Filtering, scanning, and updating data are important operations in databases, and many data structures are used to perform these operations. In real-world situations, it’s important to manage multidimensional data, and the Kd-tree and its variations are popular structures used for this purpose. Various research studies have focused on improving data structures by learning the distribution of data and queries using machine learning models, which has led to the development of learned indexes. A significant challenge with learned multidimensional indexes is that many do not support data update operations, and even when the updates are supported, the time complexity for these operations is often not specified. Due to update operations, the search performance significantly decreases when the distribution of data stored in the data structure becomes skewed.Â
Current structures like Kd-tree, R-tree, and Z-order curves handle multidimensional data using a special sorting technique. In contrast, learned indexes combine machine learning models with traditional ones like B-trees and Bloom Filters to enhance performance by taking advantage of the distribution of data and queries. Although efficient, learned indexes face challenges with data updates, as distribution changes affect accuracy and search efficiency. Multidimensional learned indexes like Flood, Tsunami, Lisa, RLR-tree, and Waffle address this. However, Flood and Tsunami lack update support, and the time complexity of Lisa, RLR-tree, and Waffle remains unexplored.
To mitigate these issues, researchers from The University of Tokyo proposed FlexFlood, a data updating algorithm that ensures fast search even if data distribution changes. It is a flexible variant of Flood that supports efficient data updating by adaptively modifying the internal structure of the existing learned multidimensional index.
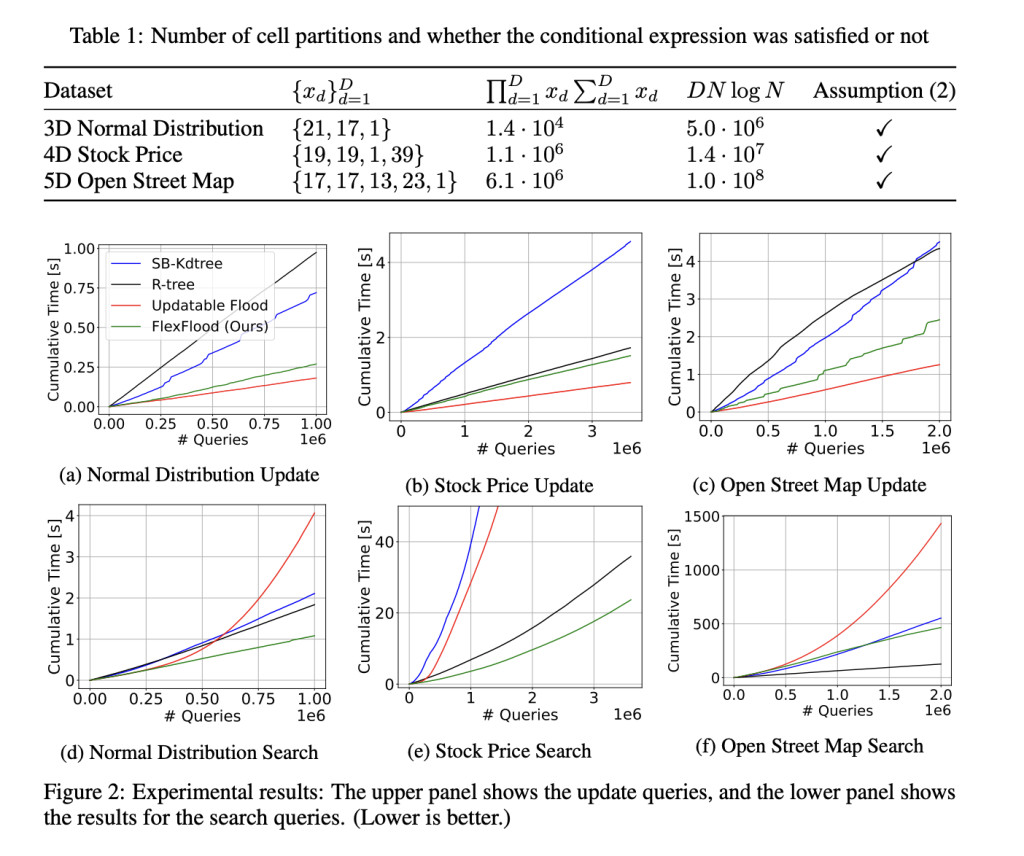
FlexFlood maintains fast search performance even when data distribution changes due to updates. It achieves this by dynamically re-partitioning cells: splitting cells with too many vectors, merging cells with too few, or balancing vector counts between neighboring cells. These adjustments require significant data movement, and the algorithm ensures efficiency by amortizing the update cost and proving the overall time complexity of O(DlogN) under certain assumptions. This makes FlexFlood slightly slower than updatable Flood for updates but better suited for maintaining high search speed with skewed data distributions.
Results showed that FlexFlood outperformed SB-Kdtree and R-tree by 1.1 to 2.9 times in update tests but was slightly slower than the updatable Flood, taking up to 2 times longer. FlexFlood performed 3.3 to 10 times better in search queries than the updatable Flood and surpassed SB-Kdtree and R-tree on most datasets. It fell behind R-tree on the Open Street Map dataset but outperformed SB-Kdtree.Â
In conclusion, the proposed FlexFlood supports efficient data updating. The experimental results showed that FlexFlood does not reduce the search speed and has the upper hand over classical data structures. Also, the researchers proved the amortized time complexity of data updating is O(DlogN) under two experimentally valid assumptions. Conversely, FlexFlood does not guarantee optimality regarding the sort dimension and the number of cell divisions after data updates. Therefore, there is scope for further research, and Flexflood can act as the baseline!
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter.. Don’t Forget to join our 55k+ ML SubReddit.
[FREE AI VIRTUAL CONFERENCE] SmallCon: Free Virtual GenAI Conference ft. Meta, Mistral, Salesforce, Harvey AI & more. Join us on Dec 11th for this free virtual event to learn what it takes to build big with small models from AI trailblazers like Meta, Mistral AI, Salesforce, Harvey AI, Upstage, Nubank, Nvidia, Hugging Face, and more.
The post Researchers at the University of Tokyo Propose FlexFlood: A Data Updating Algorithm that Ensures Fast Search Even if Data Distribution Changes appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ