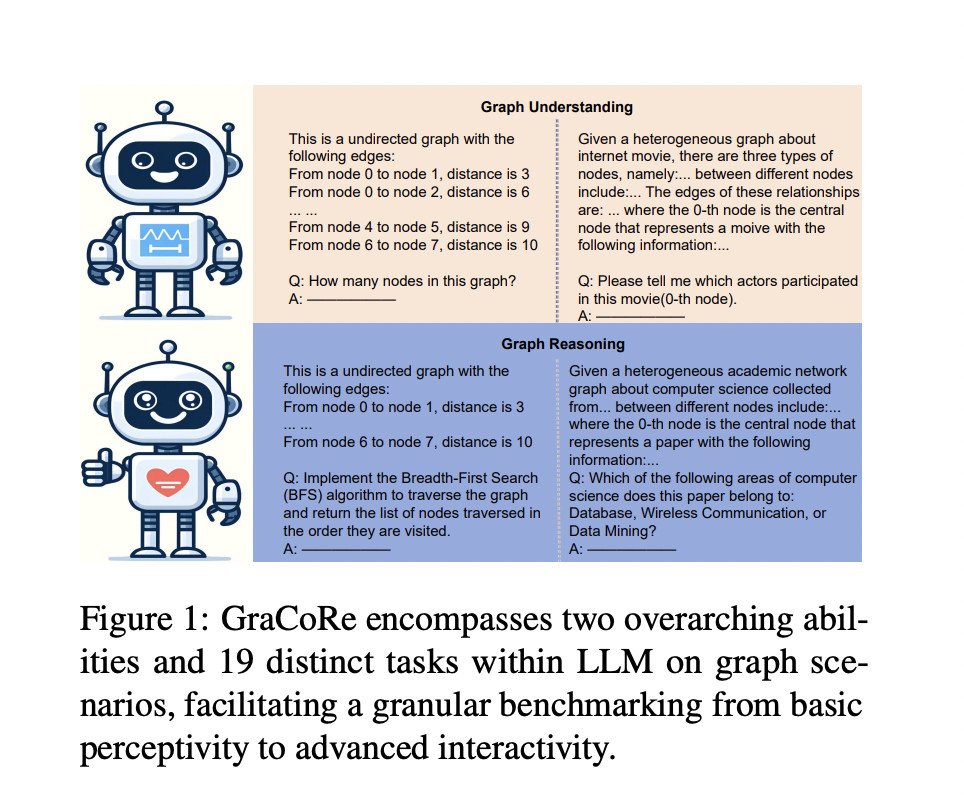
Graph comprehension and complex reasoning in artificial intelligence involve developing and evaluating the abilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) to understand and reason about graph-structured data. This field is critical for various applications, including social network analysis, drug discovery, recommendation systems, and spatiotemporal predictions. The goal is to advance the capabilities of AI to handle complex graph data effectively, ensuring they can interpret and analyze intricate relationships and structures within various types of graphs.
A significant problem in evaluating LLMs is the lack of comprehensive benchmarks that assess their ability to understand and reason about different types of graphs. Existing benchmarks often focus on pure graph understanding and fail to address the diverse capabilities of handling heterogeneous graphs. This gap limits the development and assessment of LLMs in complex graph-related tasks, as current benchmarks need to provide a unified and systematic evaluation framework. The challenge lies in designing benchmarks that can extensively test the diverse capabilities of LLMs across different graph structures and complexity levels.
Current methods for evaluating graph comprehension in LLMs include task-driven benchmarks that predominantly test either pure or heterogeneous graphs in isolation. These benchmarks often need a more systematic approach to assess LLMs’ full range of capabilities. Traditional methods focus on direct mappings from graph structures to answers, overlooking deeper reasoning capabilities. For instance, most benchmarks need to adequately assess the ability of LLMs to handle long textual descriptions of graph-structured data, which is essential for understanding complex relationships within graphs. This limitation hinders the comprehensive evaluation of LLMs’ graph reasoning abilities, affecting their practical applications.
A research team at the Harbin Institute of Technology and Peng Cheng Laboratory introduced GraCoRe, a new benchmark designed to systematically assess LLMs’ graph comprehension and reasoning abilities. GraCoRe uses a three-tier hierarchical taxonomy to categorize and test models on graph-related tasks. The benchmark includes 11 datasets with over 5,000 graphs of varying complexity. GraCoRe aims to fill the gaps left by existing benchmarks by providing a comprehensive framework that tests LLMs on both pure and heterogeneous graphs. This approach ensures a thorough evaluation of LLMs’ capabilities, enabling the development of more advanced models.
The GraCoRe benchmark employs a three-tier hierarchical taxonomy to evaluate LLMs’ graph comprehension and reasoning abilities across 19 distinct tasks using 11 datasets. The benchmark includes pure and heterogeneous graphs, such as ACM and IMDB datasets, converted into text-based graph data. Tasks range from node classification, link prediction, and graph traversal to more complex functions like maximum flow calculation and shortest path determination. The complexity of these graphs is controlled by adjusting factors such as graph size and network sparsity. Specific prompts are meticulously designed for each task to test various capabilities in a structured and detailed manner. This comprehensive methodology thoroughly assesses the LLMs’ proficiency in understanding and reasoning about graph-structured data, providing a clear benchmark for future advancements.
The evaluation of ten LLMs, including GPT-4o, GPT-4, and GPT-3.5, yielded significant quantitative findings. GPT-4o achieved the highest overall performance with a total score of 1419.69, excelling in both graph understanding and reasoning tasks. For instance, in node number calculation, GPT-4o scored 75.012, while it achieved 99.268 in simple graph theory problems. The research highlighted that semantic enrichment improved reasoning performance, and the ordered naming of nodes significantly enhanced task success. Furthermore, the ability to handle longer texts did not necessarily correlate with better graph comprehension or reasoning performance. These results pinpoint specific strengths and weaknesses in current LLM capabilities, indicating areas that require further research and development to enhance overall performance.
To conclude, the research addresses the critical problem of assessing LLMs’ graph comprehension and reasoning abilities. By introducing GraCoRe, the researchers provide a comprehensive benchmark highlighting various LLMs’ strengths and weaknesses. This benchmark paves the way for further advancements in developing more capable LLMs for complex graph-related applications. The detailed evaluation provided by GraCoRe offers valuable insights into the performance of LLMs, guiding future improvements and innovations in the field.Â
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our 46k+ ML SubReddit, 26k+ AI Newsletter, Telegram Channel, and LinkedIn Group.
If You are interested in a promotional partnership (content/ad/newsletter), please fill out this form.
The post GraCoRe: A New AI Benchmark for Unveiling Strengths and Weaknesses in LLM Graph Comprehension and Reasoning appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ