Supporting the health and well-being of diverse global populations necessitates a nuanced understanding of the complex relationships between human behavior and local environments. This requires identifying vulnerable populations and optimizing resource allocation for maximum impact. Traditional methods often rely on manually curated features and task-specific models, making them rigid and challenging to adapt to new or related tasks. Population dynamics models, by contrast, provide a flexible framework for examining how environmental, social, and economic factors influence public health outcomes. The research underscores that local ecological factors can better predict long-term health outcomes than genetics, highlighting the critical role of geospatial modeling in tackling public health challenges, including disease management and climate-related health impacts.
Machine learning has significantly enhanced geospatial modeling by leveraging diverse data sources to increase spatial and temporal resolution. Studies have utilized mobile phone data, web search trends, satellite imagery, and weather information to predict population movement, disease outbreaks, and economic trends. Despite offering actionable insights, these methods often depend on labor-intensive, hand-crafted features and custom models, limiting scalability and interoperability. To address this, recent developments such as GPS2Vec, SatCLIP, and GeoCLIP focus on creating versatile geographic encoders by using geotagged data, satellite imagery, and image-to-GPS alignment. Building on these innovations, newer models aim to integrate human behavior signals with environmental data to produce general-purpose frameworks for improved geospatial inference.
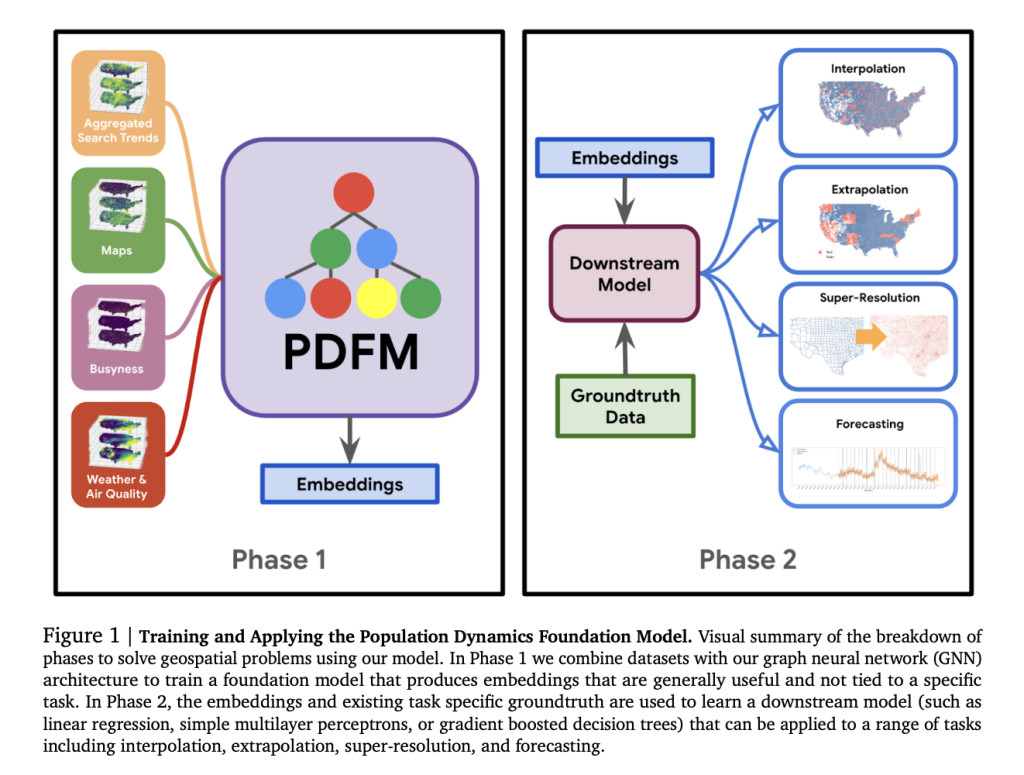
Researchers from Google Research and the University of Nevada, Reno, introduced the Population Dynamics Foundation Model (PDFM), a versatile framework for geospatial modeling. By constructing a geo-indexed dataset incorporating human behavior (e.g., aggregated search trends) and environmental signals (e.g., weather, air quality), PDFM uses graph neural networks to create embeddings for diverse tasks. Benchmarked across 27 health, socioeconomic, and environmental tasks, PDFM achieves state-of-the-art geospatial interpolation, extrapolation, and super-resolution performance. It enhances forecasting models like TimesFM, surpassing supervised methods without fine-tuning. With publicly available embeddings and code, PDFM offers scalable geospatial solutions for research, social good, health, and business applications.
The study curated five datasets at the postal code level within the contiguous US (CONUS) for training and evaluation, focusing on aggregated search trends, maps, busyness, weather, and satellite imagery. Search trends involved the top 1,000 queries from July 2022, scaled and anonymized for privacy. Maps and busyness data provided insights into facilities and activity levels by category. Weather and air quality metrics included climate and pollutant data for July 2022. Satellite embeddings utilized SatCLIP’s Sentinel-2 imagery from 2021–2023. While temporal alignment varied, these datasets covered 28,000 postal codes, representing over 95% of the US population, with exclusions for sparsely populated regions.
To develop PDFM, five datasets covering maps, busyness, search trends, weather, and air quality were collected at postal code and county levels. Using GNNs, PDFM was trained to generate versatile embeddings for solving 27 downstream health, socioeconomic, and environmental tasks. Interpolation and extrapolation experiments simulated missing data scenarios at postal code levels, with PDFM outperforming benchmarks like SatCLIP and GeoCLIP across most tasks. Ablation studies revealed search trends and maps as key contributors. In super-resolution tasks, PDFM showed superior performance, achieving high correlation in postal code-level predictions, highlighting its effectiveness in geospatial forecasting and downstream applications.
In conclusion, The PDFM framework addresses diverse geospatial challenges across the U.S., outperforming existing models like SatCLIP and GeoCLIP on various tasks and enhancing forecasting models such as TimesFM. It integrates diverse datasets, demonstrating adaptability to new tasks, limited data scenarios, and varying resolutions. Future directions include addressing temporal alignment issues, incorporating dynamic embeddings, exploring additional datasets, and leveraging non-spatial graph edges. Limitations include reliance on aggregated data and regional data disparities. The PDFM’s privacy-preserving design ensures broad applicability, with potential global extensions requiring innovative solutions for low-data regions and reliability estimates to enhance predictions in underrepresented areas.
Check out the Paper and GitHub Repo. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter.. Don’t Forget to join our 60k+ ML SubReddit.
 [Must Attend Webinar]: ‘Transform proofs-of-concept into production-ready AI applications and agents’ (Promoted)
[Must Attend Webinar]: ‘Transform proofs-of-concept into production-ready AI applications and agents’ (Promoted)
The post Google AI Releases Population Dynamics Foundation Model (PDFM): A Machine Learning Framework Designed to Power Downstream Geospatial Modeling appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ