Edge AI has long faced the challenge of balancing efficiency and effectiveness. Deploying Vision Language Models (VLMs) on edge devices is difficult due to their large size, high computational demands, and latency issues. Models designed for cloud environments often struggle with the limited resources of edge devices, resulting in excessive battery usage, slower response times, and inconsistent connectivity. The demand for lightweight yet efficient models has been growing, driven by applications such as augmented reality, smart home assistants, and industrial IoT, which require rapid processing of visual and textual inputs. These challenges are further complicated by increased hallucination rates and unreliable results in tasks like visual question answering or image captioning, where quality and accuracy are essential.
Nexa AI Releases OmniVision-968M: World’s Smallest Vision Language Model with 9x Tokens Reduction for Edge Devices. OmniVision-968M has been engineered with improved architecture over LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant), achieving a new level of compactness and efficiency, ideal for running on the edge. With a design focused on the reduction of image tokens by a factor of nine—from 729 to just 81—the latency and computational burden typically associated with such models have been drastically minimized.

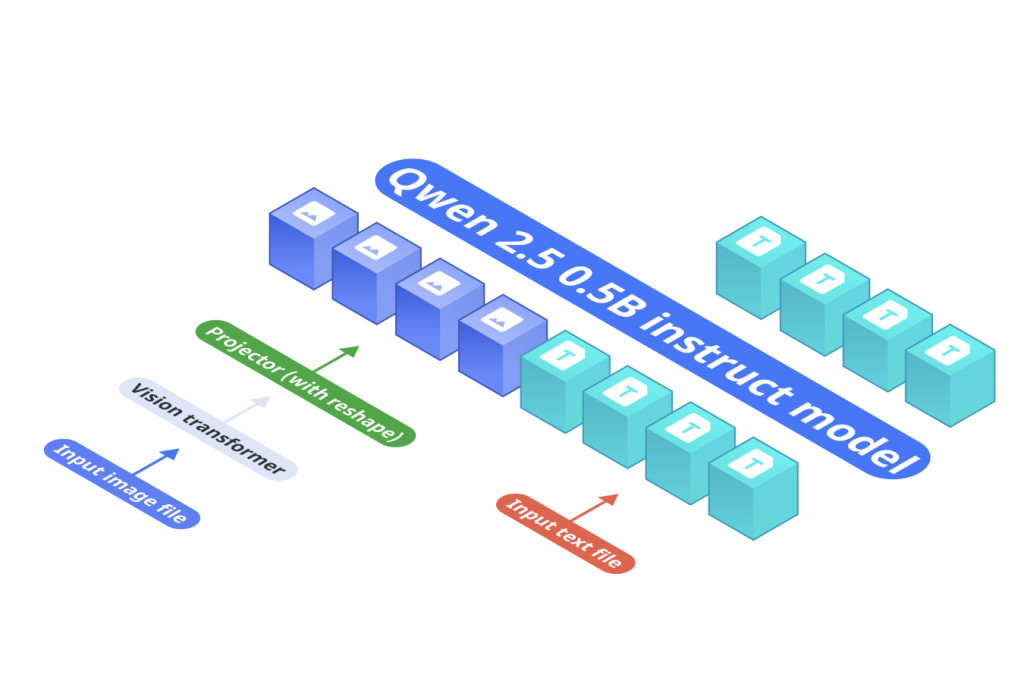
OmniVision’s architecture is built around three main components:
- Base Language Model: Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct serves as the core model for processing text inputs.
- Vision Encoder: SigLIP-400M, with a 384 resolution and 14×14 patch size, generates image embeddings.
- Projection Layer: A Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) aligns the vision encoder’s embeddings with the token space of the language model. Unlike the standard Llava architecture, our projector reduces the number of image tokens by 9 times.
OmniVision-968M integrates several key technical advancements that make it a perfect fit for edge deployment. The model’s architecture has been enhanced based on LLaVA, allowing it to process both visual and text inputs with high efficiency. The image token reduction from 729 to 81 represents a significant leap in optimization, making it almost nine times more efficient in token processing compared to existing models. This has a profound impact on reducing latency and computational costs, which are critical factors for edge devices. Furthermore, OmniVision-968M leverages Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) training with trustworthy data sources, which helps mitigate the problem of hallucination—a common challenge in multimodal AI systems. By focusing on visual question answering and image captioning, the model aims to offer a seamless, accurate user experience, ensuring reliability and robustness in edge applications where real-time response and power efficiency are crucial.


The release of OmniVision-968M represents a notable advancement for several reasons. Primarily, the reduction in token count significantly decreases the computational resources required for inference. For developers and enterprises looking to implement VLMs in constrained environments—such as wearables, mobile devices, and IoT hardware—the compact size and efficiency of OmniVision-968M make it an ideal solution. Furthermore, the DPO training strategy helps minimize hallucination, a common issue where models generate incorrect or misleading information, ensuring that OmniVision-968M is both efficient and reliable. Preliminary benchmarks indicate that OmniVision-968M achieves a 35% reduction in inference time compared to previous models while maintaining or even improving accuracy in tasks like visual question answering and image captioning. These advancements are expected to encourage adoption across industries that require high-speed, low-power AI interactions, such as healthcare, smart cities, and the automotive sector.
In conclusion, Nexa AI’s OmniVision-968M addresses a long-standing gap in the AI industry: the need for highly efficient vision language models that can run seamlessly on edge devices. By reducing image tokens, optimizing LLaVA’s architecture, and incorporating DPO training to ensure trustworthy outputs, OmniVision-968M represents a new frontier in edge AI. This model brings us closer to the vision of ubiquitous AI—where smart, connected devices can perform sophisticated multimodal tasks locally without the need for constant cloud support.
Check out the Model on Hugging Face and Other Details. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter.. Don’t Forget to join our 55k+ ML SubReddit.
[FREE AI WEBINAR] Implementing Intelligent Document Processing with GenAI in Financial Services and Real Estate Transactions
The post Nexa AI Releases OmniVision-968M: World’s Smallest Vision Language Model with 9x Tokens Reduction for Edge Devices appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ