Artificial intelligence (AI) applications have become increasingly complex, often involving multiple interconnected tasks and components. These systems can include elements such as data loaders, language models, vector databases, and external services, all of which must be integrated seamlessly to execute advanced operations. The challenge lies in orchestrating these diverse components to ensure efficient and reliable application performance.
The core problem in AI application development is managing the orchestration of multiple tasks and components in a cohesive manner. Traditional methods, such as Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) and query pipelines, have been used to address this challenge. However, these methods often fall short when dealing with dynamic and iterative processes, such as handling errors or performing complex decision-making that requires looping back to previous steps for correction or retrying.
Current orchestration frameworks frequently rely on DAGs, designed to prevent cycles and ensure a one-way flow of information. This limitation means that it is difficult to revisit or modify previous steps once a task is completed. For instance, query pipelines that implement DAGs can become overly complex and hard to debug, especially as the number of steps and edge cases increases. The inability to incorporate loops and self-correction in such frameworks can significantly hamper their effectiveness in real-world applications.
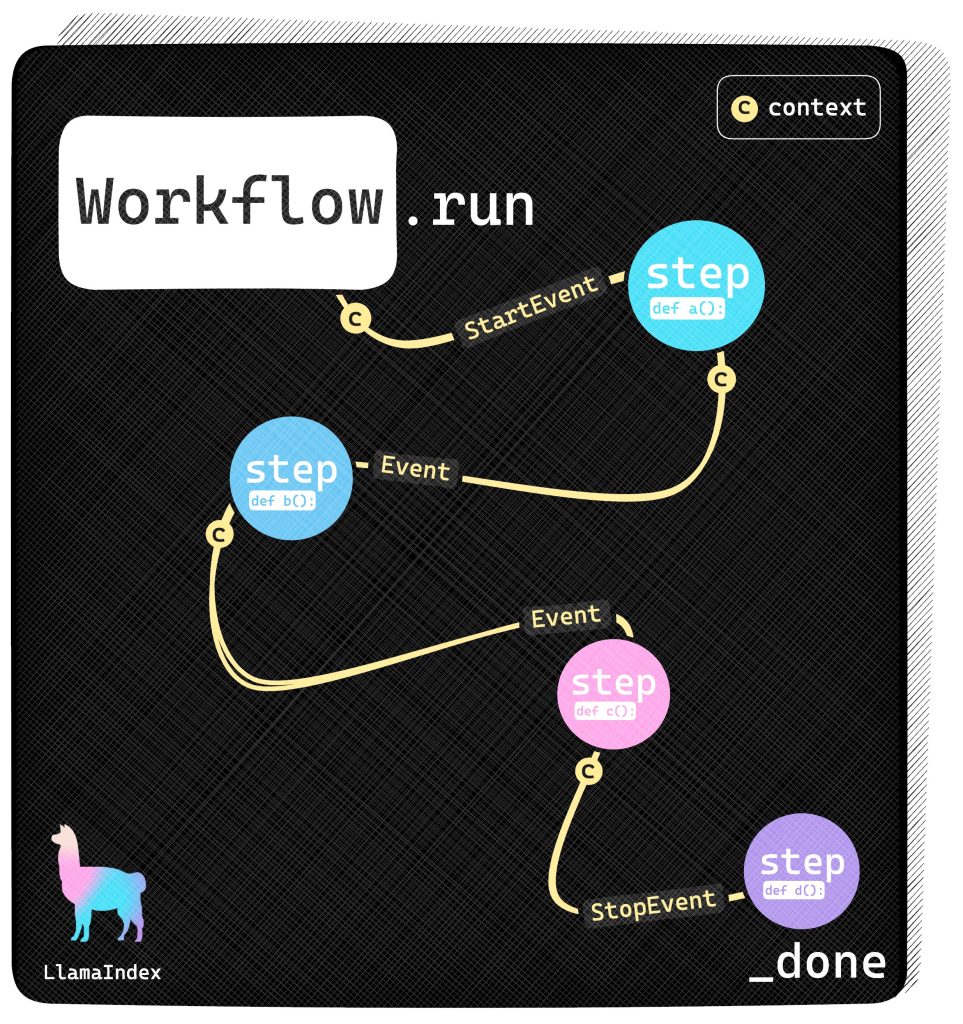
To overcome these limitations, LlamaIndex has introduced a new feature called workflows (beta version). This feature represents a shift from traditional graph-based approaches to an event-driven architecture. LlamaIndex’s workflow enables the orchestration of AI tasks by using events to communicate between various steps rather than relying on a fixed graph structure. Each step in a workflow handles specific events and can produce new ones, allowing for greater flexibility and adaptability in managing complex processes.
LlamaIndex’s workflows leverage an event-driven architecture to transform task orchestration. Unlike static graph-based methods, this system allows each component to subscribe to specific events and determine actions based on received data. This flexibility facilitates iterative processes, including error handling and self-correction. For instance, if a component produces incorrect results, the workflow can trigger retry mechanisms through events, addressing issues that traditional DAG systems struggle with. Each workflow comprises steps, marked with a ‘@step’ decorator, which handles various events and interacts dynamically, enabling real-time adjustments and corrections.
This feature entails several advantages. A few of them are as follows:
Flexible Event Handling: Workflows in LlamaIndex enable components to subscribe to specific events and act based on real-time data, allowing for dynamic adjustments and error handling.
Iterative Processing: Unlike static Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs), the new system supports loops and iterative processes, making it easier to implement retry and correction mechanisms for components.
Enhanced Error Correction: The event-driven model facilitates automatic retries or corrections if a component generates incorrect results, overcoming the limitations of traditional DAG-based systems.
Simplified Workflow Management: Components in workflows can interact dynamically, streamlining the orchestration of complex tasks and adapting to changing conditions more effectively.
Improved Debugging: Workflows include tools for visualizing all potential paths through a workflow, aiding in understanding and troubleshooting event flows.
Better Visualization: Users can review the most recent execution to gain insights into how events are processed, making it easier to identify and resolve issues.
Increased Efficiency: The new features significantly enhance the ability to manage and debug complex AI applications compared to previous methods reliant on static graph-based approaches.
In conclusion, LlamaIndex’s introduction of workflows marks a significant advancement in the orchestration of complex AI applications. By moving to an event-driven architecture, the company has addressed the limitations of traditional DAG-based methods, providing a more flexible and efficient approach to managing intricate AI tasks. The enhanced performance and debugging capabilities of the new system offer substantial benefits for developers working with sophisticated AI applications.
Check out the Blog and Documentation. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 47k+ ML SubReddit
Find Upcoming AI Webinars here
The post LlamaIndex Workflows: An Event-Driven Approach to Orchestrating Complex AI Applications appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ