One of the significant challenges in AI research is the computational inefficiency in processing visual tokens in Vision Transformer (ViT) and Video Vision Transformer (ViViT) models. These models process all tokens with equal emphasis, overlooking the inherent redundancy in visual data, which results in high computational costs. Addressing this challenge is crucial for the deployment of AI models in real-world applications where computational resources are limited and real-time processing is essential.
Current methods like ViTs and Mixture of Experts (MoEs) models have been effective in processing large-scale visual data but come with significant limitations. ViTs treat all tokens equally, leading to unnecessary computations. MoEs improve scalability by conditionally activating parts of the network, thus maintaining inference-time costs. However, they introduce a larger parameter footprint and do not reduce computational costs without skipping tokens entirely. Additionally, these models often use experts with uniform computational capacities, limiting their ability to dynamically allocate resources based on token importance.
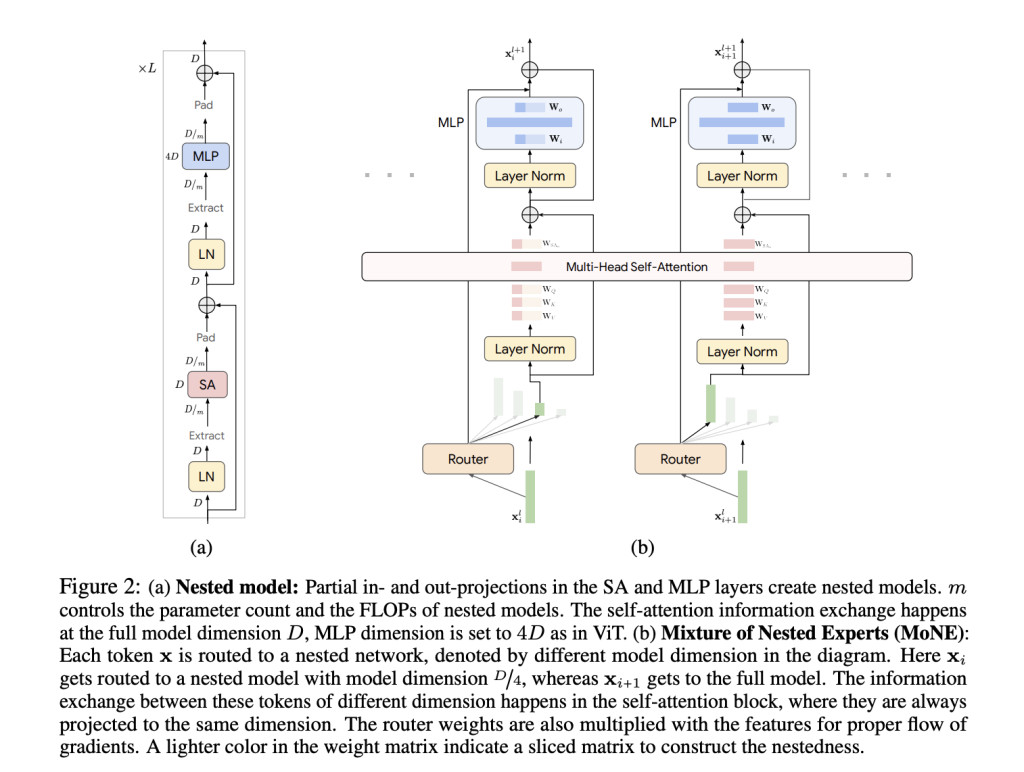
A team of researchers from Google DeepMind and the University of Washington propose the Mixture of Nested Experts (MoNE) framework, which leverages a nested structure for experts to address the inefficiencies of existing methods. MoNE dynamically allocates computational resources by routing tokens to different nested experts based on their importance. This approach allows redundant tokens to be processed through smaller, cheaper models while more important tokens are routed to larger, more detailed models. The novelty lies in using a nested architecture that maintains the same parameter count as the baseline models but achieves a two-fold reduction in inference time compute. This adaptive processing not only enhances efficiency but also retains performance across different computational budgets.
MoNE integrates a nested architecture within Vision Transformers, where experts with varying computational capacities are arranged hierarchically. Each token is dynamically routed to an appropriate expert using the Expert Preferred Routing (EPR) algorithm. The model processes tokens through partial in- and out-projections in the Self-Attention (SA) and MLP layers, facilitating efficient computation. The framework is validated on datasets such as ImageNet-21K, Kinetics400, and Something-Something-v2. The routing decisions are made based on the importance of tokens, which is determined by the router network’s probability distribution. MoNE’s effectiveness is demonstrated through rigorous experiments showing strong performance across different inference-time compute budgets.
The proposed method achieves significant improvements in computational efficiency and performance across various datasets. On the ImageNet-21K dataset, MoNE achieves an accuracy of 87.5%, which is a substantial improvement over the baseline models. In video classification tasks, such as those involving the Kinetics400 and Something-Something-v2 datasets, MoNE demonstrates a two- to three-fold reduction in computational costs while maintaining or exceeding the accuracy of traditional methods. The adaptive processing capabilities of MoNE enable it to maintain robust performance even under constrained computational budgets, showcasing its effectiveness in both image and video data processing.
In conclusion, The Mixture of Nested Experts (MoNE) framework offers a significant advancement in processing visual tokens efficiently. By dynamically allocating computational resources based on token importance, MoNE overcomes the limitations of existing ViT and MoE models, achieving substantial reductions in computational costs without sacrificing performance. This innovation holds great potential for enhancing real-world applications of AI, making high-performance models more accessible and practical. The contributions are validated through rigorous experiments, demonstrating MoNE’s adaptability and robustness across different datasets and computational budgets.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 47k+ ML SubReddit
Find Upcoming AI Webinars here
The post Google DeepMind Presents MoNE: A Novel Computer Vision Framework for the Adaptive Processing of Visual Tokens by Dynamically Allocating Computational Resources to Different Tokens appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ