Protein language models (PLMs) are trained on large protein databases to predict amino acid sequences and generate feature vectors representing proteins. These models have proven useful in various applications, such as predicting protein folding and mutation effects. A key reason for their success is their ability to capture conserved sequence motifs, which are often important for protein fitness. However, evolutionary and environmental factors can influence the relationship between sequence conservation and fitness, making it complex. PLMs rely on pseudo-likelihood objectives, but incorporating additional data sources, such as text annotations describing protein functions and structures, could improve their accuracy.
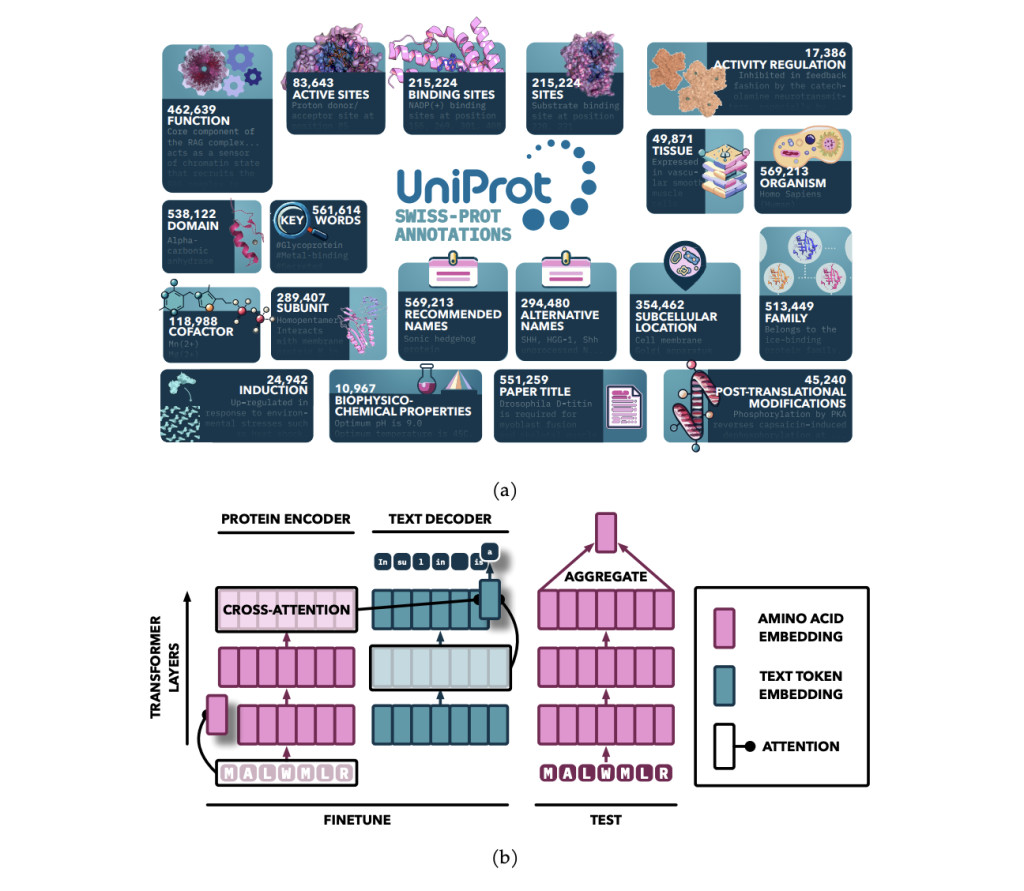
Researchers from the University of Toronto and the Vector Institute conducted a study that enhanced PLMs by fine-tuning them with text annotations from UniProt, focusing on nineteen types of expert-curated data. They introduced the Protein Annotation-Improved Representations (PAIR) framework, which uses a text decoder to guide the model’s training. PAIR significantly improved the models’ performance on function prediction tasks, even outperforming the BLAST search algorithm, especially for proteins with low sequence similarity to training data. This approach highlights the potential of incorporating diverse text-based annotations to advance protein representation learning.
The field of protein labeling traditionally relies on methods like BLAST, which detects protein sequence homology through sequence alignment, and Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) that incorporate additional data such as protein family and evolutionary information. These classical approaches perform well with sequences of high similarity but struggle with remote homology detection. This challenge has led to the development of PLMs, which apply deep learning techniques to learn protein representations from large-scale sequence data inspired by natural language processing models. Recent advancements also integrate text annotations, with models like ProtST leveraging diverse data sources to improve protein function prediction.
The model utilizes an attention-based sequence-to-sequence architecture, initialized with pretrained models and enhanced by adding cross-attention between the encoder and decoder. The encoder processes protein sequences into continuous representations using self-attention, while the decoder generates text annotations in an auto-regressive manner. Pretrained protein models from the ProtT5 and ESM families serve as the encoder, while SciBERT is the text decoder. The model is trained on multiple annotation types using a specialized sampling approach, with training conducted on an HPC cluster using multi-node training with bfloat16 precision.
The PAIR framework enhances protein function prediction by fine-tuning pre-trained transformer models, like ESM and ProtT5, on high-quality annotations from databases like Swiss-Prot. By integrating a cross-attention module, PAIR allows text tokens to attend to amino acid sequences, improving the relationship between protein sequences and their annotations. PAIR significantly outperforms traditional methods like BLAST, especially for proteins with low sequence similarity, and shows strong generalization to new tasks. Its ability to handle limited data scenarios makes it a valuable tool in bioinformatics and protein function prediction.
The PAIR framework enhances protein representations by utilizing diverse text annotations that capture essential functional properties. By combining these annotations, PAIR significantly improves the prediction of various functional properties, including those of previously uncharacterized proteins. PAIR consistently outperforms base protein language models and traditional methods like BLAST, especially for sequences with low similarity to training data. The results suggest incorporating additional data modalities, such as 3D structural information or genomic data, could enrich protein representations. PAIR’s flexible design also has potential applications for representing other biological entities, such as small molecules and nucleic acids.
Check out the Paper and Model. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 47k+ ML SubReddit
Find Upcoming AI Webinars here
The post Protein Annotation-Improved Representations (PAIR): A Flexible Fine-Tuning Framework that Employs a Text Decoder to Guide the Fine-Tuning Process of the Encoder appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ