Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional performance on isolated code tasks, such as HumanEval and MBPP, but they struggle significantly when faced with the challenge of handling entire code repositories. The key difficulty lies in the inability of LLMs to manage long-context inputs and perform complex reasoning across intricate code structures within large projects. This challenge is compounded by the need for these models to comprehend and navigate dependencies and project structures within a codebase. Successfully addressing this challenge is essential for advancing automated software engineering, particularly in enabling LLMs to handle real-world software development tasks that require a deep understanding of large-scale repositories.
Current methods aimed at improving LLM interaction with code repositories typically rely on similarity-based retrieval or manual tools and APIs. Similarity-based retrieval approaches often suffer from low recall, particularly in complex tasks that require deep reasoning about code structures. This limitation reduces their effectiveness in retrieving relevant code snippets or structures, especially when handling large, multifaceted codebases. On the other hand, manual tools and APIs, while effective in certain scenarios, require extensive expert knowledge and are often tailored to specific tasks, thereby lacking the flexibility and generalizability needed for broader applications. These shortcomings highlight the need for more advanced methods that can effectively support LLMs in navigating and understanding large code repositories.
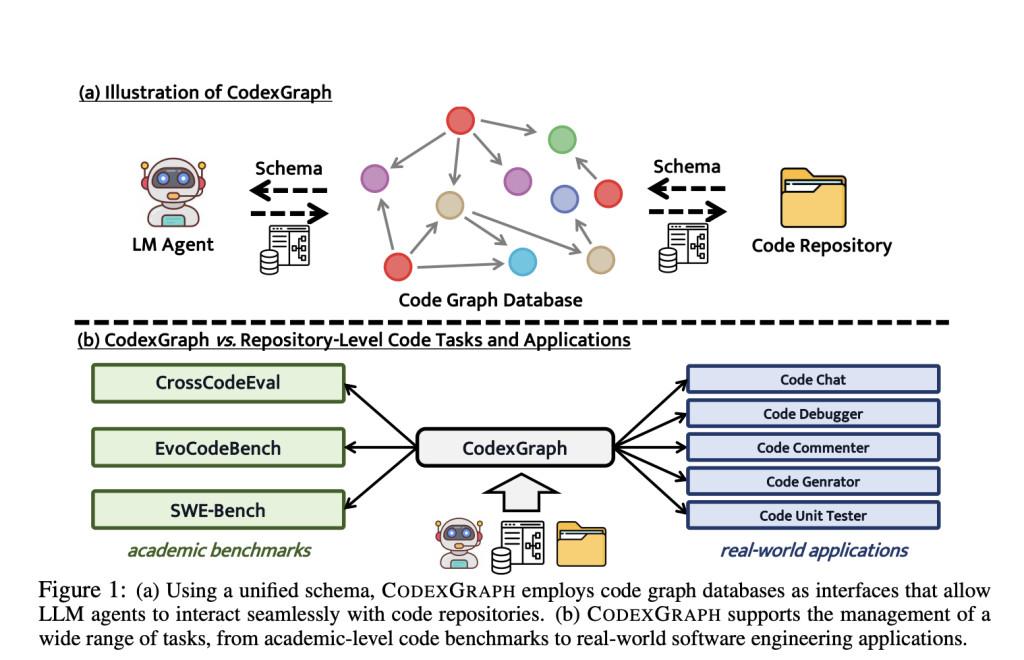
A team of researchers from National University of Singapore, Alibaba Group, and Xi’an Jiaotong University proposes CODEXGRAPH, a system that integrates LLMs with graph database interfaces derived from code repositories. This approach leverages the structural properties of graph databases, coupled with the flexibility of graph query languages, to enable precise, code structure-aware context retrieval and navigation. By utilizing a task-agnostic schema, CODEXGRAPH creates a universal interface that enhances the LLM’s ability to retrieve relevant code information efficiently. This proposed method introduces a significant innovation in the field by enabling more accurate and flexible interaction between LLMs and code repositories, thereby improving performance in both academic benchmarks and real-world applications.
CODEXGRAPH constructs a code graph database where nodes represent symbols in the code (such as modules, classes, and functions), and edges represent the relationships between these symbols (such as inheritance and usage). The system employs a two-phase process: shallow indexing to quickly capture symbols and relationships, followed by a more detailed analysis to resolve cross-file relationships. LLM agents interact with this graph database by generating natural language queries, which are then translated into graph queries by a specialized LLM agent. This interaction is facilitated by a “write then translate†strategy, ensuring that the queries are syntactically correct and optimized for retrieving the most relevant information from the code repository.
CODEXGRAPH was evaluated on three repository-level benchmarks: CrossCodeEval, SWE-bench, and EvoCodeBench. The results demonstrate that this approach achieves competitive performance across all benchmarks, particularly when combined with advanced LLMs like GPT-4o, DeepSeek-Coder-V2, and Qwen2-72b-Instruct. The below key result table from the paper highlights the performance of CODEXGRAPH compared to other Retrieval-Augmented Code Generation (RACG) methods. For instance, on the CrossCodeEval Lite (Python) dataset using GPT-4o, CODEXGRAPH achieved an exact match (EM) score of 27.9%, significantly surpassing other methods. The results also indicate that CODEXGRAPH is particularly effective in complex, reasoning-heavy tasks, such as those in the SWE-bench Lite dataset, where it achieved a Pass@1 score of 22.96%, demonstrating its potential in real-world software development scenarios.
In conclusion, CODEXGRAPH represents a pioneering approach that addresses the limitations of existing RACG methods by integrating LLMs with graph database interfaces. This method enhances the ability of LLMs to navigate and retrieve relevant information from large code repositories, significantly improving performance in both academic and practical software engineering tasks. By overcoming key challenges in handling large-scale codebases, CODEXGRAPH contributes to the advancement of automated software engineering, paving the way for more efficient and accurate LLM-driven coding solutions.
Check out the Paper and GitHub. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 48k+ ML SubReddit
Find Upcoming AI Webinars here
The post CodexGraph: An Artificial Intelligence AI System that Integrates LLM Agents with Graph Database Interfaces Extracted from Code Repositories appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ