Extended Reality (XR) technology transforms how users interact with digital environments, blending the physical and virtual worlds to create immersive experiences. XR devices are equipped with advanced sensors that capture rich streams of user data, enabling personalized and context-aware interactions. The rapid evolution of this field has prompted researchers to explore the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into XR environments, aiming to enhance productivity, communication, and user engagement. As XR becomes increasingly prevalent in various domains, from gaming to professional applications, seamless and intuitive interaction methods are more critical than ever.
One of the significant challenges in XR environments is optimizing user interaction with AI-driven chatbots. Traditional methods rely heavily on explicit voice or text prompts, which can be cumbersome, inefficient, and sometimes counterintuitive in a fully immersive environment. These conventional approaches must leverage XR’s full suite of natural inputs, such as eye gaze and spatial orientation, leading to more cohesive communication between users and AI agents. This problem is particularly pronounced in scenarios where users multitask across multiple virtual windows, requiring AI systems to quickly and accurately interpret user intent without interrupting the flow of interaction.
Current methods for interacting with AI in XR, such as speech and text inputs, have several limitations. Speech input, despite being a popular choice, has an estimated universal throughput of only 39 bits per second, which restricts its effectiveness in complex queries or multitasking scenarios. Text input could be more convenient and efficient, especially when users must type in a virtual environment. The vast amount of data available in XR environments, including multiple open windows and diverse contextual inputs, poses a significant challenge for AI systems in delivering relevant and timely responses. These limitations highlight the need for more advanced interaction methods to exploit XR technology’s capabilities fully.
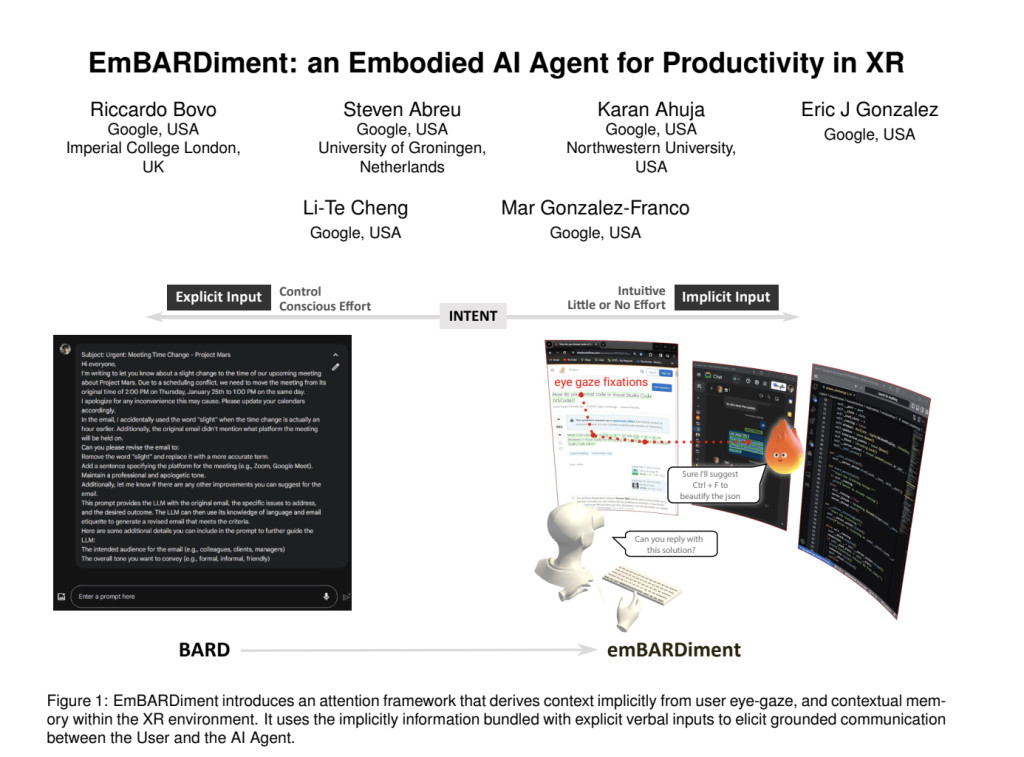
Researchers from Google, Imperial College London, University of Groningen, and Northwestern University have introduced the “EmBARDiment,†which leverages an implicit attention framework to enhance AI interactions in XR environments and address these challenges. This approach combines user eye-gaze data with contextual memory, allowing AI agents to understand and anticipate user needs more accurately and with minimal explicit prompting. The EmBARDiment system was developed by a team of researchers from Google and other institutions, and it represents a significant advancement in making AI interactions within XR more natural and intuitive. By reducing the reliance on explicit voice or text prompts, the system fosters a more fluid and grounded communication process between the user and the AI agent.
The EmBARDiment system integrates cutting-edge technologies, including eye-tracking, gaze-driven saliency, and contextual memory, to capture and utilize user focus within XR environments. The system’s architecture is designed to work seamlessly in multi-window XR environments, where users often engage with multiple tasks simultaneously. The AI can generate more relevant and contextually appropriate responses by maintaining a contextual memory of what the user is looking at and combining this information with verbal inputs. The contextual memory has a capacity of 250 words, carefully calibrated to ensure that the AI remains responsive and focused on the most relevant information without excessive data.
Performance evaluations of the EmBARDiment system demonstrated substantial improvements in user satisfaction and interaction efficiency compared to traditional methods. The system outperformed baseline models across various metrics, requiring significantly fewer attempts to provide satisfactory responses. For instance, in the eye-tracking condition, 77.7% of participants achieved the intended result on their first attempt, while the baseline condition required up to three attempts for similar success rates. These results underscore the effectiveness of the EmBARDiment system in streamlining AI interactions in complex XR environments, where traditional methods often struggle to keep pace with the demands of real-time user engagement.
In conclusion, the research introduces a groundbreaking solution to a critical gap in XR technology by integrating implicit attention with AI-driven responses. EmBARDiment enhances the naturalness and fluidity of interactions within XR and significantly improves the efficiency and accuracy of AI systems in these environments. Eye-tracking data and contextual memory allow the AI to understand better and anticipate user needs, reducing the need for explicit inputs and creating a more seamless interaction experience. As XR technology evolves, the EmBARDiment system represents a crucial step in making AI a more integral and intuitive part of the XR experience. By addressing the limitations of traditional interaction methods, this research paves the way for more sophisticated and responsive AI systems in immersive environments, offering new possibilities for productivity and engagement in the digital age.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 48k+ ML SubReddit
Find Upcoming AI Webinars here
The post EmBARDiment: An Implicit Attention Framework that Enhances AI Interaction Efficiency in Extended Reality Through Eye-Tracking and Contextual Memory Integration appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ