Large language models (LLMs) are used in various applications, such as machine translation, summarization, and content creation. However, a significant challenge with LLMs is their tendency to produce hallucinations—statements that sound plausible but are not grounded in factual information. This issue affects the reliability of AI-generated content, especially in domains requiring high accuracy, such as medical and legal documents. Therefore, mitigating hallucinations in LLMs is essential to enhance their trustworthiness and broaden their applicability.
Hallucinations in LLMs undermine their reliability and can lead to misinformation, making it critical to address this problem. The complexity arises because LLMs generate text based on patterns learned from vast datasets, which may include inaccuracies. These hallucinations can manifest as incorrect facts or misrepresentations, impacting the model’s utility in sensitive applications. Thus, developing effective methods to reduce hallucinations without compromising the model’s performance is a significant goal in natural language processing.
Researchers have explored various methods to tackle this issue, including model editing and context-grounding. Model editing involves modifying the model parameters to refine responses, while context-grounding includes relevant factual information within the prompt to guide the model’s output. These approaches aim to align the generated text with factual content, thereby reducing hallucinations. However, each method has limitations, such as increased computational complexity and the need for extensive retraining, which can be resource-intensive.
A Team of researchers from IBM Research and T. J. Watson Research Center has introduced a novel method leveraging the memory-augmented LLM named Larimar. This model integrates an external episodic memory controller to enhance text generation capabilities. Larimar’s architecture combines a BERT large encoder and a GPT-2 large decoder with a memory matrix, enabling it to store and retrieve information effectively. This integration allows the model to use past information more accurately, reducing the chances of generating hallucinated content.
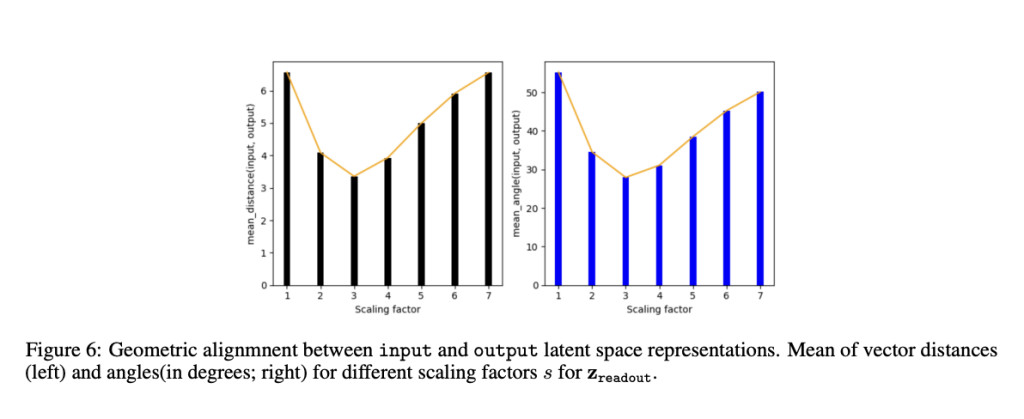
In more detail, Larimar’s method involves scaling the readout vectors, which act as compressed representations in the model’s memory. These vectors are geometrically aligned with the write vectors to minimize distortions during text generation. This process does not require additional training, making it more efficient than traditional methods. The researchers used Larimar and a hallucination benchmark dataset of Wikipedia-like biographies to test its effectiveness. By manipulating the readout vectors’ length through scaling, they found significant reductions in hallucinations.
The Larimar model demonstrated superior performance in experiments compared to the existing GRACE method, which uses dynamic key-value adapters for model editing. In particular, the Larimar model showed substantial improvements in generating factual content. For instance, when scaling by a factor of four, Larimar achieved a RougeL score of 0.72, compared to GRACE’s 0.49, indicating a 46.9% improvement. Furthermore, Larimar’s Jaccard similarity index reached 0.69, significantly higher than GRACE’s 0.44. These metrics underscore Larimar’s effectiveness in producing more accurate text with fewer hallucinations.
The Larimar model’s approach to mitigating hallucinations offers a promising solution by utilizing lightweight memory operations. This method simplifies the process faster and more effectively than training-intensive approaches like GRACE. For instance, generating a WikiBio entry with Larimar took approximately 3.1 seconds on average, compared to GRACE’s 37.8 seconds, showcasing a substantial speed advantage. Moreover, Larimar’s memory-based method aligns memory vectors to reduce hallucinations, ensuring higher factual accuracy in generated text.
In conclusion, the research from IBM Research and T. J. Watson Research Center highlights a novel and efficient method to address hallucinations in LLMs. By leveraging memory-augmented models like Larimar and employing a geometry-inspired scaling technique, the researchers have made significant strides in enhancing the reliability of AI-generated content. This approach simplifies the process and ensures better performance and accuracy. As a result, Larimar’s method could pave the way for more trustworthy applications of LLMs across various critical fields, ensuring that AI-generated content is reliable and accurate.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 47k+ ML SubReddit
Find Upcoming AI Webinars here
The post IBM Researchers Propose a New Training-Free AI Approach to Mitigate Hallucination in LLMs appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ