Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as powerful tools for understanding and generating human-like text. This paper explores the potential of LLMs to shape human perspectives and influence decisions on particular tasks. The researchers investigate using LLMs in persuasion across various domains such as investment, credit cards, insurance, retail, and Behavioral Change Support Systems (BCSS). The study aims to uncover the effectiveness and dynamics of AI-driven persuasion techniques by examining the interplay between LLM-based agents and simulated users.
Various assistive agents are employed to help customers select products that align with their specific requirements. These agents excel at understanding user preferences for personalized recommendations and can handle inquiries related to procedural, policy-related, and legal agreements. However, conducting a successful conversation that motivates users to take preferred actions requires more than just human-like responses.
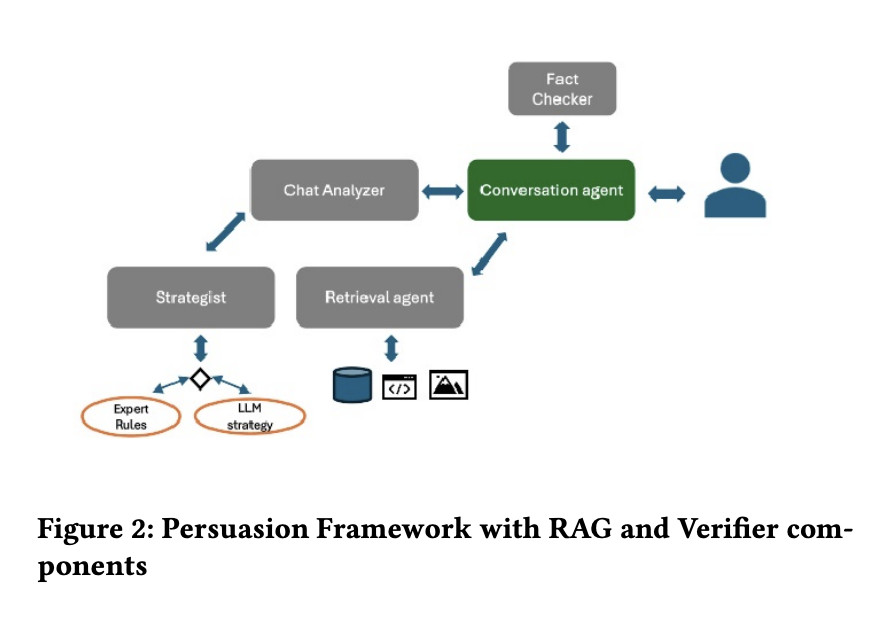
To address this challenge, the researchers propose a sophisticated multi-agent framework where a consortium of agents operates collaboratively. The primary agent engages directly with users through persuasive dialogue, while auxiliary agents perform tasks such as information retrieval, response analysis, persuasion strategies development, and facts validation. This approach aims to enhance the persuasive efficacy of the LLM by continuously analyzing user mood, resistance, and inclination throughout the conversation.
The proposed method utilizes a chat application consisting of four agents: Conversation agent, Advisor Agent, Moderator, and Retrieval Agent. The Conversation agent is responsible for making the final utterance decision, while the other agents provide support and information. The system employs a turn-based dialog approach, with the Sales agent greeting the user and stating the purpose of the conversation, alternated by user messages. The researchers conducted experiments using 25 distinct LLM-driven personas with varying demographic, financial, educational, and personal attributes. To ensure more genuine interactions, these personas were simulated using larger LLMs like GPT-4 or GPT-4O. The study generated 300 conversations between user and sales agents across three domains: banking, insurance, and investment advising.
The research evaluated the effectiveness of persuasion using three key metrics. First, surveys conducted before and after conversations captured user beliefs and perceptions changes. Second, a “call for action†based metric allowed users to make purchase decisions, providing a tangible measure of persuasion success. Lastly, language analysis was performed on entire conversations using predefined metrics and a large language model to assess the quality of persuasive communication.
The experiments yielded several important findings. Applying emotion modifiers to user agents influenced engagement, with stronger emotions generally leading to shorter conversations. Sales agents demonstrated higher efficacy in baseline scenarios, achieving a 71% positive shift in user perspectives compared to 56% when emotion modifiers were introduced. The ability of sales agents to induce positive decisions varied between baseline settings and scenarios with emotion modifiers enabled. Notably, user agents tended to terminate conversations more quickly when they perceived the provided information as inadequate, highlighting the importance of comprehensive and relevant responses in maintaining engagement and persuasive effectiveness.
In conclusion, this study demonstrates the significant potential of Large Language Models in persuasive communication. The research reveals that LLMs can both effectively persuade and resist persuasion, showcasing their ability to create perspective changes in users and influence purchase decisions. As AI continues to evolve, this research provides valuable insights into the dynamics of human-AI interaction in persuasive contexts, paving the way for more sophisticated and ethically designed AI systems in various domains such as sales, customer service, and behavioral change support.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 50k+ ML SubReddit
Here is a highly recommended webinar from our sponsor: ‘Building Performant AI Applications with NVIDIA NIMs and Haystack’
The post The Art of AI Persuasion: A Study on Large Language Model Interactions appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ