

Chemical synthesis is essential in developing new molecules for medical applications, materials science, and fine chemicals. This process, which involves planning chemical reactions to create desired target molecules, has traditionally relied on human expertise. Recent advancements have turned to computational methods to enhance the efficiency of retrosynthesis—working backward from a target molecule to determine the series of reactions needed to synthesize it. By leveraging modern computational techniques, researchers aim to solve long-standing bottlenecks in synthetic chemistry, making these processes faster and more accurate.
One of the critical challenges in retrosynthesis is accurately predicting chemical reactions that are rare or less frequently encountered. These reactions, although uncommon, are vital for designing novel chemical pathways. Traditional machine-learning models often fail to predict these reactions due to insufficient representation in training data. Also, multi-step retrosynthesis planning errors can cascade, leading to invalid synthetic routes. This limitation hinders the ability to explore innovative and diverse pathways for chemical synthesis, particularly in cases requiring uncommon reactions.
Existing computational methods for retrosynthesis have primarily focused on single-step models or rule-based expert systems. These methods rely on pre-defined rules or extensive training datasets, which limits their adaptability to new and unique reaction types. For instance, some approaches use graph-based or sequence-based models to predict the most likely transformations. While these methods have improved accuracy for common reactions, they often need more flexibility to account for the complexities and nuances of rare chemical transformations, leading to a gap in comprehensive retrosynthetic planning.
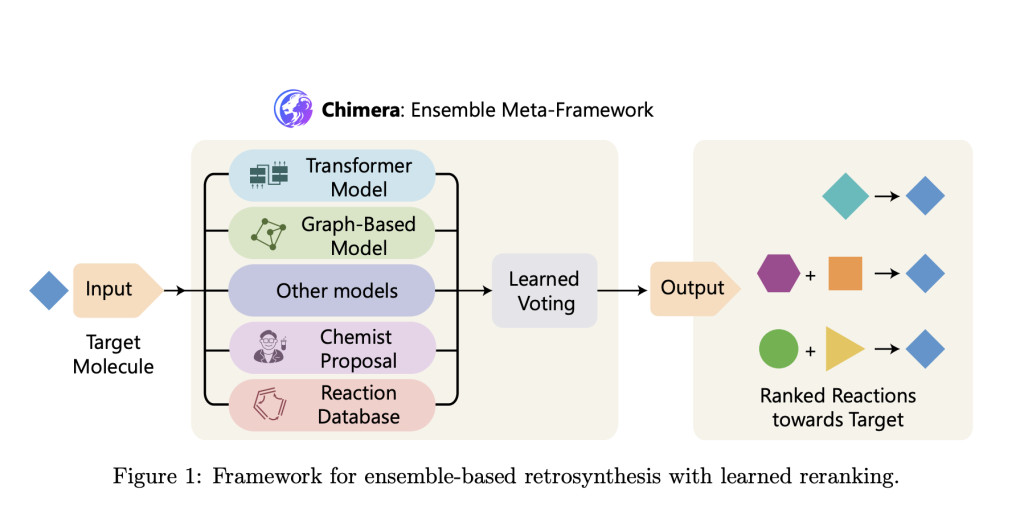
Researchers from Microsoft Research, Novartis Biomedical Research, and Jagiellonian University developed Chimera, an ensemble framework for retrosynthesis prediction. Chimera integrates outputs from multiple machine-learning models with diverse inductive biases, combining their strengths through a learned ranking mechanism. This approach leverages two newly developed state-of-the-art models: NeuralLoc, which focuses on molecule editing using graph neural networks, and R-SMILES 2, a de-novo model employing a sequence-to-sequence Transformer architecture. By combining these models, Chimera enhances both accuracy and scalability for retrosynthetic predictions.
The methodology behind Chimera relies on combining outputs from its constituent models through a ranking system that assigns scores based on model agreement and predictive confidence. NeuralLoc encodes molecular structures as graphs, enabling precise prediction of reaction sites and templates. This method ensures that predicted transformations align closely with known chemical rules while maintaining computational efficiency. Meanwhile, R-SMILES 2 utilizes advanced attention mechanisms, including Group-Query Attention, to predict reaction pathways. This model’s architecture also incorporates improvements in normalization and activation functions, ensuring superior gradient flow and inference speed. Chimera combines these predictions, using overlap-based scoring to rank potential pathways. This integration ensures that the framework balances the strengths of editing-based and de-novo approaches, enabling robust predictions even for complex and rare reactions.
The performance of Chimera has been rigorously validated against publicly available datasets such as USPTO-50K and USPTO-FULL, as well as the proprietary Pistachio dataset. On USPTO-50K, Chimera achieved a 1.7% improvement in top-10 prediction accuracy over the previous state-of-the-art methods, demonstrating its capability to accurately predict both common and rare reactions. On USPTO-FULL, it further improved top-10 accuracy by 1.6%. Scaling the model to the Pistachio dataset, which contains over three times the data of USPTO-FULL, showed that Chimera maintained high accuracy across a broader range of reactions. Expert comparisons with organic chemists revealed that Chimera’s predictions were consistently preferred over individual models, confirming its effectiveness in practical applications.
The framework was also tested on an internal Novartis dataset of over 10,000 reactions to evaluate its robustness under distribution shifts. In this zero-shot setting, where no additional fine-tuning was performed, Chimera demonstrated superior accuracy compared to its constituent models. This highlights its capability to generalize across datasets and predict viable synthetic pathways even in real-world scenarios. Further, Chimera excelled in multi-step retrosynthesis tasks, achieving close to 100% success rates on benchmarks such as SimpRetro, significantly outperforming individual models. The framework’s ability to find pathways for highly challenging molecules further underscores its potential to transform computational retrosynthesis.
Chimera represents a groundbreaking advancement in retrosynthesis prediction by addressing the challenges of rare reaction prediction and multi-step planning. The framework demonstrates superior accuracy and scalability by integrating diverse models and employing a robust ranking mechanism. With its ability to generalize across datasets and excel in complex retrosynthetic tasks, Chimera is set to accelerate progress in chemical synthesis, paving the way for innovative approaches to molecular design.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 60k+ ML SubReddit.
The post This AI Paper from Microsoft and Novartis Introduces Chimera: A Machine Learning Framework for Accurate and Scalable Retrosynthesis Prediction appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ
 Trending: LG AI Research Releases EXAONE 3.5: Three Open-Source Bilingual Frontier AI-level Models Delivering Unmatched Instruction Following and Long Context Understanding for Global Leadership in Generative AI Excellence….
Trending: LG AI Research Releases EXAONE 3.5: Three Open-Source Bilingual Frontier AI-level Models Delivering Unmatched Instruction Following and Long Context Understanding for Global Leadership in Generative AI Excellence….