Accurately modeling nonlinear dynamical systems using observable data remains a significant challenge across various fields such as fluid dynamics, climate science, and mechanical engineering. Traditional linear approximation methods often fall short in capturing the complex behaviors exhibited by these systems, leading to inaccurate predictions and ineffective control strategies. Addressing this challenge is crucial for advancing our ability to analyze, predict, and manipulate complex phenomena in both natural and engineered systems.
Current approaches, particularly Dynamic Mode Decomposition (DMD) and Extended Dynamic Mode Decomposition (EDMD), attempt to linearize nonlinear systems by approximating the Koopman operator. While these techniques have seen success under specific conditions, they exhibit notable limitations when applied to general nonlinear systems. Their reliance on stringent assumptions often results in models that overfit training data and fail to generalize effectively to new scenarios. Additionally, these methods can produce high-dimensional models that are computationally intensive and challenging to interpret, rendering them impractical for real-time applications and systems with limited computational resources.
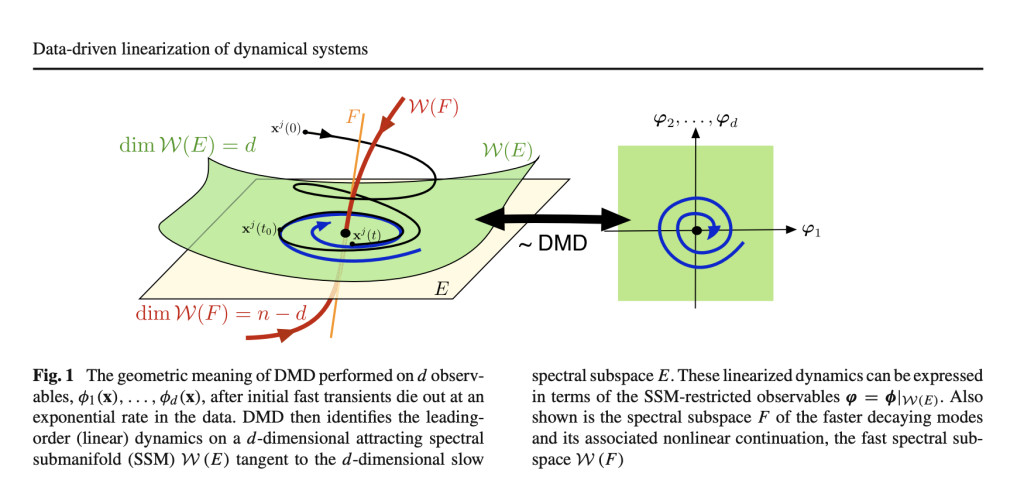
To overcome these limitations, the researchers introduce a novel technique called Data-Driven Linearization (DDL). This method constructs linearizing transformations within slow Spectral Submanifolds (SSMs) of the dynamical system, ensuring that the resulting linear models accurately capture the dominant system dynamics without succumbing to overfitting. The key innovation of DDL lies in its ability to perform higher-order, local linearizations that remain valid under conditions commonly encountered with generic observables and non-degenerate data. This approach not only enhances modeling accuracy but also improves computational efficiency, making it highly suitable for complex, real-world applications.
The DDL methodology involves developing linearizing transformations by leveraging the properties of slow SSMs, which are lower-dimensional manifolds encapsulating the essential dynamics of the system. The process begins by identifying a stable hyperbolic fixed point and ensuring non-degeneracy in both the observables and data matrices used. A cost function is then formulated to balance the invariance error along observed trajectories with the error arising from the inverse transformation. This cost function is minimized using iterative optimization algorithms such as the Levenberg–Marquardt method or gradient descent techniques. By focusing on the most influential dynamics and reducing the complexity of the model, DDL achieves a more robust and accurate representation of the original nonlinear system compared to traditional methods.
Extensive evaluations through numerical simulations and experimental data analysis demonstrate that the DDL approach significantly outperforms existing methods like DMD and EDMD. The findings reveal that models developed using DDL exhibit lower prediction errors and require less computational time, indicating a more efficient and precise capture of system dynamics. These improvements are consistent across various benchmarks and test cases, highlighting the versatility and effectiveness of the method in handling a wide range of nonlinear dynamical systems. The superior performance of DDL underscores its potential as a powerful tool for researchers and engineers seeking accurate and efficient modeling solutions.
In conclusion, The Data-Driven Linearization method presents a substantial advancement in modeling nonlinear dynamical systems by addressing the core challenges associated with traditional linearization techniques. By harnessing the dynamics within slow Spectral Submanifolds and employing higher-order linearization strategies, this approach delivers models that are both accurate and computationally efficient. The success of DDL in various evaluations suggests its broad applicability and potential to enhance predictive modeling, control system design, and simulation accuracy in numerous scientific and engineering domains. This innovation paves the way for more reliable and effective analysis of complex systems, contributing significantly to the field of dynamical systems modeling and artificial intelligence.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 48k+ ML SubReddit
Find Upcoming AI Webinars here
The post ETH Zurich Researchers Introduce Data-Driven Linearization DDL: A Novel Algorithm in Systematic Linearization for Dynamical Systems appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ