Aligning models with human preferences poses significant challenges in AI research, particularly in high-dimensional and sequential decision-making tasks. Traditional Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) methods require learning a reward function from human feedback and then optimizing this reward using RL algorithms. This two-phase approach is computationally complex, often leading to high variance in policy gradients and instability in dynamic programming, making it impractical for many real-world applications. Addressing these challenges is essential for advancing AI technologies, especially in fine-tuning large language models and improving robotic policies.
Current RLHF methods, such as those used for training large language models and image generation models, typically learn a reward function from human feedback and then use RL algorithms to optimize this function. While effective, these methods are based on the assumption that human preferences correlate directly with rewards. Recent research suggests this assumption is flawed, leading to inefficient learning processes. Moreover, RLHF methods face significant optimization challenges, including high variance in policy gradients and instability in dynamic programming, which restrict their applicability to simplified settings like contextual bandits or low-dimensional state spaces.
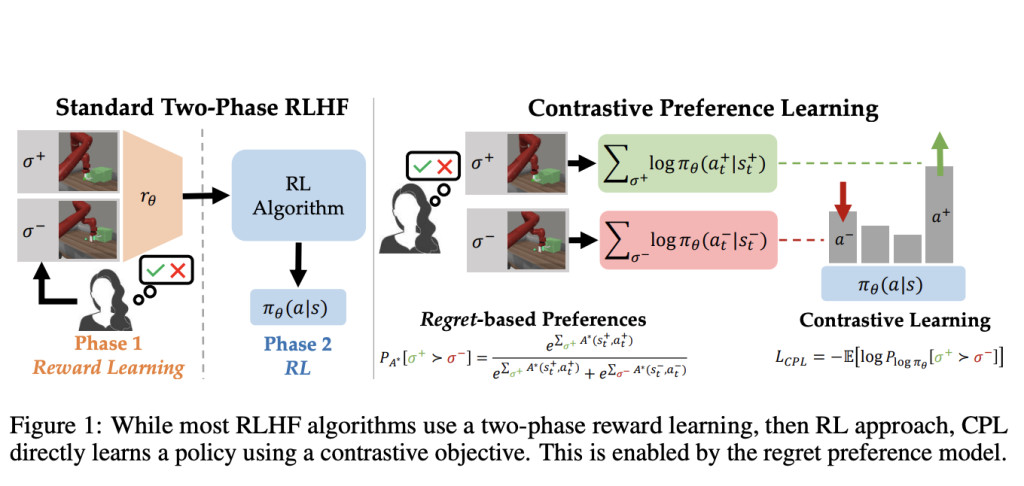
A team of researchers from Stanford University, UT Austin and UMass Amherst introduce Contrastive Preference Learning (CPL), a novel algorithm that optimizes behavior directly from human feedback using a regret-based model of human preferences. CPL circumvents the need for learning a reward function and subsequent RL optimization by leveraging the principle of maximum entropy. This approach simplifies the process by directly learning the optimal policy through a contrastive objective, making it applicable to high-dimensional and sequential decision-making problems. This innovation offers a more scalable and computationally efficient solution compared to traditional RLHF methods, broadening the scope of tasks that can be effectively tackled using human feedback.
CPL is based on the maximum entropy principle, which leads to a bijection between advantage functions and policies. By focusing on optimizing policies rather than advantages, CPL uses a simple contrastive objective to learn from human preferences. The algorithm operates in an off-policy manner, allowing it to utilize arbitrary Markov Decision Processes (MDPs) and handle high-dimensional state and action spaces. The technical details include the use of a regret-based preference model, where human preferences are assumed to follow the regret under the user’s optimal policy. This model is integrated with a contrastive learning objective, enabling the direct optimization of policies without the computational overhead of RL.
The evaluation demonstrates CPL’s effectiveness in learning policies from high-dimensional and sequential data. CPL not only matches but often surpasses traditional RL-based methods. For instance, in various tasks such as Bin Picking and Drawer Opening, CPL achieved higher success rates compared to methods like Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and Preference-based Implicit Q-learning (P-IQL). CPL also showed significant improvements in computational efficiency, being 1.6 times faster and four times as parameter-efficient compared to P-IQL. Additionally, CPL demonstrated robust performance across different types of preference data, including both dense and sparse comparisons, and effectively utilized high-dimensional image observations, further underscoring its scalability and applicability to complex tasks.
In conclusion, CPL represents a significant advancement in learning from human feedback, addressing the limitations of traditional RLHF methods. By directly optimizing policies through a contrastive objective based on a regret preference model, CPL offers a more efficient and scalable solution for aligning models with human preferences. This approach is particularly impactful for high-dimensional and sequential tasks, demonstrating improved performance and reduced computational complexity. These contributions are poised to influence the future of AI research, providing a robust framework for human-aligned learning across a broad range of applications.
Check out the Paper and GitHub. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 47k+ ML SubReddit
Find Upcoming AI Webinars here
The post Researchers at Stanford Introduce Contrastive Preference Learning (CPL): A Novel Machine Learning Framework for RLHF Using the Regret Preference Model appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ