The training of large-scale deep models on broad datasets is becoming more and more costly in terms of resources and environmental effects due to the exponential development in model sizes and dataset scales in deep learning. A new, potentially game-changing approach is deep model fusion techniques, which combine the insights of several models into one without requiring substantial retraining. Combining the strengths of numerous models in this way decreases computational costs and allows for the production of more robust and versatile models.
Model ensemble, merging, and mixing procedures are the primary groups into which model fusion approaches fall. Model ensemble techniques combine the predictions of multiple models to improve performance. It enhances training for knowledge distillation, but its memory and computation are expensive. However, model merging approaches combine different models’ parameters, usually by aligning or weighting them. More adaptable and flexible fusion tactics are made possible by model mixing methods, which incorporate numerous models through depth concatenation or gating mechanisms. When training for multiple tasks simultaneously, these techniques shine because the combined model can handle it all. Model fusion has come a long way, but some major obstacles still prevent it from reaching its full potential. Interference between model parameters, which might cause less-than-ideal performance, is a major cause for con. Furthermore, one of the biggest problems with fusion is that it needs to be more easily interpretable. To understand the combined models, knowing how parameters are combined is important.
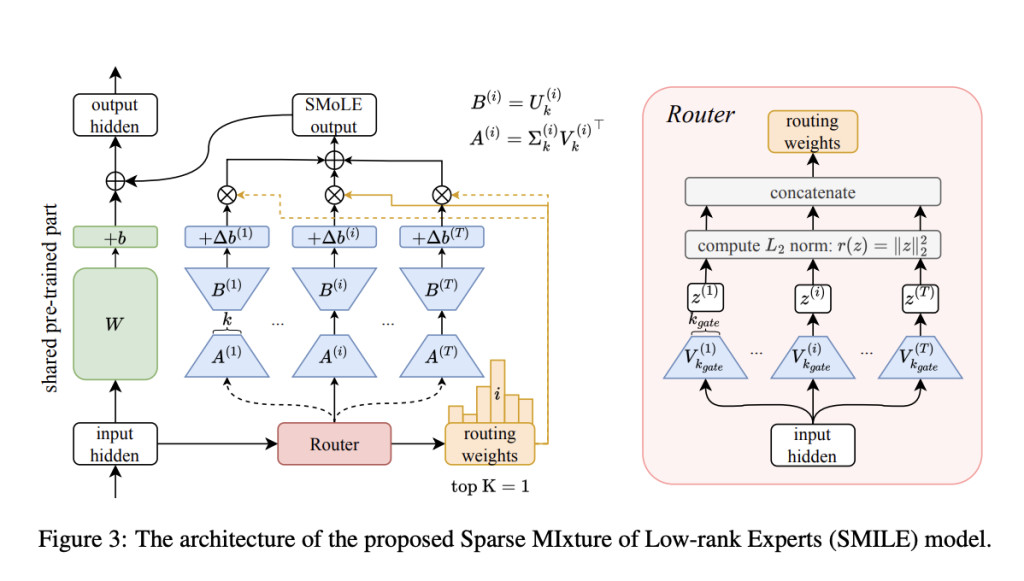
Researchers from Wuhan University, Sun Yat-sen University, JD Explore Academy, Beijing Institute of Technology, and Nanyang Technological University offer a new subspace viewpoint for comprehending and solving the parameter interference issue instead of depending on heuristic approaches or simplified assumptions. Using matrix decomposition, they started by looking into linear layer fine-tuning from a subspace analysis perspective. As a result, it becomes possible to break down the fine-tuned model’s prediction into its parts, which include both the pre-trained knowledge and the task-specific adaptation. This method can better understand models’ ability to adapt to downstream tasks while maintaining pre-trained information.Â
The researchers constructed a more thorough comprehension of fine-tuning by analyzing experimental data. They recast parameter interference as an optimization problem, offering a more scientific and quantifiable viewpoint. They present zero-shot Sparse MIxture of Low-rank Experts (SMILE), improving upon their current source models. Their approach’s zero-shot feature allows fused models to be immediately deployed in new contexts or jobs, significantly reducing the time and resources usually needed for model development.
They suggested the method’s efficacy stems from two important findings in subspace analysis:
When adapting to new tasks, it was discovered that the fine-tuning mostly uses less significant or previously unused dimensions of the parameter space while preserving the most relevant pre-trained weights. The parameter subspace needed to include new information may differ from one job to another. Still, this preservation guarantees that the crucial pre-training information encoded in the initial models is preserved while fine-tuning.
Parameter inference is intractable in the initial parameter space. However, as the dimensionality of the model increases, it becomes more tractable. This enhancement gives more “room†for task-specific parameter modifications to live in harmony.
The researchers performed comprehensive tests spanning various tasks and models in the visual and linguistic domains using both Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) and classic complete fine-tuning. According to the findings, models that are fine-tuned in their entirety can attain around 98-99% of the performance of eight separate fine-tuned models by adding about 50% more parameters. However, LoRA fine-tuned models, by keeping 99% of the individual performance with only a 2% increase in parameters, demonstrate the efficiency and practicality of the research. His system also provides performance-size trade-offs by changing the rank k of the local experts.
Even while the MoE approach is sparsely activated to make it efficient, it still adds computational cost, particularly when there are more jobs or experts to consider. The team suggests that by identifying the subspaces that have the most impact on task-specific performance, it is possible to develop fine-tuning strategies that are more efficient and focused on updating only the areas of the model that need it. Other domains, such as multimodal big language models, can benefit from this strategy since it treats various data types (modalities) as independent experts.Â
Check out the Paper and GitHub. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 49k+ ML SubReddit
Find Upcoming AI Webinars here
The post Revolutionizing Deep Model Fusion: Introducing Sparse Mixture of Low-rank Experts (SMILE) for Scalable Model Upscaling appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ