The development of vision-language models (VLMs) has faced challenges in handling complex visual question-answering tasks. Despite substantial advances in reasoning capabilities by large language models like OpenAI’s GPT-o1, VLMs still struggle with systematic and structured reasoning. Current models often lack the ability to organize information and engage in logical, sequential reasoning, limiting their effectiveness for tasks that require deep cognitive processing, particularly when dealing with multimodal inputs such as images combined with text. Traditional VLMs tend to generate immediate responses without a step-by-step reasoning approach, leading to errors and inconsistencies.
Meet LLaVA-o1
A team of researchers from Peking University, Tsinghua University, Peng Cheng Laboratory, Alibaba DAMO Academy, and Lehigh University has introduced LLaVA-o1: a visual language model capable of systematic reasoning, similar to GPT-o1. LLaVA-o1 is an 11-billion-parameter model designed for autonomous, multistage reasoning. It builds upon the Llama-3.2-Vision-Instruct model and introduces a structured reasoning process, addressing the limitations of previous VLMs with a more methodical approach. The key innovation in LLaVA-o1 is the implementation of four distinct reasoning stages: summary, caption, reasoning, and conclusion.
The model is fine-tuned using a dataset called LLaVA-o1-100k, derived from visual question answering (VQA) sources and structured reasoning annotations generated by GPT-4o. This enables LLaVA-o1 to perform multistage reasoning, extending capabilities similar to GPT-o1 into vision-language tasks, which have historically lagged behind text-based models.
Technical Details and Benefits
LLaVA-o1 employs a novel inference-time scaling technique called stage-level beam search. Unlike previous methods, such as best-of-N or sentence-level beam search, LLaVA-o1 generates multiple responses for each stage of its structured reasoning process and selects the best candidate at each step, ensuring higher-quality results. This structured approach maintains logical coherence throughout the reasoning process, leading to more accurate conclusions.
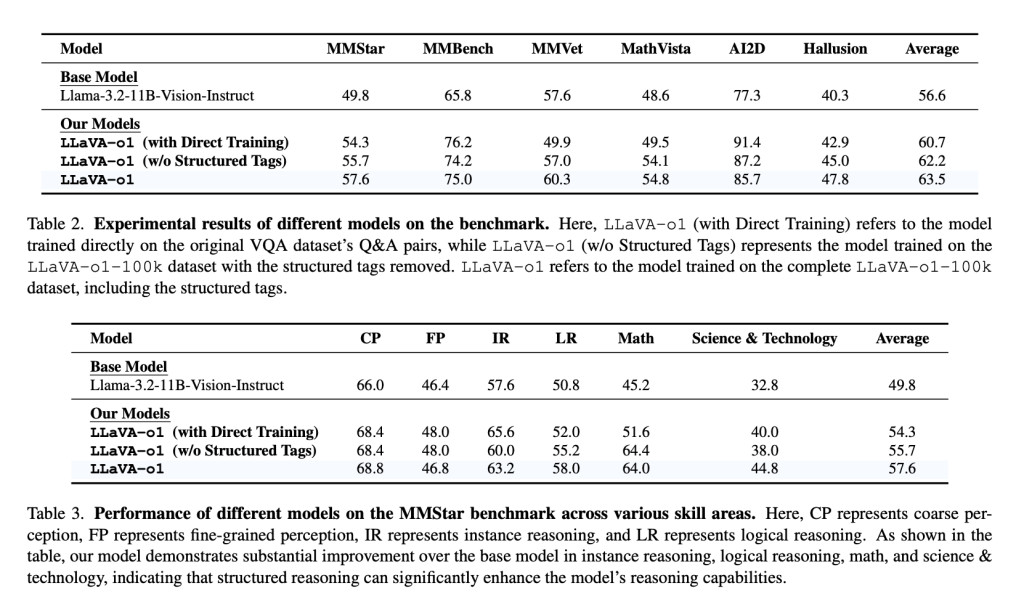
Fine-tuned from the Llama-3.2-11B-Vision-Instruct model, LLaVA-o1 shows an 8.9% improvement on multimodal reasoning benchmarks compared to its base model, even outperforming larger or closed-source competitors like Gemini-1.5-pro, GPT-4o-mini, and Llama-3.2-90B-Vision-Instruct. It achieves this with only 100,000 training samples, making LLaVA-o1 an efficient solution in terms of both performance and scalability. By employing structured thinking through distinct stages, LLaVA-o1 systematically addresses problems, minimizing reasoning errors common in other VLMs.

Importance and Results
LLaVA-o1 addresses a significant gap between textual and visual question-answering models by enabling systematic reasoning in vision-language tasks. Experimental results show that LLaVA-o1 improves performance across benchmarks like MMStar, MMBench, MMVet, MathVista, AI2D, and HallusionBench. It consistently surpasses its base model by over 6.9% across multimodal benchmarks, particularly in reasoning-intensive domains such as mathematical and scientific visual questions.

Stage-level beam search enhances the model’s reliability by generating and verifying multiple candidate responses for each stage, selecting the most appropriate one. This allows LLaVA-o1 to excel in complex visual tasks, compared to traditional inference scaling methods that can be inefficient. LLaVA-o1 demonstrates that structured responses are crucial for achieving high-quality, consistent reasoning, setting a new standard for similarly sized models.
Conclusion
LLaVA-o1 is a visual language model capable of systematic reasoning, similar to GPT-o1. Its four-stage reasoning structure, combined with stage-level beam search, sets a new benchmark for multimodal AI. By training on a relatively small yet strategically constructed dataset, LLaVA-o1 demonstrates that efficient and scalable multimodal reasoning is achievable without the massive resources required by larger closed-source models. LLaVA-o1 paves the way for future research on structured reasoning within vision-language models, promising more advanced capabilities in AI-driven cognitive processing across visual and textual domains.
Check out the Paper and GitHub Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter.. Don’t Forget to join our 55k+ ML SubReddit.
Why AI-Language Models Are Still Vulnerable: Key Insights from Kili Technology’s Report on Large Language Model Vulnerabilities [Read the full technical report here]
The post Meet LLaVA-o1: The First Visual Language Model Capable of Spontaneous, Systematic Reasoning Similar to GPT-o1 appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ