Subdomains are an essential part of a website’s infrastructure. They provide additional functions in a web application, such as APIs, admin portals, and staging environments.
As an ethical hacker, discovering subdomains is a critical step in learning the attack surface of a target. Subdomains might not be protected well, unlike the main domain. So they can be a great entry point for security auditing or bug bounty programs.
In this article, I’ll walk you through how to find subdomains using multiple methods. We will use tesla.com as our example in subdomain research.
Note: tesla.com is part of bug bounty programs, so we have permission to scan it for subdomains. If you are doing this in another web application, make sure you have permission.
Crt.sh
One of the easiest ways to start is by checking Certificate Transparency (CT) logs using crt.sh. This website records every SSL/TLS certificate issued for a domain, including subdomains.
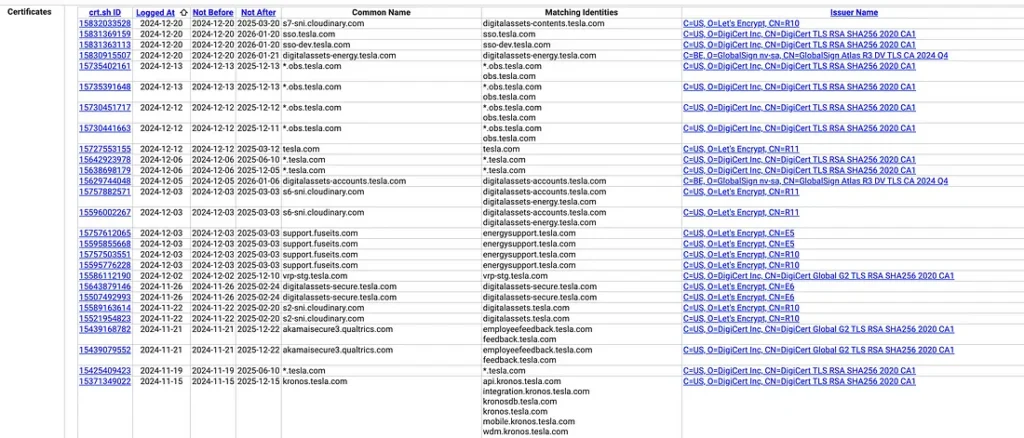
To search for Tesla’s subdomains, visit crt.sh and enter %.tesla.com as the query. The % acts as a wildcard to match any subdomains.
Let’s look at the results:
We can see a lot of interesting subdomains listed in the results. These subdomains may belong to different parts of Tesla’s infrastructure.
For example, shop.tesla.com is likely for their online store, while api.tesla.com could host application programming interfaces.
Using crt.sh is passive, meaning it doesn’t interact with the target, making it both safe and stealthy.
Note that crt.sh will only display subdomains that have valid certificates. If a subdomain uses self-signed certificates or doesn’t use SSL/TLS at all, it may not appear in these logs. Despite this limitation, crt.sh remains a quick and efficient starting point for subdomain enumeration.
Sublist3r
Sublist3r is an open-source tool to automate finding subdomains. It’s helpful in both security assessments and general reconnaissance.
By using multiple search engines (like Google, Bing, Yahoo, and more) Sublist3r finds subdomains that might otherwise remain hidden.
Sublist3r’s command-line interface is simple to use — you give it a domain, and Sublist3r goes to work.
Thanks to its open-source nature, it’s actively maintained and improved by the security community.
Sublist3r is not pre-installed on Kali, so lets go ahead and install it. First, clone the repository and install the requirements:
git clone https://github.com/aboul3la/Sublist3r.git
cd Sublist3r
sudo pip install -r requirements.txt
Now we are ready to use the sublist3r tool. Here is the syntax to use sublist3r:
python sublist3r.py -d tesla.com
After a few minutes, Sublist3r will return a list of discovered subdomains. The -d flag tells sublist3r that the domain to use is tesla.com
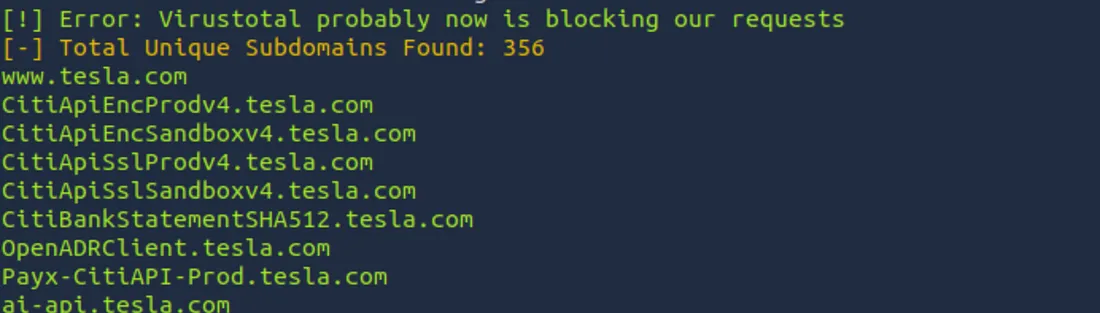
You can see that sublist3r has found more than 300 subdomains of tesla.com. Sublist3r is an excellent way to jump-start the recon process, especially if you want to automate the collection of subdomains without installing numerous separate tools.
Note that Sublist3r relies on the APIs of these search engines and other data sources. So it can sometimes miss subdomains that haven’t been crawled or indexed.
Google Dorking
Google dorking (sometimes called “Google hacking”) refers to the practice of using special search queries on Google. These operators help to find hidden information, sensitive data, or other resources that would otherwise be hard to locate.
Common operators include site:, inurl:, filetype:, and intitle:, among many others. Let’s start with the site: operator:
site:*.tesla.com
This query searches for any subdomain of tesla.com. Here are some search results.
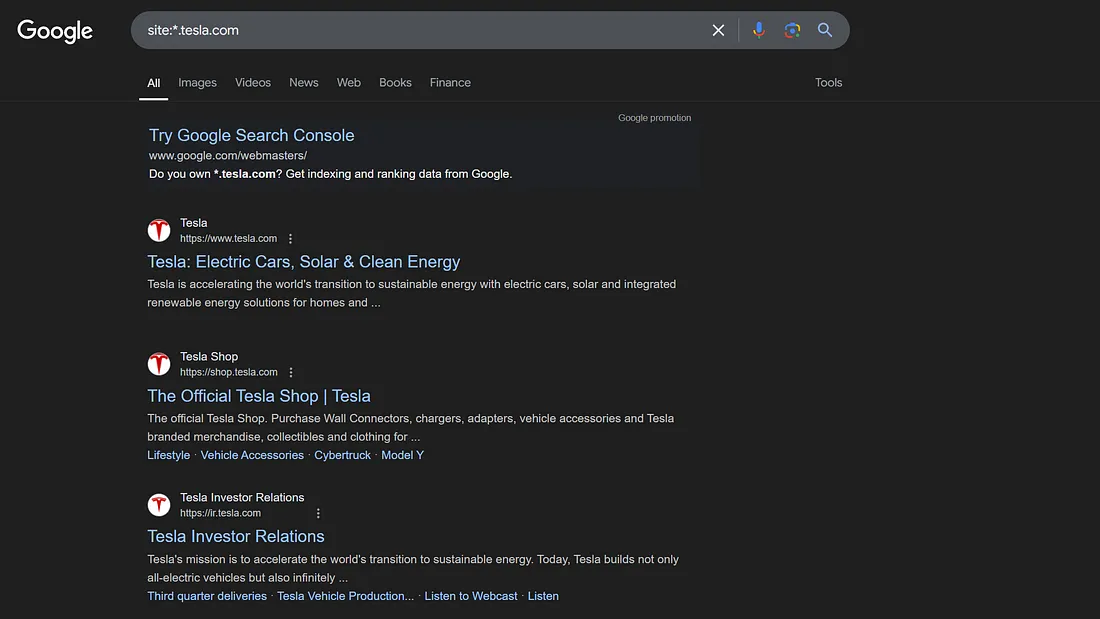
To dig deeper, try combining site: with other operators. For example, we can use the inurl operator with the keyword ‘admin’ to find URLs containing the word admin.
site:*.tesla.com inurl:admi
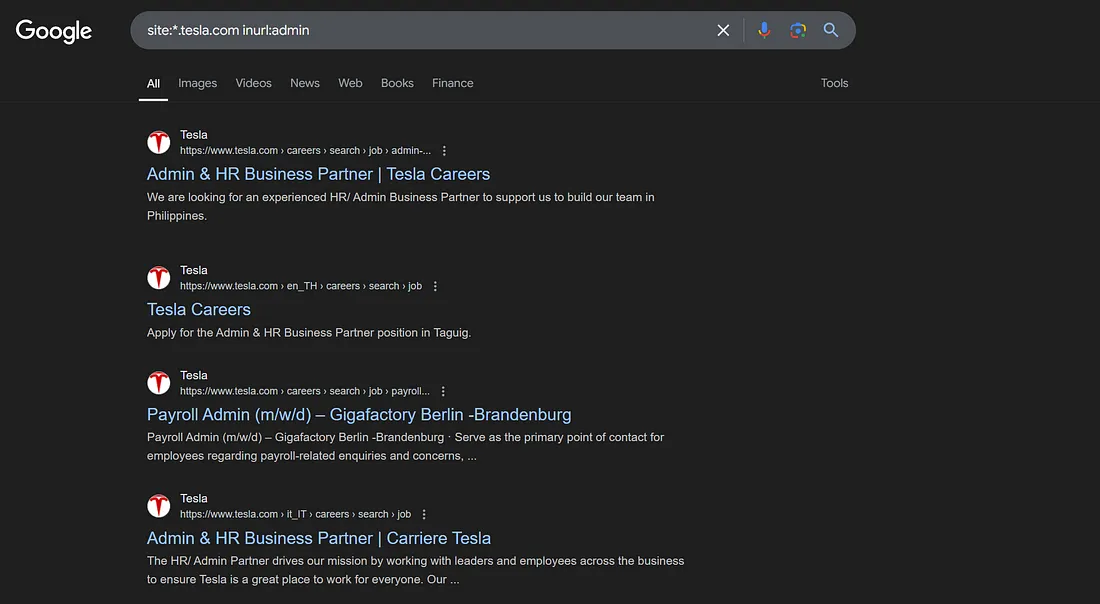
By using these operators (known as Google dorks), you can filter search results to find specific file types, directories, or even private information that may be unintentionally exposed on the internet.
Dorking can produce a lot of data, so you may need to carefully filter your searches to avoid getting flooded with irrelevant information.
Here is a full tutorial on Google dorking.
Fuzzing with GoBuster
Now what if the subdomains of a target are not listed anywhere on the internet? We fuzz for it.
Fuzzing is simply brute-forcing potential subdomain names by trying combinations from a wordlist. A wordlist is a list of words that we will use along with the fuzzing tool to see if a subdomain exists.
A subdomain wordlist can contain words like:
ftp
root
admin
portal
api
Tools like Gobuster and Ffuf can use a wordlist to check whether these subdomains exist. Here is a sample subdomain wordlist.
How Gobuster Works
Gobuster is a fast brute-force tool for discovering hidden URLs, files, and directories within websites.
Ffuf is a wonderful web fuzzer, but Gobuster is a faster and more flexible alternative. Gobuster has support for extensions with which we can increase its capabilities.
Gobuster also can scale using multiple threads and perform parallel scans to speed up results.
Gobuster comes pre-installed in Kali Linux. Let’s run the following command to look for subdomains. You can find the word list under /usr/share/wordlists/SecLists in Kali Linux.
gobuster dns -d tesla.com -w /usr/share/wordlists/SecLists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-110000.txt
The above command checks each word in the wordlist to see if it resolves to a valid subdomain. Here’s a sample output:
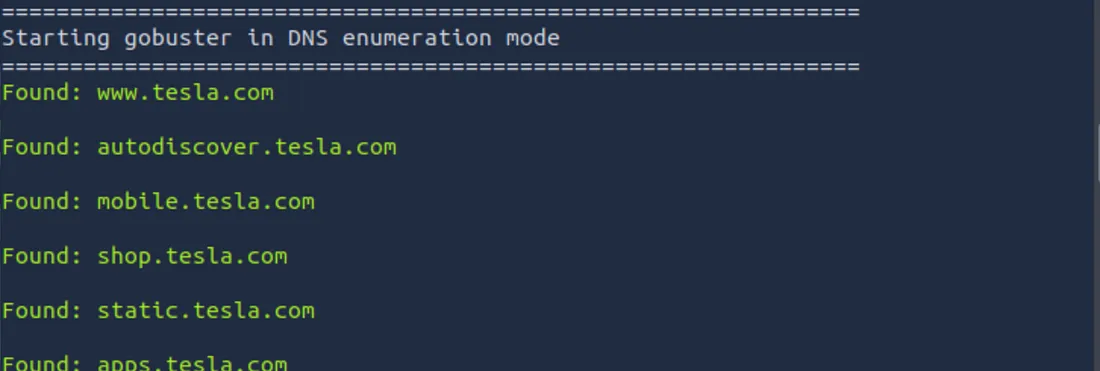
Gobuster’s results show valid subdomains, including some that might not appear in public databases, like staging.tesla.com or dev.tesla.com.
Fuzzing should be combined with other methods since the results are only as good as the wordlist. For example, prod-version-2.tesla.com can be a subdomain which may not be a part of the wordlist.
Other Methods for Subdomain Discovery
DNS Zone Transfers
While rare, misconfigured DNS servers can allow zone transfers, revealing all subdomains at once. You can test this using dig:
dig axfr @ns1.tesla.com tesla.com
If the server is properly secured, it won’t allow a zone transfer. But if it’s misconfigured, you might uncover every subdomain Tesla uses.
Online Tools
Websites like SecurityTrails, Shodan, and Censys aggregate subdomain data. These tools provide a centralized view of publicly available information.
Inspecting JavaScript Files
Subdomains often appear in a website’s JavaScript files. By examining Tesla’s website, you might find references to API endpoints or other subdomains.
Post-Subdomain Discovery
Once you have a list of subdomains, we can probe them further. We may discover sign-in portals, development pages, or API endpoints.
Ethical hackers typically use port scanning and service enumeration tools like Nmap and Nikto to find the open ports and running services on each subdomain. Identifying outdated software, insecure protocols, or default credentials is often the next critical step, as these are common weak points in any environment.
Subdomains often show us the broader infrastructure of the website if they are left unprotected.
Conclusion
Subdomain discovery is a critical skill for ethical hackers. It helps us understand the complete picture of a web application. The more we know, the better entry points we have to gain access.
Before using these techniques, always ensure you have proper authorization. Subdomain discovery helps with security audits by uncovering hidden assets and helping organizations protect themselves from potential threats.
For more practical tutorials on cybersecurity, join our weekly newsletter. If you want to practice these subdomain discovery techniques through a hands-on lab, join us at the Hacker’s Hub.
Source: freeCodeCamp Programming Tutorials: Python, JavaScript, Git & MoreÂ