Developing AI agents that can autonomously perform a wide variety of tasks with the same flexibility and capability as human software developers presents a significant challenge. These tasks include writing and executing code, interacting with command lines, and browsing the web. Current AI agents often lack the necessary adaptability and generalization for such diverse and complex operations. Addressing this challenge is crucial for advancing AI research and enhancing its applicability in real-world scenarios, such as software development, web navigation, and problem-solving across various domains.
Existing methods for developing AI agents include frameworks like AutoGPT, LangChains, and MetaGPT. These frameworks provide essential tools for agent development, such as interfaces for interaction, environments for operation, and mechanisms for communication. However, these methods have specific limitations. For instance, AutoGPT and LangChains do not natively support sandboxed code execution or built-in web browsers, which limits their applicability in tasks requiring safe code execution and web interactions. MetaGPT, while supporting multi-agent collaboration, lacks a standardized tool library, which hinders the development of diverse agent skills. Overall, these limitations restrict the performance and applicability of current AI agents, particularly in complex, multi-step tasks that require generalization across different domains.
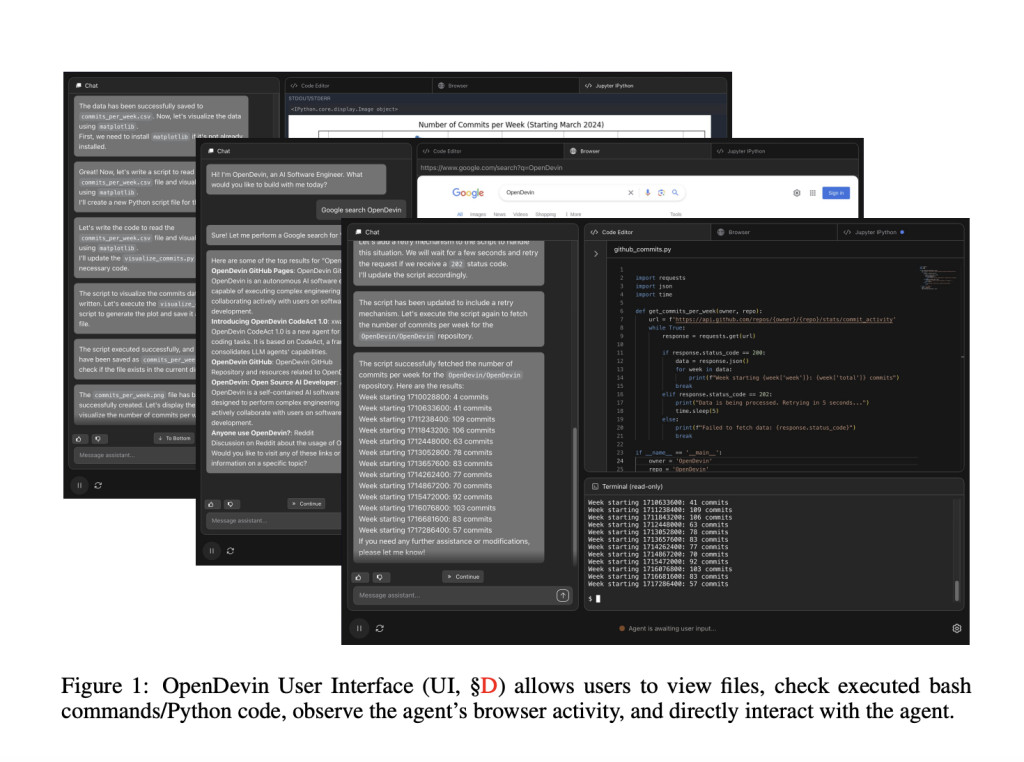
A team of researchers from UIUC, CMU, Yale, UC Berkeley, Contextual AI, KAUST, ANU, HCMUT, Alibaba, and All Hands AI propose OpenDevin. OpenDevin offers a novel approach by creating a comprehensive platform that supports the development of generalist and specialist AI agents. The platform addresses the limitations of existing methods by incorporating a powerful interaction mechanism, a sandboxed environment for safe code execution, and a built-in web browser for web-based tasks. Key components of OpenDevin include a state and event stream architecture, an agent runtime environment, and a multi-agent delegation framework. This innovative approach allows AI agents to perform a wide range of tasks by writing and executing code, interacting with command lines, and browsing the web. OpenDevin’s open-source nature and its integration with evaluation benchmarks further enhance its contribution to the field by providing a versatile and scalable platform for AI agent development and assessment.
The technical implementation of OpenDevin involves several critical components. The platform features a sandboxed operating system and a web browser, enabling agents to perform tasks safely and efficiently. Agents can interact with the environment through a core set of general actions, such as executing Python code, running bash commands, and navigating web pages using BrowserGym’s domain-specific language. The platform’s agent runtime connects agents to these environments via SSH protocol, ensuring secure and isolated task execution. OpenDevin also includes an AgentSkills library, which provides a set of utility functions that agents can use to perform complex tasks. This library is designed for easy extension, allowing community members to contribute new tools and skills. Furthermore, the platform supports multi-agent collaboration, enabling agents to delegate tasks to specialized agents for improved performance.
OpenDevin was evaluated across 15 benchmarks, including software engineering tasks like SWE-Bench and HumanEvalFix, web browsing tasks such as WebArena and MiniWoB++, and miscellaneous assistance tasks including GAIA and GPQA. OpenDevin’s agents demonstrated competitive performance across these benchmarks. In SWE-Bench Lite, the CodeActAgent achieved a resolve rate of 26%, comparable to other specialized agents. In HumanEvalFix, OpenDevin agents fixed 79.3% of Python bugs, significantly outperforming non-agentic approaches. The platform also showed strong results in web browsing tasks, with its BrowsingAgent achieving a 15.5% success rate in WebArena. These results highlight OpenDevin’s effectiveness in handling diverse tasks and its potential as a generalist AI platform.
In conclusion, OpenDevin presents a significant advancement in the development and deployment of AI agents. This proposed method addresses the critical challenge of creating flexible and powerful AI agents capable of performing complex tasks autonomously. By integrating a comprehensive set of tools, environments, and evaluation frameworks, OpenDevin overcomes the limitations of existing methods and provides a robust platform for future AI research and applications. The platform’s open-source nature and community-driven development further enhance its potential impact on the field of AI.
Check out the Paper, Code, and Benchmark. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 47k+ ML SubReddit
Find Upcoming AI Webinars here
The post OpenDevin: An Artificial Intelligence Platform for the Development of Powerful AI Agents that Interact in Similar Ways to Those of a Human Developer appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ