates synthetic data samples, while the discriminator evaluates whether these samples are real or fake. This adversarial process drives both networks to improve iteratively.
GANs have revolutionized fields like image synthesis, video generation, and even drug discovery by creating high-quality outputs indistinguishable from real data. For AI engineers, understanding GANs is crucial for tackling creative AI challenges and advancing applications in industries ranging from entertainment to healthcare.
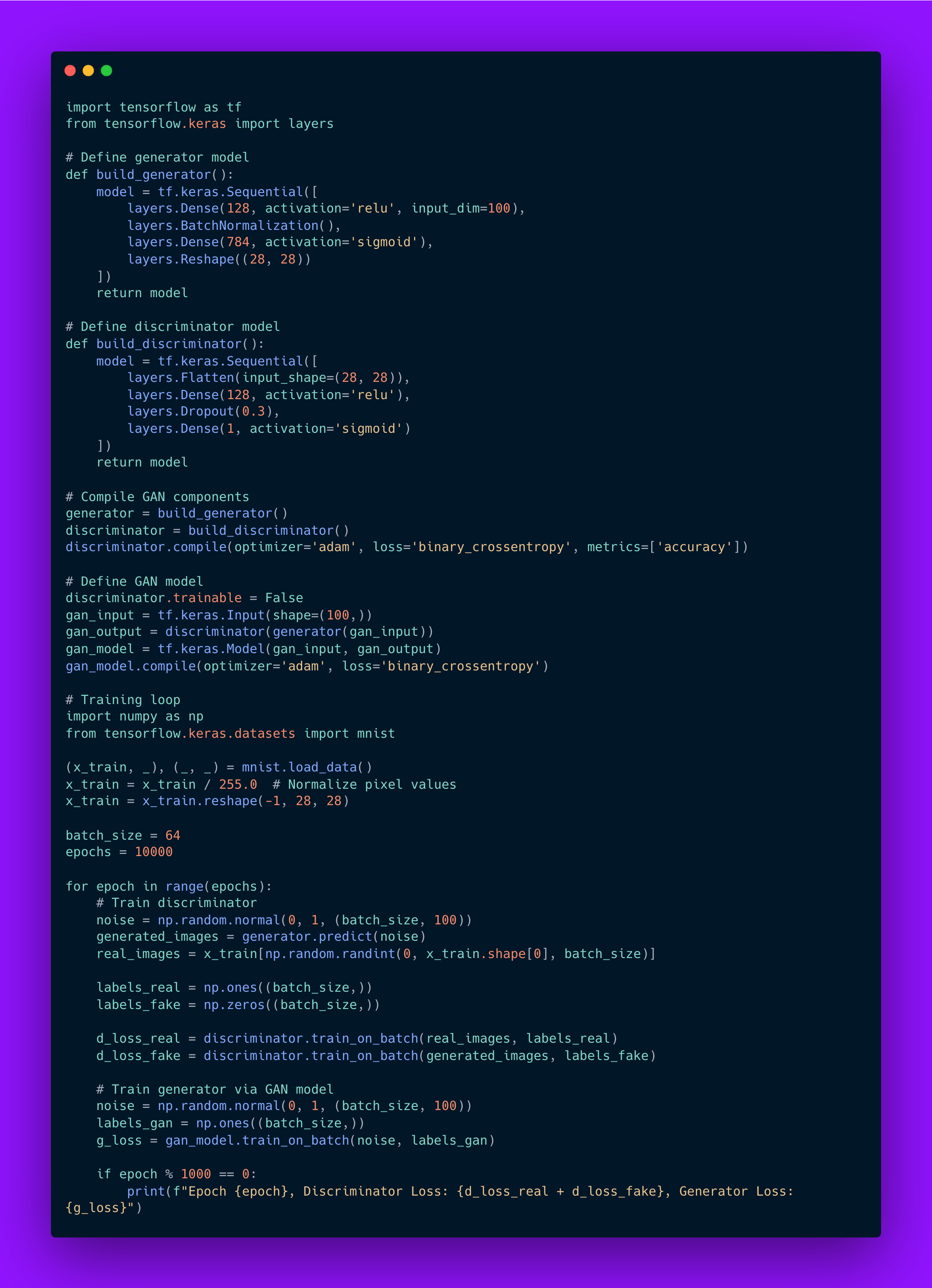
Implementing a GAN involves defining both the generator and discriminator networks, training them iteratively in an adversarial setup, and evaluating their performance. The following example demonstrates how to use a GAN to generate handwritten digits similar to those in the MNIST dataset.
Code example:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
# Define generator model
def build_generator():
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(128, activation='relu', input_dim=100),
layers.BatchNormalization(),
layers.Dense(784, activation='sigmoid'),
layers.Reshape((28, 28))
])
return model
# Define discriminator model
def build_discriminator():
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
layers.Dropout(0.3),
layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
])
return model
# Compile GAN components
generator = build_generator()
discriminator = build_discriminator()
discriminator.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# Define GAN model
discriminator.trainable = False
gan_input = tf.keras.Input(shape=(100,))
gan_output = discriminator(generator(gan_input))
gan_model = tf.keras.Model(gan_input, gan_output)
gan_model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy')
# Training loop
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
(x_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
x_train = x_train / 255.0 # Normalize pixel values
x_train = x_train.reshape(-1, 28, 28)
batch_size = 64
epochs = 10000
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Train discriminator
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, 100))
generated_images = generator.predict(noise)
real_images = x_train[np.random.randint(0, x_train.shape[0], batch_size)]
labels_real = np.ones((batch_size,))
labels_fake = np.zeros((batch_size,))
d_loss_real = discriminator.train_on_batch(real_images, labels_real)
d_loss_fake = discriminator.train_on_batch(generated_images, labels_fake)
# Train generator via GAN model
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, 100))
labels_gan = np.ones((batch_size,))
g_loss = gan_model.train_on_batch(noise, labels_gan)
if epoch % 1000 == 0:
print(f"Epoch {epoch}, Discriminator Loss: {d_loss_real + d_loss_fake}, Generator Loss: {g_loss}")
This implementation showcases how GANs can be used to generate realistic images through adversarial training. By mastering GAN architectures and training techniques, AI engineers can unlock new possibilities in creative AI applications across various domains.
Transformers for Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Transformers have revolutionized the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP), enabling machines to understand and generate human language with unprecedented accuracy.
Introduced in the seminal “Attention Is All You Need” paper by Vaswani et al., transformers leverage self-attention mechanisms to process entire sequences of text in parallel, making them more efficient and scalable than traditional RNNs or LSTMs. For AI engineers, mastering transformers is essential for building state-of-the-art NLP applications like chatbots, translation systems, and text summarizers.
The key innovation in transformers lies in their ability to capture contextual relationships between words, regardless of their position in a sentence. This makes them particularly effective for tasks that require understanding long-range dependencies, such as document summarization or question answering.
Pre-trained transformer models like BERT, GPT, and T5 have further democratized access to cutting-edge NLP capabilities, allowing engineers to fine-tune these models for specific tasks with minimal computational resources.
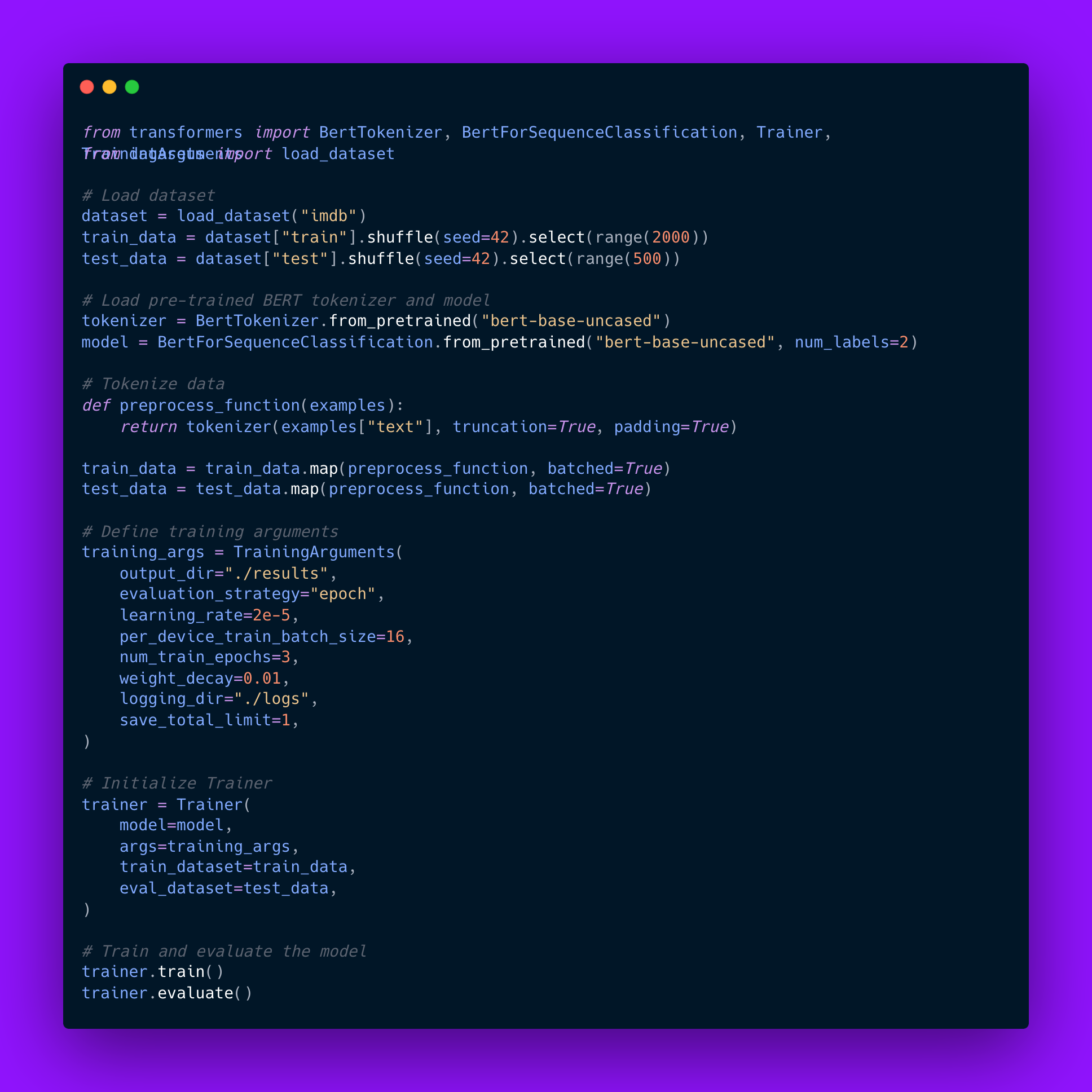
Implementing a transformer-based NLP application involves loading a pre-trained model, fine-tuning it on a domain-specific dataset, and deploying it for inference. The following example demonstrates how to use Hugging Face’s Transformers library to fine-tune a BERT model for sentiment analysis on a custom dataset.
Code example:
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertForSequenceClassification, Trainer, TrainingArguments
from datasets import load_dataset
# Load dataset
dataset = load_dataset("imdb")
train_data = dataset["train"].shuffle(seed=42).select(range(2000))
test_data = dataset["test"].shuffle(seed=42).select(range(500))
# Load pre-trained BERT tokenizer and model
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
model = BertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased", num_labels=2)
# Tokenize data
def preprocess_function(examples):
return tokenizer(examples["text"], truncation=True, padding=True)
train_data = train_data.map(preprocess_function, batched=True)
test_data = test_data.map(preprocess_function, batched=True)
# Define training arguments
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir="./results",
evaluation_strategy="epoch",
learning_rate=2e-5,
per_device_train_batch_size=16,
num_train_epochs=3,
weight_decay=0.01,
logging_dir="./logs",
save_total_limit=1,
)
# Initialize Trainer
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=train_data,
eval_dataset=test_data,
)
# Train and evaluate the model
trainer.train()
trainer.evaluate()
This implementation showcases how pre-trained transformer models can be fine-tuned efficiently for specific NLP tasks. By mastering transformers and libraries like Hugging Face, AI engineers can build powerful language models that drive innovations across industries.
Reinforcement Learning (RL) for Game AI
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a paradigm where agents learn optimal behaviors through trial and error by interacting with an environment.
RL has been instrumental in groundbreaking achievements like AlphaGo’s victory over human Go champions and OpenAI’s Dota 2 bots. For AI engineers, RL offers a framework to solve complex decision-making problems across domains like robotics, finance, and gaming.
The core idea of RL is to maximize cumulative rewards by learning policies that map states to actions. Advanced techniques like Deep Q-Networks (DQN) and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) combine RL with deep learning to handle high-dimensional state spaces effectively. These methods enable agents to learn strategies in environments with continuous action spaces or delayed rewards.
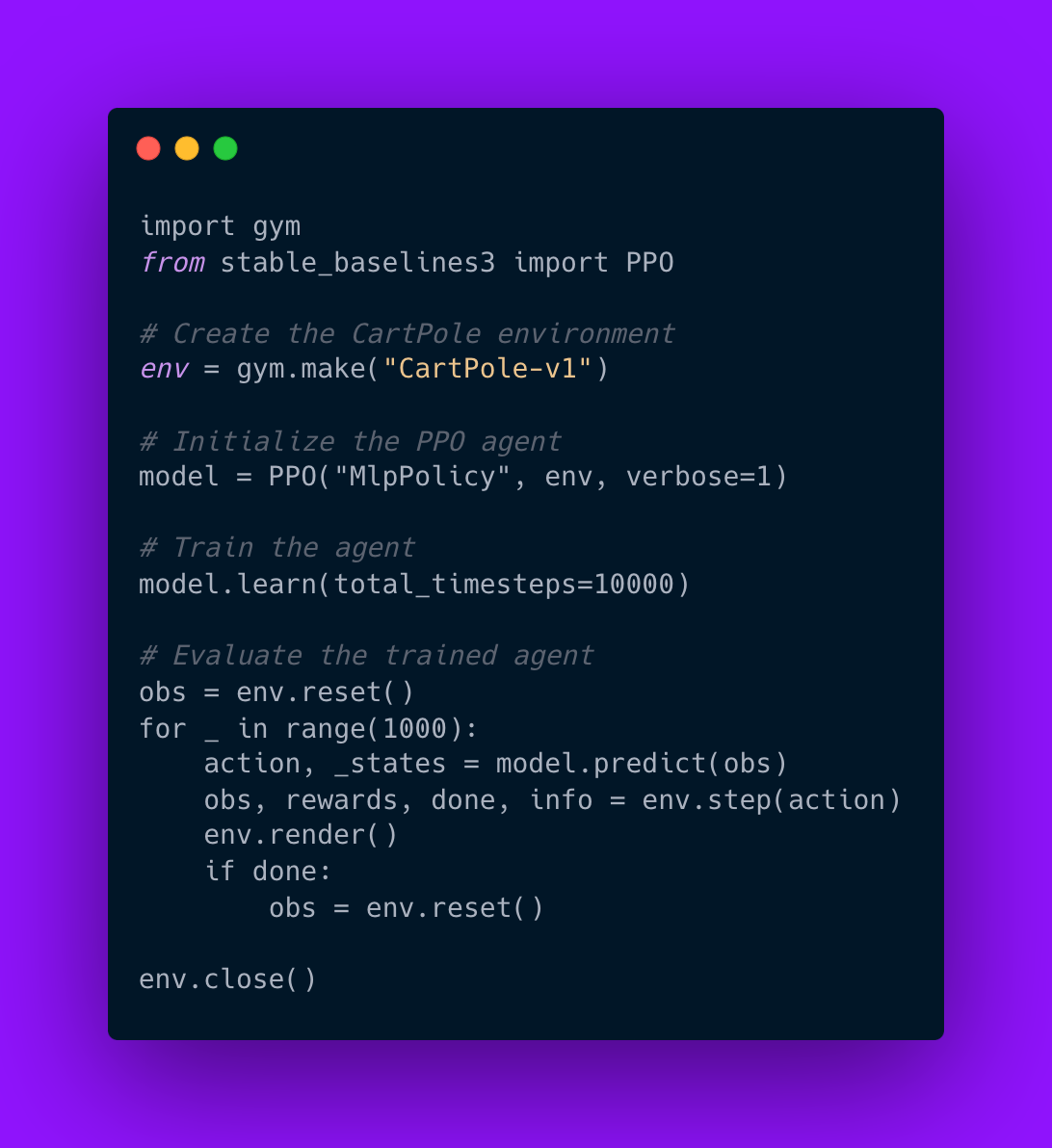
Implementing RL involves defining the environment, reward structure, and training algorithm. The following example demonstrates how to train an agent using PPO in OpenAI Gym’s CartPole environment with Stable-Baselines3.
Code example:
import gym
from stable_baselines3 import PPO
# Create the CartPole environment
env = gym.make("CartPole-v1")
# Initialize the PPO agent
model = PPO("MlpPolicy", env, verbose=1)
# Train the agent
model.learn(total_timesteps=10000)
# Evaluate the trained agent
obs = env.reset()
for _ in range(1000):
action, _states = model.predict(obs)
obs, rewards, done, info = env.step(action)
env.render()
if done:
obs = env.reset()
env.close()
This implementation highlights the simplicity of using modern RL frameworks like Stable-Baselines3 to train agents efficiently. By mastering RL techniques and tools, AI engineers can design intelligent systems capable of solving complex real-world challenges.
Explainable AI (XAI) with SHAP
Explainable AI (XAI) addresses one of the most critical challenges in modern AI: understanding how models make decisions.
As machine learning models grow more complex—especially deep learning architectures—they often become “black boxes,” making it difficult to interpret their predictions. XAI techniques like SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) provide insights into feature importance and decision-making processes, enabling transparency and trustworthiness in AI systems.
SHAP is based on cooperative game theory and assigns each feature an importance value for a particular prediction. This makes it particularly useful for industries like healthcare and finance, where understanding model decisions is crucial for compliance and ethical considerations. For AI engineers, mastering XAI techniques is essential for building models that are not only accurate but also interpretable.
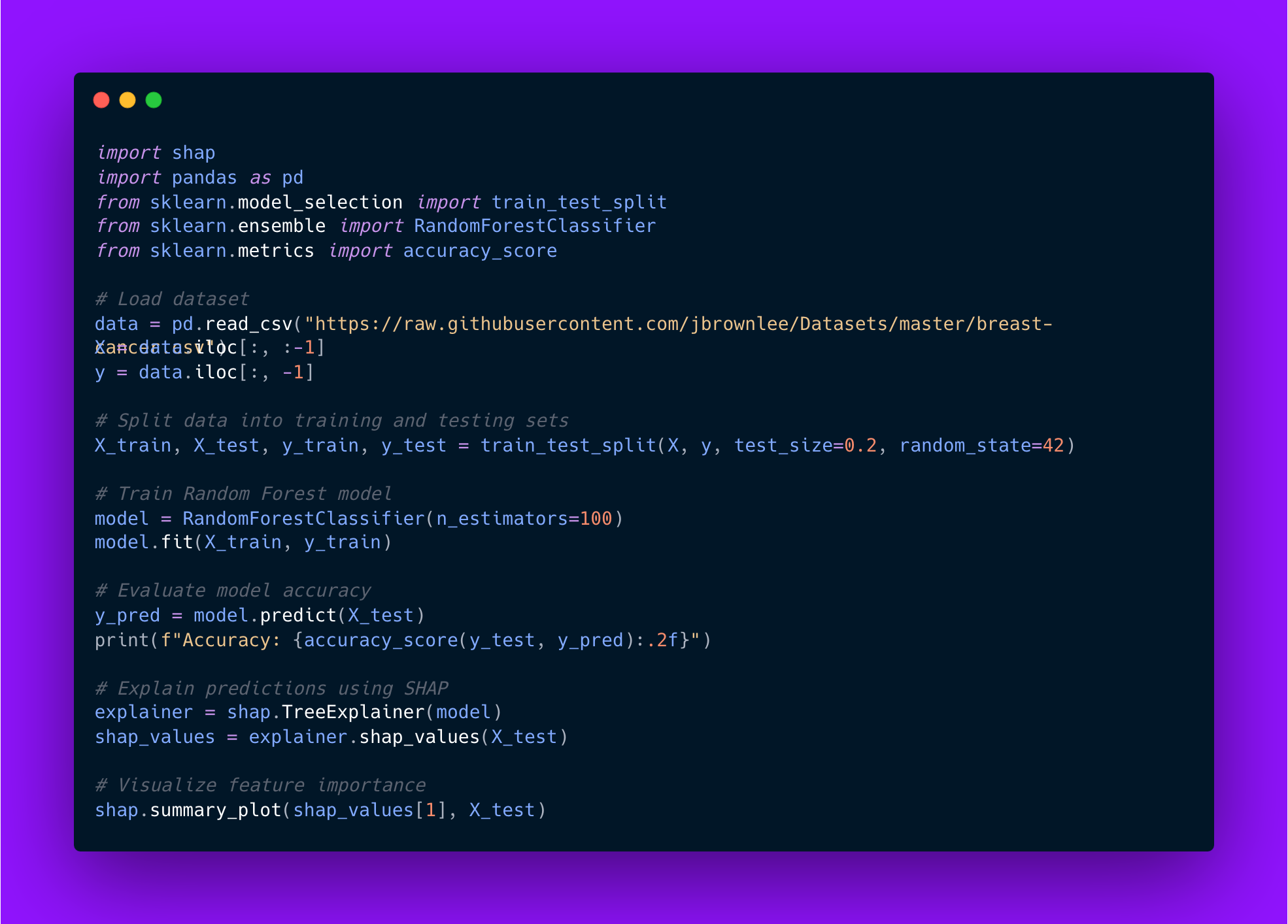
Implementing SHAP involves training a machine learning model and using SHAP’s library to explain its predictions visually. The following example demonstrates how to use SHAP with a Random Forest classifier on the UCI Breast Cancer dataset.
Code example:
import shap
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# Load dataset
data = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jbrownlee/Datasets/master/breast-cancer.csv")
X = data.iloc[:, :-1]
y = data.iloc[:, -1]
# Split data into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# Train Random Forest model
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Evaluate model accuracy
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred):.2f}")
# Explain predictions using SHAP
explainer = shap.TreeExplainer(model)
shap_values = explainer.shap_values(X_test)
# Visualize feature importance
shap.summary_plot(shap_values[1], X_test)
This implementation demonstrates how SHAP can make machine learning models interpretable by visualizing feature contributions to predictions. By incorporating XAI techniques into their workflows, AI engineers can build transparent systems that foster trust and accountability in AI applications.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) with Named Entity Recognition (NER)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has become a cornerstone of AI applications, enabling machines to understand and process human language.
Named Entity Recognition (NER), a key NLP task, focuses on identifying and classifying entities such as names, locations, dates, and organizations within text.
NER is widely used in applications like information retrieval, customer support automation, and document summarization. For AI engineers, mastering NER is critical for building systems that extract structured information from unstructured text.
NER models leverage advanced machine learning techniques, including transformers like BERT, to achieve state-of-the-art performance. These models use contextual embeddings to capture the relationships between words in a sentence, making them effective at identifying entities even in complex or ambiguous contexts.
By fine-tuning pre-trained models on domain-specific datasets, engineers can adapt NER systems to specialized tasks such as legal document analysis or medical record processing.
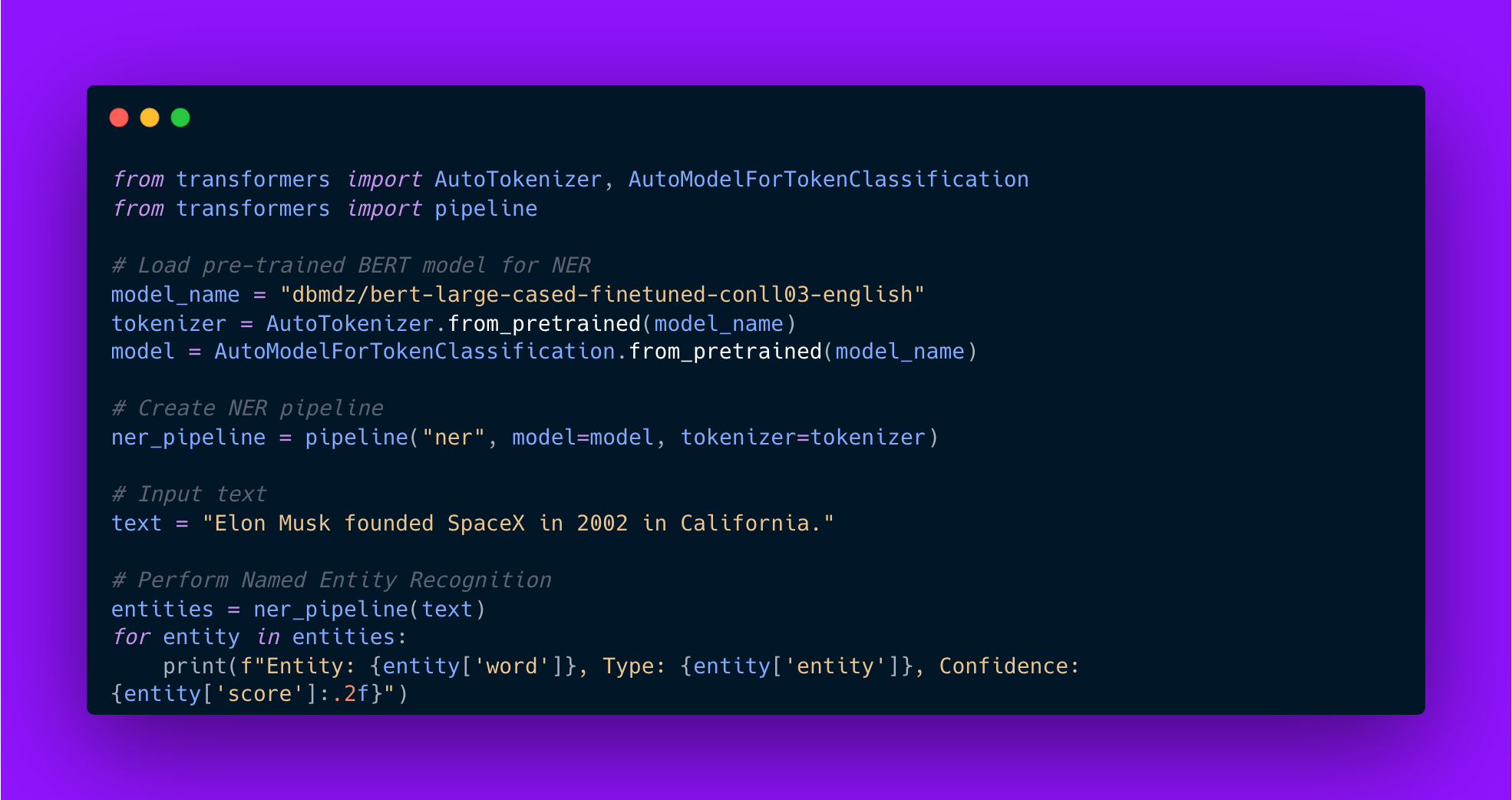
Implementing an NER system involves preprocessing text data, training or fine-tuning a model, and deploying it for inference. The following example demonstrates how to use Hugging Face’s Transformers library to build an NER system using a pre-trained BERT model.
Code example:
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForTokenClassification
from transformers import pipeline
# Load pre-trained BERT model for NER
model_name = "dbmdz/bert-large-cased-finetuned-conll03-english"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForTokenClassification.from_pretrained(model_name)
# Create NER pipeline
ner_pipeline = pipeline("ner", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
# Input text
text = "Elon Musk founded SpaceX in 2002 in California."
# Perform Named Entity Recognition
entities = ner_pipeline(text)
for entity in entities:
print(f"Entity: {entity['word']}, Type: {entity['entity']}, Confidence: {entity['score']:.2f}")
This implementation highlights how pre-trained transformer models can be used to quickly build robust NLP systems. By mastering NER and other NLP techniques, AI engineers can create applications that extract valuable insights from vast amounts of textual data.
Computer Vision with Object Detection Using YOLOv5
Object detection is one of the most impactful areas of computer vision, enabling machines to identify and locate objects within images or videos. Applications range from autonomous vehicles detecting pedestrians to surveillance systems identifying suspicious activities.
YOLO (You Only Look Once) is a state-of-the-art object detection algorithm known for its speed and accuracy, making it ideal for real-time applications.
YOLOv5 improves upon its predecessors by offering better performance and ease of use. It employs a single neural network to predict bounding boxes and class probabilities directly from images. This streamlined approach enables YOLOv5 to achieve high accuracy while maintaining low latency, making it suitable for edge devices and resource-constrained environments.
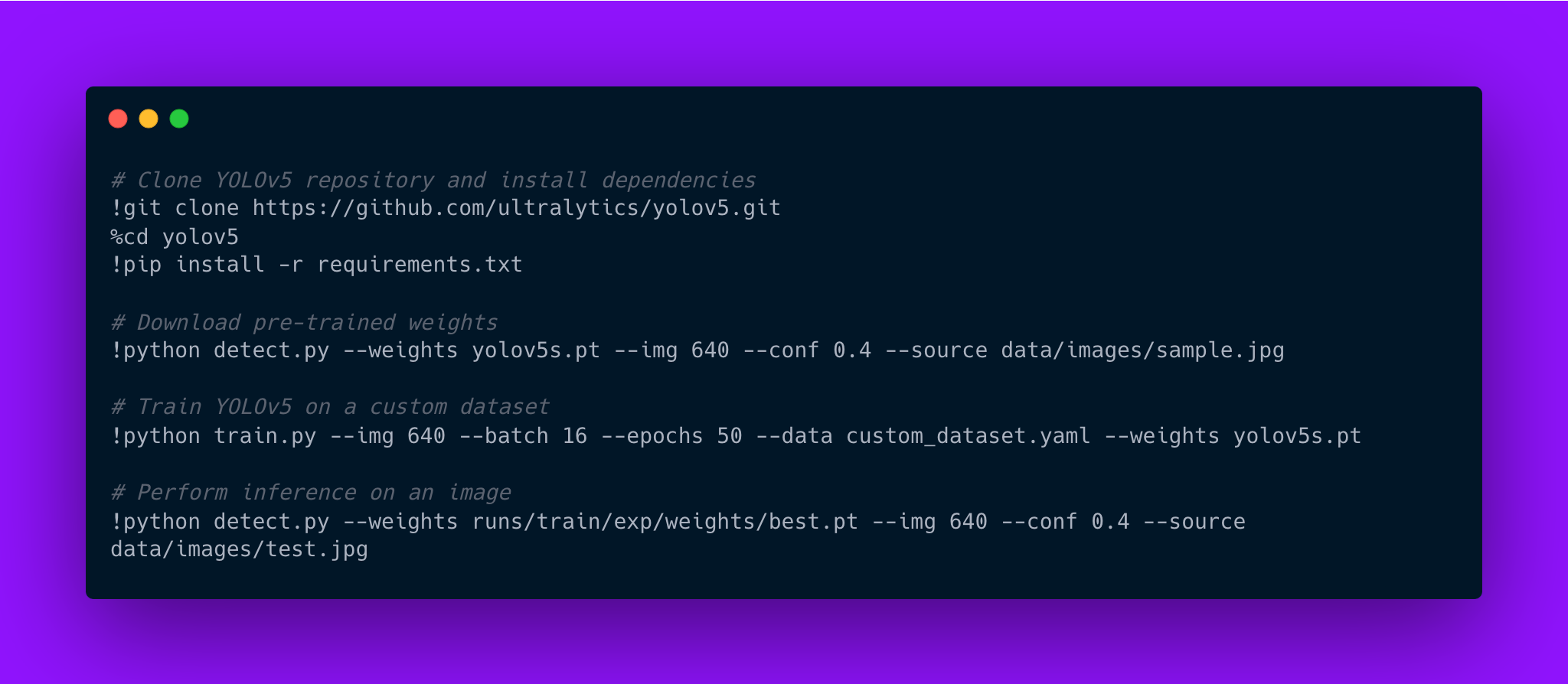
Implementing YOLOv5 involves training the model on a custom dataset or using pre-trained weights for common object detection tasks. The following example demonstrates how to use YOLOv5 for detecting objects in an image.
Code example:
# Clone YOLOv5 repository and install dependencies
!git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
%cd yolov5
!pip install -r requirements.txt
# Download pre-trained weights
!python detect.py --weights yolov5s.pt --img 640 --conf 0.4 --source data/images/sample.jpg
# Train YOLOv5 on a custom dataset
!python train.py --img 640 --batch 16 --epochs 50 --data custom_dataset.yaml --weights yolov5s.pt
# Perform inference on an image
!python detect.py --weights runs/train/exp/weights/best.pt --img 640 --conf 0.4 --source data/images/test.jpg
This example showcases how YOLOv5 can be used for both training on custom datasets and performing inference with pre-trained weights. Mastery of object detection techniques like YOLO equips AI engineers with the skills needed to tackle complex computer vision challenges across industries.
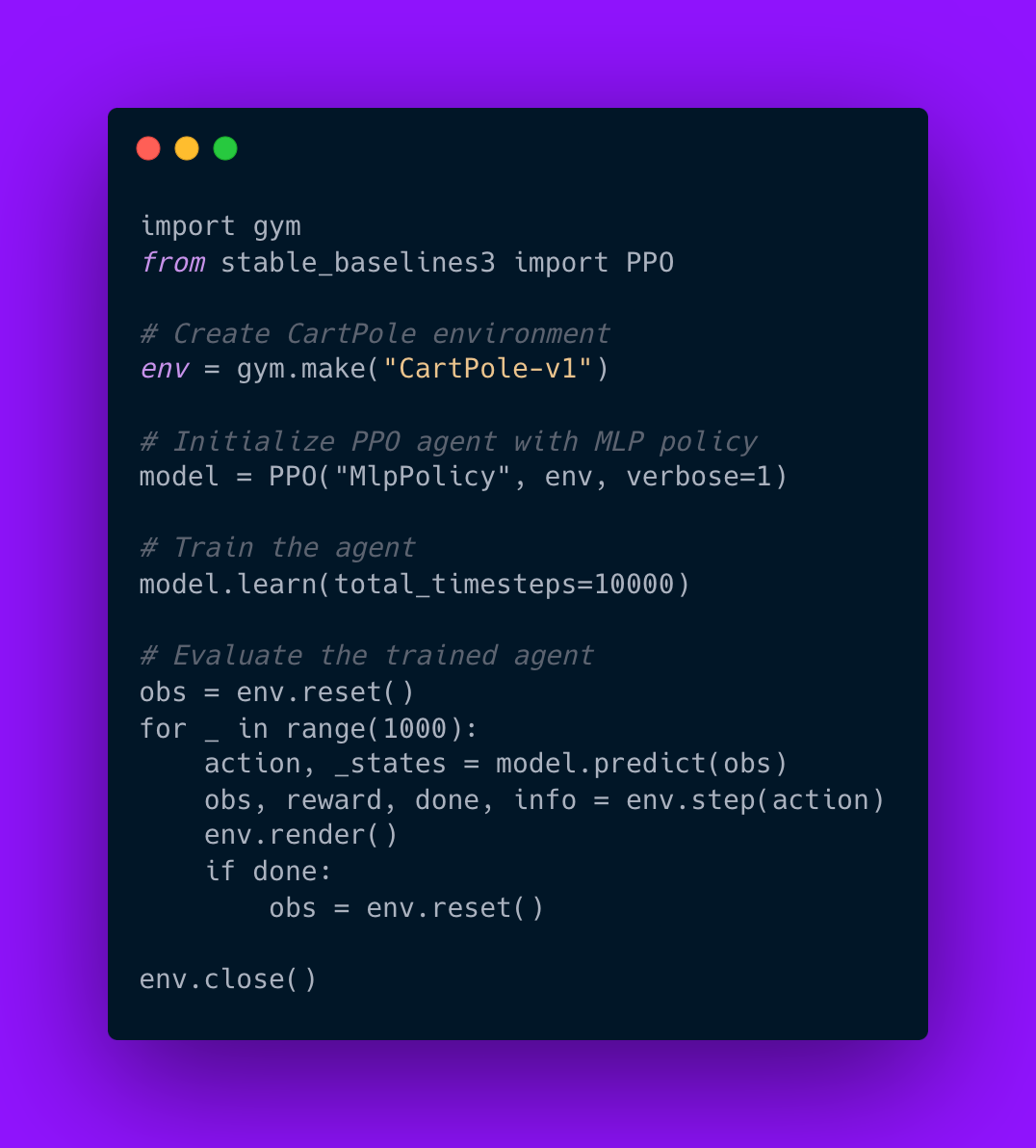
Reinforcement Learning (RL) with Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a paradigm where agents learn optimal behaviors by interacting with an environment and receiving rewards or penalties based on their actions. Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) is one of the most popular RL algorithms due to its stability and efficiency in training agents for complex tasks. PPO has been successfully applied in robotics, gaming, and resource optimization.
PPO works by iteratively improving a policy while ensuring that updates do not deviate too far from the previous policy, maintaining stability during training. This balance between exploration and exploitation makes PPO suitable for environments with continuous action spaces or delayed rewards.
Implementing PPO involves defining an environment using frameworks like OpenAI Gym, setting up the PPO algorithm using libraries like Stable-Baselines3, and training the agent through interactions with the environment. The following example demonstrates how to train an agent to play CartPole using PPO.
Code example:
import gym
from stable_baselines3 import PPO
# Create CartPole environment
env = gym.make("CartPole-v1")
# Initialize PPO agent with MLP policy
model = PPO("MlpPolicy", env, verbose=1)
# Train the agent
model.learn(total_timesteps=10000)
# Evaluate the trained agent
obs = env.reset()
for _ in range(1000):
action, _states = model.predict(obs)
obs, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
env.render()
if done:
obs = env.reset()
env.close()
This implementation demonstrates how PPO can be used to train agents efficiently for decision-making tasks in dynamic environments. By mastering RL techniques like PPO, AI engineers can design intelligent systems capable of solving real-world problems autonomously.
Real-World Global Applications of AI Engineering
In this section, we will explore AI engineering applications across various industries, providing concrete examples and detailed insights.
These practical examples—like how companies such as BlackRock, ING, and others are successfully applying AI—are one of the best ways to illustrate the transformative potential of AI. These examples and case studies will help you understand and relate to the myriad ways AI can augment various processes.
We’ll explore the following industries:
-
Healthcare
-
Energy
-
Finance
-
Manufacturing
-
Retail
-
Logistics and Supply Chain
-
Marketing
-
Agriculture
-
Content Creation
-
Entertainment
-
Autonomous Vehicles
-
Robotics
Each section will dive into the specific ways AI is driving innovation and transforming industries through advanced technologies and applications.
AI Engineering in Healthcare
AI is revolutionizing healthcare by enhancing diagnosis, treatment, and patient care, leading to more accurate results, better treatment options, and improved efficiency in medical practices.
With advancements in predictive analytics, imaging, and personalized care, AI is empowering healthcare professionals to make faster, more informed decisions, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Below are some of the most cutting-edge examples of AI applications in healthcare:
1. Philips
Philips, based in the Netherlands, develops AI-powered patient monitoring systems that predict complications and optimize critical care. The company’s AI-driven systems continuously monitor vital signs and detect early warning signals for potential health issues, such as sepsis or cardiac arrest.
These systems help healthcare providers intervene earlier, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes, particularly in critical care units.
2. Google DeepMind
Google DeepMind, based in the United Kingdom, collaborates with the NHS (National Health Service) to predict acute kidney injuries (AKI), which are a leading cause of hospital-related deaths.
DeepMind’s AI algorithms analyze patient data in real-time to identify those at risk of developing AKI, allowing for early intervention that reduces fatality rates.
The collaboration has led to a significant improvement in the early detection of kidney injury, resulting in better patient care and fewer preventable deaths.
3. Fujifilm
Fujifilm, based in Japan, uses advanced imaging AI to detect early signs of cancer, particularly in radiology and pathology. The company’s AI algorithms analyze medical images, such as mammograms and CT scans, to identify abnormalities that may indicate cancer.
By improving the accuracy and speed of cancer detection, Fujifilm helps doctors diagnose cancer earlier, when treatment is more likely to be effective and outcomes are better.
4. Dassault Systèmes
Dassault Systèmes, based in France, applies AI and molecular simulations to accelerate drug discovery. The company uses AI-driven simulations to predict how different molecules interact with each other, enabling the faster identification of potential drug candidates.
This helps pharmaceutical companies reduce the time and cost associated with drug development, bringing life-saving medications to market more quickly and efficiently.
5. IBM Watson Health
In the United States, IBM Watson Health integrates AI into oncology to recommend personalized treatment options. The platform analyzes vast amounts of clinical data, including medical literature, genetic information, and patient health records, to provide oncologists with evidence-based treatment suggestions tailored to individual patients.
This personalized approach improves treatment outcomes and helps oncologists make more informed decisions about cancer care.
6. Mayo Clinic
The Mayo Clinic, based in the United States, uses machine learning for disease prediction and resource optimization. The organization applies AI algorithms to electronic health records to predict the likelihood of diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
These predictions enable early interventions and help optimize resource allocation within hospitals, ensuring that patients receive timely care and that healthcare systems function more efficiently.
7. Mubadala Health
In the UAE, Mubadala Health employs AI for patient analytics. By using AI algorithms to analyze health data from patient records, wearable devices, and diagnostic tests, Mubadala Health can gain deeper insights into patient conditions and predict potential health risks.
This data-driven approach allows for more personalized care and proactive management of chronic diseases, ultimately improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
8. King Faisal Specialist Hospital
King Faisal Specialist Hospital, based in Saudi Arabia, uses AI to streamline radiology diagnostics. The hospital employs AI-driven tools to assist radiologists in analyzing medical images, such as MRIs and CT scans, for signs of disease or abnormalities.
AI-powered systems help detect issues like tumors, fractures, and infections more quickly and accurately, supporting healthcare providers in making faster, more reliable diagnoses.
9. Siemens Healthineers
Siemens Healthineers, based in Germany, uses AI to enhance medical imaging and diagnostics. The company’s AI-powered imaging systems assist in detecting conditions like cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders by providing enhanced image clarity and precision. AI also helps reduce the time needed for radiologists to analyze images, improving both efficiency and the speed at which patients receive diagnoses.
10. Tempus
Tempus, based in the United States, uses AI to analyze clinical and molecular data to improve cancer care. The company’s AI platform processes genetic and clinical data from cancer patients to help oncologists understand the unique characteristics of each patient’s tumor and recommend personalized treatment plans.
By leveraging AI, Tempus accelerates the process of identifying the most effective therapies for individual patients, improving treatment success rates.
As you can see from these examples, AI is reshaping healthcare by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, enabling personalized treatment, and improving patient care. Companies like Philips, Google DeepMind, Fujifilm, and Dassault Systèmes are at the forefront of AI applications in healthcare, helping detect diseases earlier, optimize treatment plans, and accelerate drug discovery.
IBM Watson Health and the Mayo Clinic are using AI to improve oncology and disease prediction, while institutions like Mubadala Health and King Faisal Specialist Hospital are utilizing AI for patient analytics and radiology diagnostics.
As AI continues to evolve, its impact on healthcare will only grow, giving healthcare providers the tools they need to deliver better, more efficient care while improving patient outcomes globally.
AI Engineering in Energy
AI is revolutionizing energy management and renewable energy optimization, providing the tools needed to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve sustainability.
Through innovative applications in smart grids, energy storage, cooling systems, and predictive maintenance, AI is enabling a more efficient, environmentally friendly energy future.
Below are some of the most cutting-edge examples of how AI is transforming the energy sector:
1. Schneider Electric
Schneider Electric, based in France, integrates AI into its energy management solutions to optimize energy distribution in smart grids. Their EcoStruxure platform uses AI to enhance grid stability and optimize energy usage in real time, allowing utilities to better manage fluctuating energy demand and supply from renewable sources.
The AI-driven platform helps predict energy consumption patterns, manage peak demand, and integrate renewable energy efficiently, all while reducing operational costs and improving the resilience of energy systems.
2. Tesla’s Powerwall
Tesla, based in the United States, uses AI in its Powerwall technology to manage home energy storage and solar panel integration. Powerwall uses machine learning algorithms to optimize the charging and discharging of energy storage systems based on real-time energy consumption data and weather forecasts.
This allows homeowners to maximize the use of solar energy while reducing reliance on grid electricity, cutting energy costs, and contributing to a more sustainable energy ecosystem. The AI also integrates with the grid, helping to stabilize energy demand during peak times.
3. DeepMind
DeepMind, based in the United Kingdom, applies AI to optimize energy use in Google’s data centers. By using machine learning algorithms, DeepMind has developed an AI system that dynamically adjusts the cooling systems in real-time to minimize energy consumption.
This cutting-edge AI system analyzes vast amounts of data, including temperature, humidity, and airflow, to improve the efficiency of cooling, reducing energy consumption by up to 40%.
This innovation has significantly reduced the carbon footprint of Google’s data centers, showcasing how AI can drive sustainable energy practices in large-scale operations.
4. Saudi Aramco
Saudi Aramco, based in Saudi Arabia, incorporates AI in various aspects of its operations, from exploration and drilling to predictive maintenance in the oil and gas sector. The company uses AI-driven systems for seismic data analysis, allowing for faster and more accurate exploration of oil reserves.
Saudi Aramco also uses AI to optimize drilling processes, minimizing energy use and improving the extraction efficiency of oil. The company applies machine learning algorithms for predictive maintenance, reducing the risk of equipment failure and ensuring more efficient resource utilization, ultimately lowering costs and enhancing sustainability in the sector.
5. Enel X
Enel X, an energy innovation company based in Italy, uses AI for advanced energy storage and grid optimization. The company’s AI-powered virtual power plants (VPPs) aggregate distributed energy resources, such as home solar panels, battery storage systems, and electric vehicles, to create a more flexible and resilient energy grid. The AI algorithms optimize the use of these resources, balancing supply and demand, enabling users to sell excess energy back to the grid.
This cutting-edge system not only reduces energy costs for consumers but also improves grid stability and accelerates the transition to renewable energy.
6. Orsted
Orsted, a Danish renewable energy company, uses AI to optimize the operation of its offshore wind farms. Orsted employs AI-driven predictive maintenance to monitor the performance of turbines, anticipating issues before they occur and minimizing downtime.
The company’s AI algorithms analyze environmental conditions, turbine performance, and historical data to predict when maintenance is needed, helping improve the efficiency and longevity of wind turbines. Orsted also uses AI to optimize the energy production from its offshore wind farms, adjusting turbine operations based on real-time weather and grid demand data.
7. Exelon
Exelon, a leading energy provider in the United States, uses AI to enhance the efficiency of its energy grid and reduce energy waste. The company’s Smart Grid technology applies AI to monitor and manage energy distribution in real time.
Exelon uses machine learning algorithms to predict demand patterns, detect faults, and optimize the performance of the grid. AI also helps the company integrate renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into the grid, ensuring a stable and reliable supply of clean energy.
8. Siemens Gamesa
Siemens Gamesa, a global leader in renewable energy, employs AI to optimize the operation of its wind turbines. Through AI-powered algorithms, Siemens Gamesa monitors the condition of its turbines in real-time, enabling predictive maintenance and minimizing the risk of downtime.
The company’s AI systems analyze data from sensors on the turbines to detect early signs of wear and tear, allowing for proactive maintenance and optimizing the energy output of each turbine.
This AI-driven approach improves the efficiency of wind power generation, making it a more reliable and cost-effective renewable energy source.
9. C3.ai
C3.ai, based in the United States, provides AI-driven solutions for energy management, focusing on optimizing energy production and consumption across industries. Their AI platform enables companies to monitor and predict energy usage patterns, identify inefficiencies, and reduce operational costs.
C3.ai helps energy companies optimize grid management, improve forecasting for renewable energy production, and enhance predictive maintenance for equipment.
By using AI to analyze vast datasets, C3.ai is helping energy providers transition to a more sustainable and efficient energy landscape.
10. Vestas
Vestas, a Danish wind turbine manufacturer, utilizes AI to optimize the performance and efficiency of wind farms. By employing machine learning models, Vestas analyzes data from thousands of turbines worldwide to predict maintenance needs, optimize turbine performance, and improve energy output.
The AI system can adjust turbine operations in real-time based on weather conditions and demand, ensuring that wind farms generate the maximum amount of energy while minimizing downtime. This cutting-edge approach is helping Vestas lead the way in efficient, sustainable wind energy production.
AI is at the forefront of revolutionizing energy management and renewable energy optimization. Companies like Schneider Electric, Tesla, DeepMind, and Saudi Aramco are using cutting-edge AI technologies to optimize energy distribution, improve storage systems, and reduce energy consumption.
From smart grids and wind farms to predictive maintenance in oil and gas operations, AI is making energy systems more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable. As AI continues to evolve, its impact on the energy sector will only grow, enabling a more efficient, cleaner, and more reliable energy future for all.
AI Engineering in Finance
AI is revolutionizing the financial industry by enhancing security, optimizing operations, and providing valuable insights for decision-making. From risk analysis and fraud detection to customer service automation and investment predictions, AI is becoming an essential tool for financial institutions worldwide.
Below are examples of how AI is transforming the finance sector, with companies integrating AI-driven solutions into their operations:
1. BlackRock
BlackRock, based in the United States, uses its Aladdin platform to analyze risks and provide predictive analytics for asset management. Aladdin combines data from a variety of sources and uses AI to assess the risk associated with different investments. It helps portfolio managers make informed decisions by providing them with insights into market trends, asset volatility, and financial performance.
The AI-driven platform enables better risk management and more effective asset allocation, improving investment strategies and maximizing returns.
2. PayPal
PayPal, also based in the United States, applies machine learning to detect fraudulent transactions in real time, protecting millions of users worldwide. PayPal uses AI algorithms to analyze transaction patterns and identify suspicious activity, enabling the platform to flag potential fraud before it occurs.
By using machine learning models trained on vast datasets, PayPal improves its ability to spot fraud in its early stages, ensuring the safety and security of its users’ financial transactions.
3. BNP Paribas
BNP Paribas, based in France, employs AI for credit risk assessment. The company uses machine learning models to analyze customer data and predict the likelihood of loan default, which helps in making more accurate lending decisions.
BNP Paribas’s AI-driven credit risk assessment tools improve loan approval processes by evaluating factors such as credit history, financial behavior, and market conditions, reducing the risk of defaults and improving profitability.
4. Nomura
Nomura, based in Japan, integrates AI into stock market predictions. The company uses machine learning algorithms to analyze historical stock market data, news, and economic reports to predict market trends and stock movements.
Nomura’s AI tools help investors make more informed decisions by providing real-time analysis and forecasts, enabling better strategies for portfolio management and investment decisions.
5. Mashreq Bank
In the UAE, Mashreq Bank uses AI chatbots to enhance customer service. The AI-powered chatbots provide real-time assistance to customers, answering queries related to account management, transactions, and services.
By using natural language processing (NLP), the bank’s chatbots can understand customer inquiries and respond with relevant information, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction. This AI integration helps reduce wait times and frees up human agents to handle more complex requests.
6. Riyad Bank
Riyad Bank, based in Saudi Arabia, incorporates machine learning for fraud detection and dynamic credit scoring. The bank uses AI algorithms to analyze customer transactions in real time, detecting unusual patterns that may indicate fraudulent activity.
Riyad Bank also uses machine learning to dynamically adjust credit scores based on a customer’s financial behavior, ensuring that creditworthiness assessments are more accurate and reflective of current financial conditions.
7. HSBC
HSBC, a global bank, uses AI for risk management and fraud prevention. The company applies machine learning algorithms to detect financial crimes and analyze transaction data for signs of fraudulent activities. HSBC also uses AI to improve customer service by offering personalized financial advice and recommendations based on a customer’s spending patterns and financial goals.
8. JP Morgan Chase
JP Morgan Chase, one of the largest financial institutions in the United States, uses AI to enhance trading strategies and investment management. The company applies machine learning models to analyze vast amounts of financial data and identify profitable trading opportunities.
AI also plays a crucial role in JP Morgan Chase’s algorithmic trading system, which helps execute large trades at optimal prices.
9. Goldman Sachs
Goldman Sachs, based in the United States, integrates AI into investment management and risk modeling. The company uses machine learning algorithms to predict market trends, identify emerging risks, and optimize investment portfolios.
AI helps Goldman Sachs create more accurate risk models, enabling better financial forecasting and improved decision-making in portfolio management.
10. ING
ING, a global financial services company based in the Netherlands, uses AI to improve customer engagement and personalize banking services.
The company employs machine learning to analyze customer data and provide tailored product recommendations, such as personalized savings plans, credit offerings, and investment advice.
AI also enhances ING’s fraud detection capabilities, allowing the bank to monitor transactions in real time and identify suspicious activity.
AI is revolutionizing the financial sector by enhancing security, improving decision-making, and driving efficiency. Companies like BlackRock, PayPal, BNP Paribas, and Nomura are leveraging AI to analyze risks, predict market trends, and detect fraud. In the Middle East, Mashreq Bank and Riyad Bank are using AI for customer service automation and real-time fraud detection.
As AI continues to advance, its role in the financial industry will only grow, enabling institutions to provide better, faster, and more secure services to their customers, while optimizing operations and improving profitability.
AI Engineering in Manufacturing
AI is significantly enhancing productivity, efficiency, and predictive maintenance in manufacturing worldwide. By integrating AI technologies into industrial processes, manufacturers can streamline operations, reduce downtime, and improve product quality.
Below are examples of how AI is transforming the manufacturing industry, with specific companies implementing innovative AI solutions:
1. Siemens
Siemens, based in Germany, leverages its MindSphere platform to monitor industrial equipment and predict failures, reducing downtime in factories.
MindSphere collects and analyzes data from machines and sensors, allowing manufacturers to identify potential issues before they lead to costly breakdowns.
By using AI to monitor performance, Siemens helps businesses improve the reliability of their machinery, optimize maintenance schedules, and reduce operational disruptions, ultimately increasing productivity.
2. GE
GE, based in the United States, applies AI to optimize turbine efficiency and enhance the performance of industrial equipment. Through its Predix platform, GE uses AI to analyze data from turbines, engines, and other industrial machinery to improve energy production and operational efficiency.
The AI-powered system helps detect inefficiencies, predict equipment failures, and enable predictive maintenance, which reduces downtime and enhances the longevity of assets. GE’s AI systems also assist in real-time optimization of industrial processes, leading to increased output and cost savings.
3. Foxconn
Foxconn, based in Taiwan, uses AI-powered robotics for precision assembly and defect detection in electronics manufacturing. The company integrates AI-driven robots and automated systems on production lines to assemble electronic components with high precision.
AI is also employed for quality control, with deep learning algorithms analyzing images from cameras to detect defects in products that might be missed by human inspectors. This helps Foxconn reduce errors, improve product quality, and increase the speed of production, making its manufacturing processes more efficient.
4. NEOM Industrial City
In Saudi Arabia, NEOM Industrial City integrates AI to automate large-scale manufacturing processes while achieving zero-waste production goals.
NEOM uses AI for predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, and energy management, ensuring that industrial operations are both efficient and environmentally friendly.
By leveraging machine learning and AI algorithms, NEOM’s manufacturing systems can anticipate failures, optimize energy consumption, and reduce waste during production, aligning with its sustainability goals.
5. BMW
BMW, based in Germany, uses AI in its production lines to enhance productivity and optimize logistics. AI is employed to monitor and manage supply chains, ensuring that the right parts are available at the right time to keep the production process running smoothly. AI-driven robots are also used for tasks like welding and assembly, increasing the speed and precision of these processes.
BMW’s AI tools help reduce production costs, improve efficiency, and maintain high product quality standards.
6. Toyota
Toyota, based in Japan, integrates AI to optimize its manufacturing operations and improve production processes. The company uses AI for predictive maintenance, helping detect issues in machinery before they cause significant downtime.
Toyota also uses machine learning to enhance the automation of its assembly lines, enabling greater precision in tasks like painting and welding. AI further helps optimize inventory management, ensuring the efficient use of materials and reducing waste in the production process.
7. Tesla
Tesla, based in the United States, employs AI to optimize manufacturing processes in its electric vehicle production plants. Tesla uses AI-powered robots and automation to assemble vehicles with high efficiency and precision. AI is also used for quality control, detecting defects in components and vehicles before they leave the factory. Tesla integrates machine learning algorithms to optimize supply chain logistics and inventory management, ensuring that the right materials are available at the right time for production.
8. ABB
ABB, a global leader in industrial automation, uses AI to enhance manufacturing processes, focusing on robotics, predictive maintenance, and energy management.
ABB’s AI-driven robots are used in assembly lines to improve productivity and precision. In addition, AI is utilized to analyze data from industrial equipment, predict potential failures, and optimize maintenance schedules, thereby reducing downtime and ensuring more efficient factory operations.
9. Rockwell Automation
Rockwell Automation, based in the United States, employs AI to improve factory automation and predictive maintenance. The company’s FactoryTalk platform uses AI to monitor and control industrial processes in real-time, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing disruptions.
Rockwell’s AI solutions help manufacturers predict when equipment needs maintenance, reducing unexpected downtime and extending the life of machinery.
10. Samsung
Samsung, based in South Korea, integrates AI into its manufacturing processes to improve efficiency and quality control. The company uses AI-driven robots for assembly tasks, helping automate repetitive processes and reduce human error. AI is also applied in quality inspection, where deep learning models analyze images of products to detect defects that human inspectors might miss.
Samsung’s AI systems enable faster production cycles, improve accuracy, and enhance overall product quality.
AI is transforming the manufacturing industry by improving efficiency, reducing downtime, and enhancing product quality. Companies like Siemens, GE, Foxconn, and NEOM Industrial City are leading the way in utilizing AI for predictive maintenance, optimization of production processes, and sustainability goals. AI-driven solutions in robotics, machine learning, and data analytics are helping manufacturers around the world reduce costs, improve operational performance, and increase productivity.
As AI technology continues to evolve, its role in manufacturing will only grow, enabling smarter, more efficient, and sustainable production systems.
AI Engineering in Retail
AI is revolutionizing the retail industry by enhancing customer experiences, streamlining operations, and providing data-driven insights for decision-making.
Retailers are leveraging AI to optimize everything from inventory management and pricing to personalized shopping experiences and trend forecasting.
Below are examples of how AI is making a significant impact in the retail sector, highlighting specific companies and their innovations:
1. Amazon
Amazon, based in the United States, utilizes advanced recommendation systems powered by collaborative filtering and deep learning algorithms to personalize the shopping experience for its customers.
The platform analyzes customer behavior, browsing history, and purchase patterns to suggest products tailored to individual preferences. Amazon also uses AI to optimize inventory management and dynamically adjust pricing in real-time, ensuring that the company can meet demand efficiently while maximizing profitability.
2. Alibaba
Alibaba, based in China, employs AI-powered virtual assistants to improve logistics and enhance customer interactions. The company uses natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to allow customers to interact with chatbots for instant assistance, from product recommendations to answering queries.
Alibaba’s AI also plays a key role in logistics, helping to optimize warehouse operations, manage inventory, and streamline supply chain processes, improving the efficiency and speed of order fulfillment.
3. Zara
Zara, based in Spain, integrates AI to predict fashion trends, which helps the company reduce waste and accelerate production cycles. By using machine learning and data analytics, Zara can analyze social media, sales data, and customer preferences to identify emerging trends. This allows the company to quickly design and produce new collections that align with current consumer demands, leading to faster turnaround times and more accurate inventory management.
4. Noon
Noon, based in the UAE, uses machine learning to create personalized shopping experiences for customers. By analyzing purchase history, browsing behavior, and preferences, Noon can recommend products that are more likely to resonate with individual customers. AI is also used to automate warehouse operations, improving inventory management and fulfillment speed.
Noon’s AI-driven systems ensure that customers receive relevant product recommendations while also streamlining the order fulfillment process.
5. Jarir Bookstore
Jarir Bookstore, based in Saudi Arabia, optimizes inventory and pricing using AI algorithms. By analyzing sales data and market trends, Jarir uses AI to forecast demand and manage stock levels more efficiently. This helps the company reduce the risk of overstocking or running out of popular products.
AI is also employed in dynamic pricing strategies, allowing Jarir to adjust prices in real-time based on factors such as demand, competition, and inventory levels.
6. Walmart
Walmart, based in the United States, uses AI for inventory management and supply chain optimization. AI-powered systems help Walmart predict demand for specific products, allowing for more efficient stock replenishment and reducing instances of out-of-stock products.
Walmart also employs machine learning to analyze customer preferences and shopping behavior, improving personalized recommendations and enhancing the online shopping experience. Additionally, AI is used to optimize delivery routes and automate warehouse operations, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
7. Sephora
Sephora, a global beauty retailer based in France, uses AI-powered tools like its Sephora Virtual Artist to enhance the customer shopping experience. Customers can try on makeup virtually through augmented reality (AR) technology, powered by AI, which simulates how different products will look on their skin. The company also uses AI to recommend beauty products based on personal preferences and skin tone, providing a personalized and engaging shopping experience.
8. Target
Target, based in the United States, uses AI to predict customer preferences and optimize inventory management. The company uses AI-based demand forecasting tools to ensure that popular items are always in stock and to reduce excess inventory. AI is also used for personalized marketing, delivering tailored promotions and discounts to customers based on their shopping history and preferences, leading to higher engagement and conversion rates.
9. H&M
H&M, based in Sweden, employs AI to improve its inventory management and supply chain processes. By analyzing customer purchase data, H&M can predict which items will be in demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly. The company also uses AI to optimize product recommendations for customers, ensuring a more personalized shopping experience both online and in-store.
10. Best Buy
Best Buy, based in the United States, integrates AI into its customer service operations with virtual assistants that can help customers find products, compare features, and make purchasing decisions. AI is also used to personalize marketing campaigns and optimize inventory management, ensuring that Best Buy can offer competitive prices and meet customer demand without overstocking.
11. Macy’s
Macy’s, based in the United States, uses AI to enhance its in-store and online shopping experiences. The company employs AI-driven chatbots that provide personalized recommendations, answer customer questions, and guide shoppers through the store. Macy’s also uses machine learning algorithms to analyze customer behavior and optimize its marketing strategies, ensuring more targeted and effective promotions.
12. Talabat
Talabat, a leading food delivery service in the UAE, uses AI to personalize user experiences and optimize delivery logistics. AI-powered recommendation engines suggest dishes or restaurants based on customers’ past orders and preferences, enhancing customer satisfaction. Additionally, Talabat leverages AI to optimize delivery routes, reducing delivery times and improving operational efficiency.
AI is revolutionizing retail by enhancing customer experiences, improving inventory management, and streamlining operations. Companies like Amazon, Alibaba, and Zara are leveraging AI to personalize shopping experiences, optimize logistics, and improve supply chain efficiency. AI-driven solutions in predictive analytics, machine learning, and natural language processing are helping retailers like Jarir Bookstore, Sephora, and Walmart stay ahead of trends, reduce costs, and deliver better products and services to their customers.
As AI continues to evolve, its role in retail will only increase, providing companies with smarter, more efficient ways to meet customer demands and drive business growth.
AI Engineering in Logistics and Supply Chain
AI is revolutionizing the logistics and supply chain sector by enhancing efficiency, reducing operational costs, and improving decision-making processes. Through the use of AI, companies can optimize everything from routing and warehouse management to real-time tracking and predictive analytics.
Below are some examples of how AI is transforming logistics and supply chain operations, highlighting specific companies and their innovations:
1. DHL
DHL, based in Germany, employs machine learning and AI technologies to optimize various aspects of logistics, including route optimization, warehousing, and delivery prediction. By using AI algorithms, DHL can predict the most efficient delivery routes, minimizing delivery time and reducing fuel consumption.
AI is also used in warehouse management to improve inventory tracking, streamline order fulfillment, and predict stock levels, ultimately enhancing supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction.
2. FedEx
FedEx, based in the United States, applies AI for dynamic routing and package tracking, ensuring timely deliveries and better management of logistics operations. Using AI-driven route optimization, FedEx adjusts delivery paths in real-time based on factors like traffic, weather conditions, and delivery priority, significantly improving the accuracy of delivery times.
FedEx also uses AI for predictive analytics, forecasting package volumes and tracking shipments in real-time, helping customers stay informed and improving operational efficiency.
3. Aramex
Aramex, a global logistics and transportation company based in the UAE, integrates AI to streamline cross-border logistics and enhance last-mile delivery solutions. AI helps Aramex predict demand and optimize delivery routes, especially in complex international shipping environments.
The use of AI-powered tools allows for better inventory management, improved warehouse automation, and efficient tracking of packages, which ultimately leads to faster and more reliable deliveries across regions.
4. Maersk
Maersk, a leading shipping and logistics company based in Denmark, uses AI to optimize shipping routes, reduce fuel consumption, and manage container logistics more effectively. AI algorithms analyze factors like weather patterns, port congestion, and shipping schedules to determine the most efficient routes for vessels.
Maersk also utilizes AI to track container movements in real-time, allowing for better visibility into supply chain operations and enabling predictive maintenance to prevent delays or equipment failures.
5. UPS
UPS, based in the United States, uses AI to enhance its logistics operations, particularly for route optimization and predictive maintenance. The company’s ORION (On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation) system employs machine learning algorithms to optimize delivery routes, minimizing fuel consumption and reducing operational costs. UPS also uses AI for predictive analytics, forecasting package volumes and adjusting staffing levels accordingly, helping to ensure that resources are allocated efficiently.
6. Kuehne + Nagel
Kuehne + Nagel, based in Switzerland, uses AI for predictive analytics and demand forecasting to improve supply chain management. By leveraging machine learning, Kuehne + Nagel can predict market trends, optimize inventory management, and adjust logistics strategies based on real-time data. AI is also used to improve the efficiency of warehouse operations and streamline order fulfillment processes, ensuring timely deliveries and better customer satisfaction.
7. XPO Logistics
XPO Logistics, based in the United States, applies AI to automate various aspects of its supply chain, from inventory management to last-mile delivery. AI-driven robots are used in warehouses to enhance sorting and packaging, improving operational efficiency. Additionally, XPO utilizes AI to optimize delivery routes and track shipments in real-time, reducing delays and improving transparency for customers.
8. Siemens
Siemens, based in Germany, employs AI and machine learning in its logistics and supply chain operations to optimize warehouse management and distribution networks. Using AI, Siemens can analyze historical data to forecast demand, manage inventory levels, and streamline supply chain operations.
The company also utilizes AI for route optimization and improving the accuracy of predictive maintenance for transportation assets, reducing downtime and ensuring smoother operations.
9. IBM
IBM, based in the United States, offers AI-driven supply chain solutions, such as IBM Sterling Supply Chain, which uses machine learning and AI to improve visibility, optimize inventory, and manage risks. The platform provides real-time insights into supply chain performance, helping companies make data-driven decisions about production, inventory management, and distribution.
IBM’s AI tools also use historical data and predictive analytics to forecast demand, minimize disruptions, and optimize shipping routes.
10. Toyota Logistics
Toyota Logistics, based in Japan, uses AI and robotics to streamline its manufacturing and distribution processes. The company integrates AI for route optimization in its transportation network, helping to ensure that products are delivered efficiently and cost-effectively. Additionally, Toyota uses AI-driven robots in warehouses to assist with inventory management, automating sorting and packaging tasks, which enhances productivity and reduces human error.
AI engineering is fundamentally reshaping the logistics and supply chain sectors by optimizing routes, enhancing operational efficiency, and enabling predictive analytics for better decision-making. Companies like DHL, FedEx, Aramex, and Maersk are utilizing AI to optimize everything from route planning and real-time tracking to warehouse management and demand forecasting.
AI-driven solutions are not only improving the speed and accuracy of deliveries but also reducing costs, minimizing environmental impact, and providing better customer experiences.
As AI continues to advance, its role in logistics and supply chain management will only grow, providing businesses with smarter, more efficient ways to manage global operations.
AI Engineering in Marketing
AI engineering is transforming the field of marketing by providing innovative tools that automate processes, personalize experiences, and optimize campaigns.
With the power of AI, companies are able to better understand customer behavior, predict trends, and create more targeted and engaging content.
Below are some key examples of AI-driven innovations in marketing, with a focus on specific products and companies making strides in this area:
1. Phoenix
Phoenix from LunarTech plays a significant role in email marketing, digital marketing strategies, and highSEO content creation. It can draft engaging email campaigns, design personalized content, and optimize outreach efforts by analyzing user preferences and behavior.
Phoenix’s AI engine tailors content to specific audiences, improving engagement rates and overall marketing performance. Phoenix is also great for drafting social media posts, creating SEO-optimized content, and assisting in highSEO blog creation. This makes it a powerful tool for companies looking to boost their digital marketing efforts and maintain a consistent presence across platforms.
2. HubSpot
HubSpot integrates AI to enhance its inbound marketing platform. The platform uses AI to analyze customer behavior and interactions, helping marketers create more personalized experiences.
Through predictive lead scoring, HubSpot identifies high-potential leads and automates follow-up tasks, ensuring that marketers can focus on the most promising opportunities. AI is also used to optimize email marketing campaigns, delivering personalized messages based on user actions, improving open rates and conversions.
3. Marketo
Marketo, part of Adobe, leverages AI and machine learning to help marketers automate and optimize their marketing campaigns. The platform uses predictive analytics to forecast customer behavior, segment audiences, and personalize content at scale.
AI-driven tools in Marketo enable marketers to create highly targeted campaigns, deliver content based on customer journeys, and track the effectiveness of campaigns in real time.
4. Hootsuite
Hootsuite uses AI to enhance social media marketing and management. The platform’s AI-driven insights help marketers understand audience sentiment, predict engagement levels, and optimize the timing of social media posts.
AI is also used to monitor brand mentions and track competitors, providing valuable data that can inform marketing strategies. Hootsuite automates scheduling and content curation, helping companies stay ahead of trends and interact with customers in real time.
5. Mailchimp
Mailchimp, a leading email marketing platform, uses AI to automate the creation and delivery of personalized email campaigns. The platform uses machine learning to analyze user behavior and segment audiences based on their preferences and actions. This allows marketers to send tailored messages that resonate with their audience, increasing engagement and conversion rates. AI-powered tools like Smart Send Time optimize when emails are sent to maximize open rates.
6. Salesforce Marketing Cloud
Salesforce Marketing Cloud uses AI, particularly its Einstein AI platform, to help marketers deliver personalized experiences at scale. Einstein uses data analytics to predict customer behavior and recommend the best next steps for engagement, ensuring that marketers can create timely, relevant content.
The AI-powered platform also provides insights into customer journeys, helping businesses improve customer retention and conversion rates by delivering the right content at the right time.
7. Cortex
Cortex uses AI to optimize visual content for digital marketing. The platform analyzes millions of data points to determine the best-performing images, colors, and designs for different types of content. AI in Cortex helps marketers create visuals that align with brand identity and attract the highest levels of engagement. The platform also provides insights into how specific types of content perform across various channels, allowing for data-driven decision-making.
8. Adext AI
Adext AI uses machine learning to optimize paid advertising campaigns across various digital platforms. The AI analyzes audience data and campaign performance to adjust ad targeting and bidding in real-time. Adext AI ensures that ad spend is optimized for the best return on investment (ROI), automating much of the process and providing marketers with actionable insights to refine campaigns for greater effectiveness.
9. Canva
Canva uses AI to help users create engaging marketing graphics quickly and easily. The platform’s AI-powered tools, such as its Magic Resize feature, automatically adjust designs to fit different social media platforms. Canva also offers AI-driven templates and suggestions, allowing marketers to create high-quality visuals for email campaigns, social media posts, and digital ads. The AI in Canva helps streamline the design process, making it accessible to both professionals and non-designers.
10. Semrush
Semrush is a comprehensive SEO tool that uses AI to analyze website performance, keywords, and search engine rankings. The platform helps marketers optimize their websites by providing AI-driven recommendations for improving SEO strategies. Semrush uses machine learning to track changes in search trends, competitor activities, and user behavior, enabling businesses to adjust their strategies in real time for maximum visibility.
11. ChatGPT for Marketing
ChatGPT, the technology behind this assistant, is transforming content creation and customer service in marketing. Marketers can use ChatGPT to generate blog posts, product descriptions, email content, and even social media posts. The AI can be customized to reflect a brand’s tone and voice, providing businesses with the ability to scale their content creation efforts.
ChatGPT is also useful in customer support for providing quick, personalized responses to customer queries, enhancing the overall customer experience.
12. Surfer SEO
Surfer SEO uses AI to help marketers optimize their websites for search engines. The platform analyzes top-ranking pages for specific keywords and provides AI-driven recommendations to improve content structure, keyword usage, and overall SEO performance. Surfer SEO’s AI tools are designed to help businesses improve their online visibility and attract organic traffic, ensuring that their content ranks higher in search results.
AI engineering is fundamentally transforming digital marketing by automating processes, improving targeting, and enhancing content personalization. Tools like Phoenix for email and digital marketing as well as for content creation, as well as highSEO content creation, HubSpot, Marketo, and Salesforce Marketing Cloud, help businesses deliver more relevant and engaging content to their audiences.
Platforms like Mailchimp, Hootsuite, and Canva are making it easier for marketers to create and manage campaigns efficiently, while AI-driven advertising optimization tools like Adext AI and Semrush ensure that marketing budgets are spent more effectively.
As AI continues to evolve, it will further enhance marketers’ ability to deliver personalized, impactful campaigns that engage audiences, drive conversions, and maximize ROI.
AI Engineering in Education
AI is revolutionizing education by providing personalized learning experiences, enhancing student engagement, and offering more efficient ways to learn and teach.
AI-powered platforms are now used to tailor content to individual learning styles and needs, ensuring that education is accessible and adaptive.
Below are some examples of how AI engineering is transforming education, with specific companies and their products making significant strides in this field:
1. LunarTech Academy
LunarTech Academy uses its AI-powered platform to offer specialized courses, such as its AI Engineering Bootcamp and Data Science courses. These programs deliver advanced training on their AI-powered platform, which adapts to individual learning paces and provides tailored content.
Phoenix, LunarTech’s flagship innovation, features over 200 AI agents that support education and training by simulating real-world problem-solving scenarios. The platform also offers personalized curriculum recommendations using Generative AI, ensuring students receive the most relevant content based on their progress and preferences.
2. Khan Academy
Khan Academy integrates AI-powered tutors like Khanmigo to provide personalized, real-time feedback to students. This makes learning more interactive and adaptive by adjusting to the learner’s level and pace. Khanmigo can help with everything from answering questions to guiding students through challenging concepts, ensuring a more tailored and efficient learning experience.
3. Coursera
Coursera, a leading online learning platform, uses AI to recommend courses tailored to students’ career goals. By analyzing user behavior, career paths, and learning history, Coursera’s AI system suggests courses that best align with a learner’s aspirations.
This personalized course recommendation system ensures that students are guided toward the content that will help them develop the skills necessary for their professional growth.
4. Duolingo
Duolingo, a language learning app, adapts its lessons based on the user’s progress using AI algorithms. The platform tracks the learner’s strengths and weaknesses, providing customized lessons that focus on areas requiring more attention.
This AI-driven adaptive learning makes language acquisition more engaging and efficient by ensuring that users are constantly challenged at the right level.
5. Carnegie Learning
Carnegie Learning applies machine learning to personalize math education. Their AI-driven platform adapts to individual student needs, offering targeted exercises and feedback to improve learning outcomes.
By analyzing student responses and progress, the platform adjusts the difficulty of problems and provides hints to help learners overcome challenges, improving both engagement and understanding of mathematical concepts.
6. Squirrel AI Learning
Squirrel AI Learning, based in China, uses AI to deliver personalized tutoring to K-12 students. The platform employs adaptive learning technology to assess students’ knowledge gaps and creates customized learning plans to address individual needs.
By continuously analyzing performance and providing real-time feedback, Squirrel AI helps students learn more efficiently while promoting deeper understanding.
7. Smart Sparrow
Smart Sparrow provides adaptive learning platforms that allow educators to create personalized learning experiences for their students. The platform uses AI to analyze student performance and adapt the course material in real time. This helps teachers identify struggling students and adjust lesson plans accordingly, ensuring that every student receives the support they need to succeed.
8. McGraw-Hill Education
McGraw-Hill Education integrates AI in its learning tools to provide personalized learning experiences. Their platform, ALEKS, uses adaptive learning algorithms to assess students’ knowledge and personalize their learning paths in real-time. This AI-driven system helps students grasp difficult concepts in subjects like math, chemistry, and business, providing targeted lessons and feedback based on their performance.
9. Content Technologies, Inc.
Content Technologies, Inc. (CTI) uses AI to create personalized textbooks and learning materials. The AI system automatically generates customized content based on the learner’s needs, allowing for a more tailored and effective educational experience. The platform can modify textbook layouts, sections, and practice problems to better align with each student’s learning objectives.
10. Quizlet
Quizlet, an AI-driven study tool, uses machine learning algorithms to generate personalized study sets and flashcards based on the user’s learning behavior. The platform tracks the student’s performance on various topics and adapts the difficulty of the flashcards accordingly. Quizlet’s AI also helps improve retention by offering spaced repetition of terms and concepts based on the learner’s past performance.
11. Edmentum
Edmentum applies AI technology to develop personalized learning programs for students in grades K-12. Their platform offers a range of adaptive learning tools that can adjust content based on individual student performance, helping to close achievement gaps. Edmentum’s AI-driven system provides teachers with detailed insights into student progress and identifies areas where additional support is needed.
12. IBM Watson Education
IBM Watson Education leverages AI to help educators and institutions personalize learning at scale. Using AI-driven insights, the platform supports teachers in creating individualized learning plans for students and provides recommendations on how to optimize their teaching strategies. By analyzing student data, IBM Watson Education helps identify potential learning challenges and provides solutions to improve outcomes.
13. Nuance Communications
Nuance Communications uses AI-driven speech recognition and natural language processing (NLP) to enhance language learning and educational accessibility. Their tools help students practice speaking and improve language skills by providing feedback on pronunciation, grammar, and fluency. This AI technology is especially helpful for non-native speakers and those learning new languages, offering immediate corrections and suggestions.
AI engineering is transforming education by providing personalized, adaptive learning experiences that enhance engagement, improve learning outcomes, and streamline teaching processes.
From platforms like LunarTech Academy offering AI-driven curriculum recommendations and real-world simulations to Khan Academy’s AI tutors providing real-time feedback, AI is making education more accessible and effective.
With Coursera’s career-tailored recommendations, Duolingo’s adaptive language lessons, and Carnegie Learning’s AI-driven math education, the possibilities are vast.
As AI continues to evolve, its role in education will only grow, providing more personalized, efficient, and impactful learning opportunities for learners around the world.
AI Engineering in Content Creation
AI enables creators to produce innovative and personalized content at scale. OpenAI’s DALL-E and Leonardo generate stunning visuals for art and advertising. MidJourney empowers artists to create hyper-realistic images, while Sora allows creators to develop engaging videos with minimal manual effort. Phoenix further revolutionizes content creation by enabling users to work with 200+ AI agents, automating tasks like ideation, editing, and optimization.
Creative AI Lab employs AI for Arabic language content generation, and Rotana integrates machine learning to curate music recommendations and automate video editing workflows.
Here are some other areas in which AI can help create engaging content:
1. Automated Text Generation
AI models like OpenAI’s GPT and other NLP algorithms are being used to automatically generate written content. These models can write articles, blog posts, product descriptions, and even poetry or fiction.
AI is capable of understanding context, generating human-like text, and tailoring writing styles to fit different tones and audiences. These models are widely used by news outlets, content marketers, and writers to quickly outline or draft articles and generate ideas, saving time and increasing productivity.
Tools like Phoenix (featuring a high-SEO blog writer, LinkedIn profile generator, newsletter drafter, and blog writer) are also enabling businesses to create high-quality content effortlessly.
2. AI in Video Creation and Editing
AI is playing a crucial role in video content creation and editing. Tools powered by AI, such as Sora by OpenAI, can help automate the video editing process by suggesting cuts, transitions, color corrections, and effects based on the content.
AI is also used to enhance visual effects, stabilize shaky footage, and even generate video content from text prompts. Open-source tools like DaVinci Resolve AI are revolutionizing the way creators approach video content production.
Platforms like Runway, Adobe Premiere Pro, and Synthesia, streamline video creation, making it easier for creators to produce high-quality videos without needing advanced technical skills.
3. AI-Powered Image and Graphic Design
AI is transforming graphic design by enabling designers to use intelligent tools that can create logos, layouts, and visual elements automatically. AI systems can analyze current design trends and generate visually appealing graphics or adapt existing designs to different formats.
For example, AI can automatically resize images, adjust fonts, or create social media posts tailored to various platforms. Canva, Adobe Sensei, and Designify are tools that simplify design tasks, making it easier for both professionals and amateurs to create high-quality graphics.
4. AI for Music Composition
AI is making waves in the music industry by helping composers create original music. AI algorithms analyze musical patterns, structures, and styles to generate new compositions. These AI systems can create background music for videos, jingles for ads, or even full-length compositions that resemble particular genres or artists.
Platforms like Aiva, Amper Music, and OpenAI’s MuseNet offer AI-driven music composition, allowing content creators, advertisers, and filmmakers to quickly produce soundtracks that fit their needs without hiring a composer.
5. AI in Art Generation
AI-driven tools have enabled the creation of digital art that mimics traditional artistic styles or generates entirely new forms of artwork. These AI systems are trained on vast datasets of art history, enabling them to create pieces in the style of famous artists, generate surreal visuals, or even collaborate with human artists to produce new works.
DeepArt, Artbreeder, DALL-E, and NightCafe are examples of platforms that use AI to create custom digital artwork, which has applications in advertising, gaming, social media, and personal projects.
It is worth keeping in mind, however, that there are differing opinions about the use of AI to create art. Here’s an interesting article from the IEEE Computer Society that explains why some artists are angry about AI art if you’re interested.
6. AI for Content Curation and Personalization
AI is also being used to curate and personalize content for audiences. By analyzing user behavior, preferences, and engagement patterns, AI can recommend articles, videos, music, and other content that is most likely to interest individual users. This personalization helps increase user engagement and enhances the overall content consumption experience.
Platforms like Spotify, Netflix, YouTube, and Curio use AI to recommend content to users based on their previous interactions, creating a more personalized experience that encourages users to engage with more content.
7. AI for Interactive and Immersive Content
AI is enabling the creation of more interactive and immersive content, particularly in the fields of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). AI-powered systems help track user movements, create responsive virtual environments, and simulate realistic interactions. These technologies are being applied in gaming, education, marketing, and entertainment.
Companies like Oculus (Meta), Magic Leap, Unreal Engine, and Microsoft’s HoloLens use AI to power interactive and immersive VR/AR experiences, enhancing how users engage with content.
8. AI-Driven Language Translation and Localization
AI-driven language translation tools are revolutionizing content creation for global audiences by enabling real-time translations and content localization. AI can automatically translate text, audio, and video in multiple languages, making it easier for creators to reach diverse, international audiences.
Platforms like DeepL, Google Translate, and Meta’s No Language Left Behind initiative use AI to break down language barriers, allowing creators to publish content in multiple languages and reach a wider global audience.
9. AI in Podcasting and Audio Enhancement
AI is also being used to enhance audio content, such as podcasts and voiceovers. Tools like Eleven Labs, Descript, and Adobe Podcast Enhancer use AI to improve audio quality, remove noise, adjust levels, and even modify voice tones. This helps podcasters, content creators, and media producers create professional-quality audio content without requiring expensive equipment or expert-level skills.
AI platforms also provide automated transcription and editing features, saving time and effort for creators.
10. AI for Content Creation in Gaming
AI is playing a crucial role in video game development, particularly in creating immersive and dynamic environments. AI systems can generate procedurally created worlds, adapt to player actions, and even create narratives and quests.
Unity’s ML-Agents Toolkit and Phoenix from LunarTech are used for creating text for documents, speaking live with users, and enhancing content in various areas of gaming, social media, and digital marketing. AI in gaming elevates the user experience by making games more engaging and interactive.
11. AI for Social Media and SEO Optimization
AI tools like Copy.ai and Surfer SEO are widely used for drafting LinkedIn profiles, social media posts, and generating content that is optimized for high SEO rankings. These tools help users create engaging content that performs well in search engine results, enhancing visibility and engagement across platforms. Phoenix from LunarTech is especially helpful for businesses and professionals looking to improve their online presence and social media outreach.
AI engineering is revolutionizing content creation across multiple industries by providing powerful tools that enhance creativity, streamline workflows, and personalize experiences. From automated text generation to music composition, AI is enabling content creators to produce high-quality work more efficiently and effectively.
Platforms like Canva, Adobe Premiere Pro, Notion, DALL-E, Eleven Labs, Adobe Podcast Enhancer, Synthesia, Descript, Phoenix, Sora by OpenAI, and ChatGPT are just a few examples of how AI is improving everything from design and video editing to language translation and audio enhancement.
Also, Phoenix from LunarTech is advancing content creation by generating high-quality text for SEO, social media, speaking with documents live and much more.
As AI technology continues to evolve, it will likely unlock even more innovative possibilities for content creators, empowering them to push the boundaries of creativity and reach broader, more diverse audiences. Whether it’s creating immersive experiences, automating repetitive tasks, or personalizing content, AI is poised to continue reshaping the content creation landscape in profound ways.
AI Engineering in Entertainment
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the entertainment industry by delivering immersive, personalized experiences and streamlining creative processes. Companies like Netflix and Spotify use AI to recommend tailored content, while tools like Adobe Sensei automate editing tasks in visual and audio media. AI-driven innovations enhance efficiency, creativity, and user engagement across film, music, and gaming.
Major players are leveraging AI to adapt experiences to individual preferences and create dynamic, interactive content. Platforms like Twitch enhance content discovery and moderation, while gaming companies like Electronic Arts use AI for adaptive gameplay. Virtual and augmented reality powered by AI further push the boundaries of entertainment, offering unprecedented interactivity.
AI is also enabling entirely new forms of creativity, from AI-generated music and art to automated video production. Tools like Aiva and MidJourney democratize artistic expression, while AI-powered platforms ensure creators and consumers alike benefit from faster innovation and more engaging content.
1. Netflix (Personalized Recommendations and Content Creation)
Netflix uses AI extensively to personalize user experiences. Its recommendation engine leverages machine learning algorithms to analyze viewing history, user preferences, and even demographic data to suggest content. This personalization boosts user engagement by recommending shows and movies tailored to individual tastes.
Netflix also uses AI in production, where data-driven insights help determine the types of shows or films that are likely to resonate with different audiences. AI models analyze trends, demographics, and social media discussions to influence content decisions, from scriptwriting to casting choices. AI is also used in content optimization for streaming, adjusting video quality and buffering based on the user’s device and internet speed.
2. Spotify (Music Recommendation and Discovery)
Spotify uses AI and machine learning to create highly personalized playlists and recommendations for users. The platform’s playlists are generated using collaborative filtering and deep learning algorithms, which analyze listening habits, user behavior, and preferences to suggest new music.
Also, Spotify has explored AI for creating music, collaborating with AI music generator Endel to produce personalized soundscapes tailored to the user’s mood or activity, like relaxing, working, or focusing.
3. Disney (AI in Animation and Visual Effects)
Disney uses AI for various aspects of animation and visual effects. AI is used in creating realistic character animations by analyzing human movements and facial expressions, allowing animators to replicate them in digital characters more efficiently.
For instance, in a recent live-action adaptation, AI was used to create hyper-realistic animal movements, integrating deep learning to capture and mimic real-life animal behavior. AI also played a role in creating realistic simulations of snow, water, and other environmental effects in a popular animated movie.
4. Warner Music Group (AI for Music Production and Rights Management)
Warner Music Group is investing in AI to aid in music production and rights management. AI-driven tools analyze existing music tracks to help music producers craft songs that are likely to be hits based on trends, patterns, and past successful music data.
AI tools are also used to manage digital rights and detect copyright infringements by scanning online platforms for unauthorized uses of music content.
5. Electronic Arts (AI in Gaming and Game Development)
Electronic Arts (EA) uses AI to enhance gaming experiences in titles like FIFA and Madden NFL. AI-driven game physics and adaptive AI systems improve gameplay by creating more realistic player movements, team strategies, and in-game events. AI adjusts the difficulty level of the game based on the player’s skill, creating a more engaging and personalized experience.
AI also plays a key role in creating expansive and interactive game worlds, where content, such as landscapes or missions, can be procedurally generated based on AI algorithms.
6. DeepMind (AI for Gaming and Research)
DeepMind, a subsidiary of Alphabet (Google), gained global recognition for its program that defeated human world champions in the complex board game Go using deep reinforcement learning.
Another AI system developed by DeepMind demonstrated its potential in the real-time strategy game StarCraft II, where it used deep learning to make strategic decisions and adapt to evolving in-game scenarios, outperforming human players in certain situations.
7. Aiva Technologies (AI in Music Composition)
Aiva is an AI-powered music composition software used for creating original soundtracks and classical music. It uses deep learning algorithms trained on a vast dataset of classical music compositions to generate new compositions that mimic various styles, such as orchestral or film score music.
Aiva’s AI is capable of composing music for films, video games, advertisements, and other media, offering a creative tool for musicians, composers, and filmmakers.
8. SiriusXM (AI for Personalized Audio and Content Curation)
SiriusXM uses AI to enhance its music and audio streaming services by curating personalized channels based on listening history and user preferences. This technology helps deliver tailored radio stations, podcasts, and music channels that align with the tastes of individual users.
AI is also used for voice recognition in its app, which enables hands-free control of radio stations, music, and other services using natural language processing to understand and respond to voice commands.
9. ObEN (AI in Virtual Celebrities and Personalized Digital Avatars)
ObEN creates personalized AI-powered avatars and virtual celebrities. These avatars use AI, voice recognition, and deep learning to replicate real people’s voices, appearances, and personalities.
These avatars can be used in entertainment, virtual performances, advertising, and social media as virtual influencers, interacting with audiences and creating content that feels natural and human-like.
10. Adobe (AI for Content Creation and Editing)
Adobe has integrated AI into its products like Photoshop, Premiere Pro, and After Effects through its Sensei framework. AI tools such as Content-Aware Fill (which removes unwanted objects from images) and Auto Reframe (which automatically adjusts video content for different screen sizes) are powered by this AI framework.
AI-Assisted Video Editing is another key feature where Adobe Premiere Pro uses AI to suggest video edits based on a user’s preferences, saving time in video production. AI also helps in automating color grading, adjusting audio, and enhancing footage quality.
11. Twitch (AI for Gaming Streamer Discovery and Content Moderation)
Twitch, the popular live-streaming platform, uses AI for streamer discovery and content moderation. The platform’s AI-driven recommendation system analyzes user preferences, viewing history, and trends to suggest streams that users are likely to enjoy.
Twitch also employs AI tools to detect inappropriate content and provide real-time moderation in chatrooms during live streams, filtering harmful messages, spam, and abusive language.
12. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Gaming
AI is also used in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) to enhance user immersion and interaction. Companies like Meta (formerly Facebook) and Microsoft utilize AI in VR and AR to track user movements and adapt virtual environments in real-time, offering a highly interactive experience.
AI helps in understanding and interacting with the real world, overlaying virtual objects and animations on top of physical environments with the technology adjusting the interaction based on context, location, and the user’s actions.
13. Runway (AI in Creative Video Production)
Runway is an AI-powered creative suite for video production and media creation. It uses machine learning models to enable creators to generate video content from text prompts, perform real-time video editing, and remove objects from footage.
Runway’s AI tools can analyze scripts, generate scenes based on user descriptions, or even provide automatic video edits, streamlining the content creation process for filmmakers, marketers, and media producers.
AI Engineering in Autonomous Vehicles
AI engineering plays a pivotal role in the development of autonomous vehicles (AVs), enabling these vehicles to navigate safely, efficiently, and autonomously.
AI technologies, such as computer vision, machine learning, and deep learning, are used to process vast amounts of data from sensors, cameras, and other sources to make real-time driving decisions.
Below are specific examples of companies leading the development of autonomous vehicles and their AI-driven products:
1. Waymo (Self-Driving Technology)
Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet (Google’s parent company), is a leader in autonomous driving technology. Their autonomous ride-hailing service, Waymo One, uses a combination of AI, machine learning, and computer vision to operate fully autonomous vehicles in certain cities.
Waymo’s AI system processes data from a suite of sensors, including LiDAR, radar, and cameras, to detect pedestrians, vehicles, traffic signs, and other obstacles. The system makes real-time decisions about speed, lane positioning, and navigation to ensure safety and efficiency.
2. Tesla (Autopilot and Full Self-Driving)
Tesla is well-known for its electric vehicles, and its Autopilot system is one of the most advanced semi-autonomous driving systems available. The system uses AI-powered neural networks to analyze camera feeds, radar data, and other sensors to provide features such as lane-keeping, adaptive cruise control, and automatic lane changes.
Tesla is continuously developing Full Self-Driving (FSD) technology, which aims to enable fully autonomous driving. The FSD system relies heavily on AI and deep learning to make decisions on navigation, traffic signal recognition, and even urban driving scenarios.
3. Cruise (Autonomous Ride-Hailing)
Cruise, acquired by General Motors, is developing the Cruise Origin, a fully autonomous, electric vehicle designed for ride-hailing services. The vehicle is built from the ground up for autonomy, with no steering wheel or pedals, and relies on AI to navigate and operate safely.
The Cruise Origin uses a combination of LiDAR, cameras, and radar to sense its surroundings. AI algorithms process this data to detect objects, recognize road signs, and plan driving routes, allowing the vehicle to navigate urban environments and make real-time decisions.
4. Aurora (Autonomous Trucks and Vehicles)
Aurora is an autonomous technology company focused on both passenger vehicles and freight transport. Their Aurora Driver system is designed to power autonomous trucks and passenger vehicles. The system uses AI to interpret sensor data, make real-time driving decisions, and handle complex tasks such as lane merging, obstacle detection, and highway navigation.
Aurora has partnered with companies like Uber Freight to develop autonomous long-haul trucking solutions, enabling more efficient and safer freight transport with the help of AI and robotics.
5. Aptiv (Autonomous Driving Systems for Vehicles)
Aptiv is a global technology company that develops autonomous driving systems. Its Aptiv Self-Driving System integrates AI, sensor fusion, and machine learning to provide autonomous vehicle capabilities. The system includes features such as lane-keeping assistance, automatic emergency braking, and adaptive cruise control.
Aptiv has partnered with Lyft to operate a self-driving taxi service in Las Vegas, where AI algorithms control the vehicles, allowing them to safely navigate the city’s streets and respond to dynamic road conditions.
6. Mobileye (AI for Autonomous Vehicles)
Mobileye, an Intel company, is a pioneer in vision-based autonomous driving technology. Their EyeQ platform uses computer vision and AI to process data from cameras and sensors in real-time. The system is capable of detecting pedestrians, cyclists, vehicles, and road signs, helping the vehicle make safe and efficient driving decisions.
Mobileye Drive is the company’s full-stack autonomous driving system, which combines AI, machine learning, sensor fusion, and mapping to enable autonomous vehicles. Mobileye’s system is used by several major automakers to integrate semi-autonomous driving capabilities into their vehicles.
7. Zoox (Autonomous Electric Vehicles)
Zoox, acquired by Amazon, is developing a bidirectional, fully autonomous vehicle designed for ride-hailing services. The Zoox Robotaxi has no driver’s seat, steering wheel, or pedals, as it is fully designed to operate autonomously with AI systems guiding the vehicle.
The vehicle uses advanced AI algorithms for navigation, decision-making, and safety, processing data from LiDAR, radar, and cameras to detect objects, plan routes, and safely interact with pedestrians and other vehicles.
8. Nuro (Autonomous Delivery Vehicles)
Nuro focuses on developing small, autonomous vehicles specifically for last-mile delivery. The Nuro R2 is a compact, electric, self-driving vehicle designed to deliver goods such as groceries and packages. Unlike traditional cars, the Nuro R2 has no seats or driver’s cabin, as its primary function is to transport goods.
Nuro uses AI for navigation, object detection, and collision avoidance. Its system processes data from multiple sensors and cameras to ensure safe and efficient deliveries, making autonomous last-mile delivery more feasible.
9. Baidu (AI for Autonomous Driving in China)
Baidu is a leading tech company in China that has developed the Apollo autonomous driving platform. Their Apollo Go service is a fully autonomous taxi platform launched in several Chinese cities. The service uses AI to navigate urban roads, manage traffic scenarios, and handle passenger pickups and drop-offs.
The Apollo platform leverages deep learning, machine vision, and sensor fusion to enable autonomous driving in complex, urban environments. The system can identify pedestrians, cyclists, and other vehicles, making it a comprehensive solution for autonomous mobility.
10. Uber ATG (Autonomous Vehicles for Ride-Hailing)
Uber ATG (Advanced Technologies Group) has been working on self-driving technology, with its autonomous vehicles being equipped with AI and sensor systems for navigation. The vehicles use AI to process data from LiDAR, radar, and cameras to safely navigate urban streets, detect obstacles, and plan efficient routes.
Although Uber has sold its self-driving unit to Aurora, its AI-driven autonomous driving technology has influenced ride-hailing services and continues to play a role in the development of autonomous transportation.
11. Pony.ai (Autonomous Ride-Hailing and Freight)
Pony.ai is a Chinese-American company focused on developing autonomous driving technology for both ride-hailing and freight logistics. Its autonomous vehicles use AI for real-time decision-making, obstacle detection, and navigation in both urban and highway environments.
Pony.ai operates autonomous ride-hailing services in several cities in China and the U.S., where the AI-powered vehicles make decisions based on sensor data to navigate traffic and ensure passenger safety.
12. Motional (Autonomous Vehicles for Ride-Hailing)
Motional, a joint venture between Lyft and Aptiv, is developing autonomous vehicles for ride-hailing services. Their Ioniq 5 Robotaxi, based on Hyundai’s Ioniq 5 electric vehicle, is equipped with a full suite of sensors, cameras, and AI-driven systems for safe, driverless operation.
Motional’s AI system handles navigation, traffic interaction, and obstacle avoidance. The robotaxi is part of a pilot project in Las Vegas, where passengers can book autonomous rides via the Lyft app.
AI engineering in autonomous vehicles is the backbone of making self-driving cars a reality. From autonomous ride-hailing services to freight and delivery applications, AI plays a central role in helping these vehicles navigate, make decisions, and interact safely with their environments.
Companies like Waymo, Tesla, Cruise, and Aurora are pushing the boundaries of AI in transportation, enhancing the safety, efficiency, and accessibility of autonomous mobility systems. AI enables real-time data processing, decision-making, and continuous learning, ensuring that autonomous vehicles can function safely in a wide range of environments.
AI Engineering in Robotics
AI engineering drives innovation in robotics across multiple sectors. It has made significant strides across multiple industries, with agriculture, healthcare, manufacturing, logistics, and autonomous vehicles being some of the most prominent sectors benefiting from robotics powered by artificial intelligence.
Below are specific examples of companies that are leveraging AI and robotics technologies to create innovative solutions, with details about their products and applications:
1. Boston Dynamics (Robotics for Mobility and Automation)
Boston Dynamics is a leader in robotics, particularly known for its robots’ mobility and advanced AI capabilities. Spot is a quadruped robot equipped with AI that allows it to navigate complex environments. It is used in a variety of applications, including industrial inspections, security, and research. Spot can move over rough terrain, avoid obstacles, and even open doors.
Stretch is a robot designed for material handling in warehouses, equipped with an AI-powered robotic arm and a vision system that enables it to identify and manipulate boxes efficiently.
Atlas is a humanoid robot capable of complex physical tasks, such as running, jumping, and performing backflips. It showcases advanced AI in movement, balance, and coordination, which can be applied to emergency rescue operations, construction sites, and other challenging environments.
2. UiPath (AI Robotics Process Automation)
UiPath is a leading company in Robotic Process Automation (RPA), utilizing AI to automate business workflows. The UiPath RPA Platform enables enterprises to use AI-powered robots for automating repetitive, manual tasks like data entry, document processing, and customer service. These robots are capable of learning from their environment, improving efficiency, and reducing human error.
The AI integration allows these robots to understand unstructured data and adapt to new processes, making RPA more intelligent and versatile.
3. ABB (Industrial Robotics and AI Integration)
ABB is a global leader in industrial automation and robotics, developing intelligent robots for manufacturing, assembly, and other industrial applications. Their YuMi robot is a collaborative robot (cobot) designed for assembly tasks, equipped with advanced AI algorithms that enable it to work safely alongside humans without barriers. It can handle small components and perform precision tasks in industries like electronics and automotive.
IRB 6700 is a powerful industrial robot used for tasks like welding, material handling, and packaging. It integrates AI to improve efficiency, reduce cycle times, and enable high precision.
Ability™ is ABB’s cloud-based platform for robotics that integrates AI to allow robots to learn from data and improve over time, enhancing automation across various industries.
4. iRobot (Home Robots Powered by AI)
iRobot is well-known for its home cleaning robots. Their Roomba vacuum cleaners use AI and machine learning to map the layout of a home, detect dirt, and optimize cleaning paths. The AI algorithms also enable Roomba to learn from its environment, avoiding obstacles, adjusting cleaning patterns, and returning to its charging dock autonomously.
Braava is iRobot’s robotic mop that similarly uses AI for intelligent navigation, effectively cleaning floors while adapting to the layout of the home.
5. Savioke (Service Robots for Hospitality)
Savioke is a robotics company specializing in service robots. Relay is an AI-powered robot designed for hotel deliveries. It can autonomously navigate hotel hallways to deliver amenities like towels, toiletries, and food to guests. The robot uses AI for navigation, obstacle avoidance, and communication with guests through touchscreens and voice commands.
Relay’s ability to navigate complex environments, adjust to obstacles, and deliver personalized services represents a growing trend in customer-facing robots in the service industry.
6. Fetch Robotics (Warehouse Robotics and Automation)
Fetch Robotics provides autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) designed for warehouse and logistics applications. Their robots, such as Freight and Fetch, use AI to navigate through complex environments, pick up and transport items, and collaborate with human workers. AI-powered algorithms enable the robots to optimize their routes, avoid obstacles, and perform tasks like material handling and order fulfillment.
The robots can be integrated with warehouse management systems to increase operational efficiency, reduce errors, and improve safety.
7. Rethink Robotics (Collaborative Industrial Robotics)
Rethink Robotics is known for its collaborative robots (cobots), Baxter and Sawyer, which use AI to work alongside human operators in manufacturing and industrial environments. These robots are designed to be flexible, adaptable, and easy to program for tasks like assembly, packaging, and quality control.
Baxter is known for its user-friendly interface, which allows operators to teach the robot new tasks simply by guiding its arms through the desired motions. Sawyer, a more precise and dexterous robot, is used for tasks requiring fine motor skills, such as electronics assembly and inspection.
8. Clearpath Robotics (Autonomous Robotics for Industrial and Research Use)
Clearpath Robotics focuses on autonomous mobile robots for industrial and research applications. OTTO is an AI-powered robot designed for material transport in warehouses and factories. It uses AI to navigate environments, avoid obstacles, and optimize its routes, improving the efficiency of goods transportation.
Husky is a rugged robot designed for research and fieldwork, capable of navigating tough terrain and carrying heavy payloads. It’s often used in academic research, agriculture, and other outdoor applications.
9. Miso Robotics (AI for Food Industry Robotics)
Miso Robotics focuses on robotics for the food industry. Flippy is an AI-powered robot designed to assist with cooking tasks, such as flipping burgers and frying food. It uses machine learning algorithms to adapt to cooking times, temperatures, and food types, ensuring consistency and quality while reducing the risk of human error.
CookRight is a similar system that uses AI to optimize cooking processes, ensuring the right flavor, texture, and doneness for each dish.
10. Nuro (Autonomous Delivery Robots)
Nuro is a robotics company specializing in autonomous delivery vehicles. R2 is a small, fully autonomous vehicle designed to deliver goods such as groceries, food, and packages. Using AI, it navigates streets and interacts with traffic in a safe and efficient manner. The vehicle is designed for last-mile delivery, reducing the need for human drivers and improving delivery efficiency.
Nuro’s autonomous delivery system is already being tested in collaboration with companies like Domino’s and Kroger for food and grocery delivery.
11. Intuitive Surgical (Robotics for Surgery)
Intuitive Surgical is a leader in robotic-assisted surgery with its da Vinci Surgical System. The system uses AI to provide enhanced vision, precision, and control during surgeries. Surgeons use the robotic arms to perform minimally invasive procedures with high precision, while AI helps with real-time adjustments based on the patient’s anatomy and the surgeon’s commands.
AI-enhanced robotic surgery allows for less-invasive operations, faster recovery times, and better outcomes.
12. Knightscope (Security Robotics)
Knightscope develops autonomous security robots that patrol premises and provide real-time data on security threats. They’re robots, such as K5 (a stationary patrol robot) and K3 (a mobile robot), use AI to detect suspicious behavior, analyze video footage, and integrate with security systems. These robots are equipped with sensors and cameras for facial recognition, license plate recognition, and anomaly detection. Knightscope’s robots help businesses improve security while reducing the need for human security personnel in routine patrols.
AI engineering in robotics is transforming industries by improving efficiency, safety, and automation. The robots mentioned above use AI for tasks like navigation, task optimization, object recognition, and decision-making. From industrial applications in warehouses and manufacturing to healthcare and autonomous vehicles, AI-powered robotics is enhancing productivity and introducing new capabilities across sectors.
These examples illustrate how AI is not just enabling robots to perform tasks, but allowing them to learn, adapt, and collaborate with humans, offering significant improvements over traditional methods.
AI Engineering in Agriculture
AI engineering is being applied in agritech by many companies around the world, leveraging advanced technologies like machine learning, computer vision, and robotics to enhance productivity, sustainability, and efficiency in agriculture.
Here’s a full book that explores the benefits of using AI tools in agriculture that can give you more detailed insights.
And here are a few specific examples of companies and their AI-driven products:
1. John Deere (Precision Agriculture and Autonomous Tractors)
John Deere is a leading company in precision agriculture. Their See & Spray technology uses computer vision and AI to detect weeds in fields and apply herbicides precisely where needed, reducing pesticide use. The system uses cameras and machine learning algorithms to identify plants, distinguishing between crops and weeds.
John Deere is also working on autonomous tractors equipped with AI and machine learning. These tractors can operate without human intervention, increasing efficiency in tasks like plowing, planting, and spraying.
2. Corteva Agriscience (AI for Crop Protection)
Corteva, a global agricultural science company, uses AI in several applications. Their Granular platform leverages AI and machine learning to provide farmers with insights on how to manage their operations better. It helps optimize yield predictions, fertilizer applications, and field management practices.
Rivalus, a data-driven platform developed by Corteva, uses AI to assess crop health, predict outcomes, and give real-time advice on agricultural practices like planting and irrigation.
3. Blue River Technology (AI-Powered Weed Control)
Acquired by John Deere, Blue River Technology is known for its See & Spray system, which uses machine learning and computer vision to identify weeds in real time. The system applies herbicides only where needed, reducing chemical use and minimizing environmental impact.
This technology enables precision herbicide application, saving farmers money and reducing environmental harm. The AI system identifies crops and weeds by analyzing video footage captured by cameras mounted on tractors.
4. The Climate Corporation (Data-Driven Crop Management)
The Climate Corporation, a subsidiary of Bayer, offers the Climate FieldView platform, which integrates AI to provide farmers with real-time insights on field health. It helps farmers optimize planting decisions, track crop health, and predict potential yield outcomes.
FieldView’s AI algorithms use weather data, satellite imagery, and field sensors to analyze soil moisture, temperature, and crop stress, providing actionable recommendations on irrigation, planting, and fertilization.
5. Pessl Instruments (AI for Farm Monitoring)
Pessl Instruments specializes in farm monitoring solutions. Their MeteoSmart weather stations and FieldClimate platform use AI to monitor various environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, rainfall, and soil conditions. These insights help farmers make informed decisions regarding irrigation, pesticide use, and planting schedules.
AI models integrated into the system predict weather patterns and optimize resource allocation, reducing waste and improving crop productivity.
6. Aker Technologies (AI and Robotics for Livestock Management)
Aker Technologies focuses on AI solutions for livestock farming. Their AI-powered livestock monitoring system uses sensors and cameras to track animal behavior and health. The system detects signs of illness early, monitors reproductive cycles, and tracks growth rates, ensuring better overall herd management.
The system helps farmers improve animal welfare by providing timely alerts about potential health issues and optimizing breeding programs.
7. Ripe Robotics (AI-Powered Harvesting Robots)
Ripe Robotics develops AI-powered robots for harvesting crops like tomatoes and cucumbers. The robots are equipped with computer vision to identify ripe fruits and autonomously pick them without damaging the plant or the produce.
The system uses machine learning algorithms to continuously improve its fruit identification and harvesting process, allowing for more efficient, precise harvesting, especially in environments with labor shortages.
8. Farmwise (Autonomous Weeding Robots)
Farmwise uses autonomous robots equipped with AI to remove weeds from crops. The robots use computer vision to distinguish between crops and weeds and remove the weeds using mechanical tools, without the use of chemicals. This reduces herbicide use, minimizes soil disruption, and promotes sustainable farming.
The technology is particularly useful in vegetable farming, where precision and minimal disruption are critical for crop health.
9. Taranis (AI for Crop Scouting and Pest Detection)
Taranis uses AI-powered imagery analysis to help farmers monitor crop health and detect pests or diseases. Their platform collects high-resolution images via drones, planes, and satellites, then uses AI to identify any potential issues such as pests, fungal infections, or nutrient deficiencies.
Taranis’ system also analyzes weather and climate data to predict pest infestations and provide advice on preventing damage, allowing farmers to respond proactively.
10. IBM (AI and Blockchain for Agricultural Supply Chain)
IBM is using AI in agritech through its Watson Decision Platform for Agriculture, which integrates AI, weather forecasting, blockchain, and IoT to provide farmers with actionable insights to optimize their farming practices. The platform analyzes data from various sources to guide decisions on irrigation, planting, and pest management.
The IBM Food Trust blockchain technology ensures traceability of food products throughout the supply chain, improving transparency and sustainability from farm to table.
11. Prospera Technologies (AI for Crop Health and Yield Prediction)
Prospera Technologies provides a machine learning-powered platform for crop monitoring and yield prediction. The platform uses computer vision and AI to analyze visual data from fields and provide insights on plant health, pest detection, and nutrient deficiencies.
Prospera’s system can predict the future health of crops based on historical and real-time data, allowing farmers to take preventative actions early and optimize crop management practices.
These companies are at the forefront of integrating AI technologies into the agritech sector, applying them to a variety of challenges in agriculture—from crop management to livestock monitoring, and from pest control to supply chain optimization. The implementation of AI not only improves efficiency but also makes farming more sustainable, reducing chemical use, conserving resources, and enhancing overall productivity.
Wrapping Up
You are venturing into a career path in AI engineering that demands rigorous effort and encompasses a wide range of complex skills, from mathematics and programming to the deployment of advanced models. This handbook has guided you through these fundamentals, illustrating how they merge to form the core of robust AI solutions. Beyond tools and technologies, you are expected to cultivate disciplined thinking, uphold ethical standards, and remain flexible in one of the fastest-evolving industries today.
You have seen that developing expertise in areas like machine learning, generative AI, and LLMs can be particularly challenging. The subject matter insists on constant study and reinforcement, and the rapid pace of AI means you must stay current with new trends and approaches. The journey can be energy-intensive, but it lays a solid foundation for those who want to excel and ultimately outshine the competition.
You will also find abundant opportunities on the horizon. The AI market is set to expand significantly over the next few years, indicating numerous paths for your professional growth. Yet you should be prepared for more than just acquiring theoretical knowledge: the key lies in blending hard work, resilience, and hands-on practice so that your skill set truly stands out.
As your capabilities grow, you may discover strong demand for your expertise across a variety of sectors. In fact, you can even convert your knowledge into launching new products or ventures of your own. Your evolution from an enthusiastic learner to a trusted industry specialist rests on disciplined learning, consistent upskilling, and an ongoing drive to innovate.
This handbook has consistently emphasized building strong foundations—ranging from solid math and data structures to cutting-edge neural architectures and deployment know-how. These elements go hand in hand with a focus on ethical considerations and sustainability, aspects often just as critical as sheer technical prowess.
Ultimately, your success in AI engineering will depend on merging theoretical rigor with creative problem-solving, while also recognizing the far-reaching implications of these technologies. By applying the skills you have gained, you position yourself at the forefront of an ever-changing field. Through sustained commitment, a willingness to learn, and genuine initiative, you will forge a career that not only propels you forward but also shapes the future of AI.
About the Author
Tatev Aslanyan is a Senior Machine Learning and AI Engineer, CEO, and Co-founder of LunarTech, a Deep Tech Innovation startup committed to making Data Science and AI accessible globally. With over 6 years of experience in AI engineering and Data Science, Tatev has worked in the US, UK, Canada, and the Netherlands, applying her expertise to advance AI solutions in diverse industries.
Tatev holds an MSc and BSc in Econometrics and Operational Research from top tier Dutch Universities, and has authored several scientific papers in Natural Language Processing (NLP), Machine Learning, and Recommender Systems, published in respected US scientific journals.
As a top open-source contributor, Tatev has co-authored courses and books, including resources on freeCodeCamp for 2024, and has played a pivotal role in educating over 30,000 learners across 144 countries through LunarTech‘s programs.
LunarTech is Deep Tech innovation company building AI-powered products and delivering educational tools to help enterprises and people innovate, reducing operational costs and increasing profitability.
Connect With Us
-
Connect with me on LinkedIn
-
Check out YouTube Channel
-
Subscribe to LunarTech Newsletter or LENS – Our News Channel
Want to discover everything about a career in Data Science, Machine Learning and AI, and learn how to secure a Data Science job? Download this free Data Science and AI Career Handbook.
Thank you for choosing this guide as your learning companion. As you continue to explore the vast field of Artificial Intelligence, I hope you do so with confidence, precision, and an innovative spirit.
AI Engineering Bootcamp by LunarTech
If you are serious about becoming an AI Engineer and want an all-in-one bootcamp that combines deep theory with hands-on practice, then check out the LunarTech AI Engineering Bootcamp focused on Generative AI. This is a comprehensive and advanced program in AI Engineering, designed to equip you with everything you need to thrive in the most competitive AI roles and industries.
In just 3 to 6 months self-phased or cohort-based, you will learn Generative AI and foundational models like VAEs, GANs, transformers, and LLMs. Dive deep into mathematics, statistics, architecture, and the technical nuances of training these models using industry-standard frameworks like PyTorch and TensorFlow.
The curriculum includes pre-training, fine-tuning, prompt engineering, quantization, and optimization of large models, alongside cutting-edge techniques such as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAGs).
This Bootcamp positions you to bridge the gap between research and real-world applications, empowering you to design impactful solutions while building a stellar portfolio filled with advanced projects.
The program also prioritizes AI Ethics, preparing you to create sustainable, ethical models that align with responsible AI principles. This isn’t just another course—it’s a comprehensive journey designed to make you a leader in the AI revolution. Check out the Curriculum here
Spots are limited, and the demand for skilled AI engineers is higher than ever. Don’t wait—your future in AI engineering starts now. You can Apply Here.
“Let’s Build The Future Together!“ – Tatev Aslanyan, CEO and Co-Founder at LunarTech
Source: freeCodeCamp Programming Tutorials: Python, JavaScript, Git & MoreÂ